Question Number 61326 by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 01/Jun/19

$${find}\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\:\frac{{sinx}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$
Commented by perlman last updated on 01/Jun/19

$${exacte}\:{value}\:! \\ $$
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 01/Jun/19
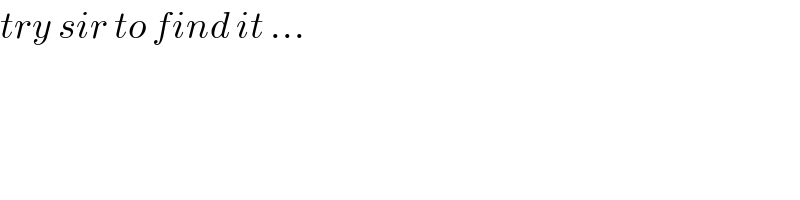
$${try}\:{sir}\:{to}\:{find}\:{it}\:… \\ $$
Commented by abdo mathsup 649 cc last updated on 01/Jun/19
![another way we have x−(x^3 /6) ≤sinx ≤x ⇒ (x/(1+x^2 )) −(x^3 /(6(1+x^2 ))) ≤ ((sinx)/(1+x^2 )) ≤ (x/(1+x^2 )) ⇒ ∫_0 ^1 (x/(1+x^2 ))dx −(1/6) ∫_0 ^1 (x^3 /(1+x^2 ))dx ≤ ∫_0 ^1 ((sinx)/(1+x^2 ))dx≤∫_0 ^1 (x/(1+x^2 ))dx ∫_0 ^1 (x/(1+x^2 ))dx =[(1/2)ln(1+x^2 )]_0 ^1 =((ln(2))/2) ∫_0 ^1 (x^3 /(x^2 +1)) dx =∫_0 ^1 ((x(x^2 +1)−x)/(x^2 +1))dx =∫_0 ^1 xdx−∫_0 ^1 ((xdx)/(x^2 +1)) =[(x^2 /2)]_0 ^1 −((ln(2))/2) =(1/2) −((ln(2))/2) ⇒ ((ln(2))/2) −(1/(12)) +((ln(2))/(12)) ≤ ∫_0 ^1 ((sinxdx)/(1+x^2 )) ≤ ((ln(2))/2) ⇒ ((7ln(2)−1)/(12)) ≤ ∫_0 ^1 ((sinx)/(1+x^2 ))dx ≤ ((ln(2))/2) so we can take v_0 =((7ln(2)−1)/(24)) +((ln(2{)/4) =((13ln(2)−1)/(24)) as approximst value for this integral .](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q61366.png)
$${another}\:{way}\:\:{we}\:{have}\:\:{x}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{6}}\:\leqslant{sinx}\:\leqslant{x}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{6}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}\:\leqslant\:\frac{{sinx}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\leqslant\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}\:\leqslant\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{sinx}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}\leqslant\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}\: \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}\:=\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:=\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}\:{dx}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{x}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)−{x}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}{dx} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} {xdx}−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{xdx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{1}}\:=\left[\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:−\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:−\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{12}}\:+\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)}{\mathrm{12}}\:\leqslant\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{{sinxdx}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\leqslant\:\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{7}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{12}}\:\leqslant\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{{sinx}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}\:\leqslant\:\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\:\:{so}\:{we}\:{can}\:{take} \\ $$$${v}_{\mathrm{0}} =\frac{\mathrm{7}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{24}}\:+\frac{{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\left\{\right.\right.}{\mathrm{4}}\:=\frac{\mathrm{13}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{24}}\:{as}\:{approximst} \\ $$$${value}\:{for}\:{this}\:{integral}\:. \\ $$
Commented by abdo mathsup 649 cc last updated on 01/Jun/19

$${let}\:{I}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{{sinx}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{dx}\:\:\:{we}\:{have}\:{sinx}\:=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} {x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)!}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${I}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\left(\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)!}\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right){dx} \\ $$$$=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)!}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx}\:{let}\:{w}_{{n}} =\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{1}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{dx} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{w}_{{n}} =_{{x}={tan}\theta} \:\:\:\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} \:\:\frac{{tan}^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} \theta\left(\mathrm{1}+{tan}^{\mathrm{2}} \theta\right){d}\theta}{\mathrm{1}+{tan}^{\mathrm{2}} \theta} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{4}}} \:{tan}^{\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}} \theta\:{d}\theta\:\:\left({the}\:{value}\:{of}\:{this}\:{integral}\:{is}\right. \\ $$$$\left.{known}\right)\:\Rightarrow{I}\:=\:\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} }{\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{1}\right)!}\:{w}_{{n}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
