Question Number 127486 by shaker last updated on 30/Dec/20
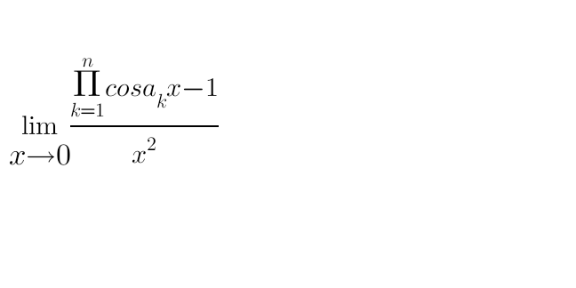
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 30/Dec/20
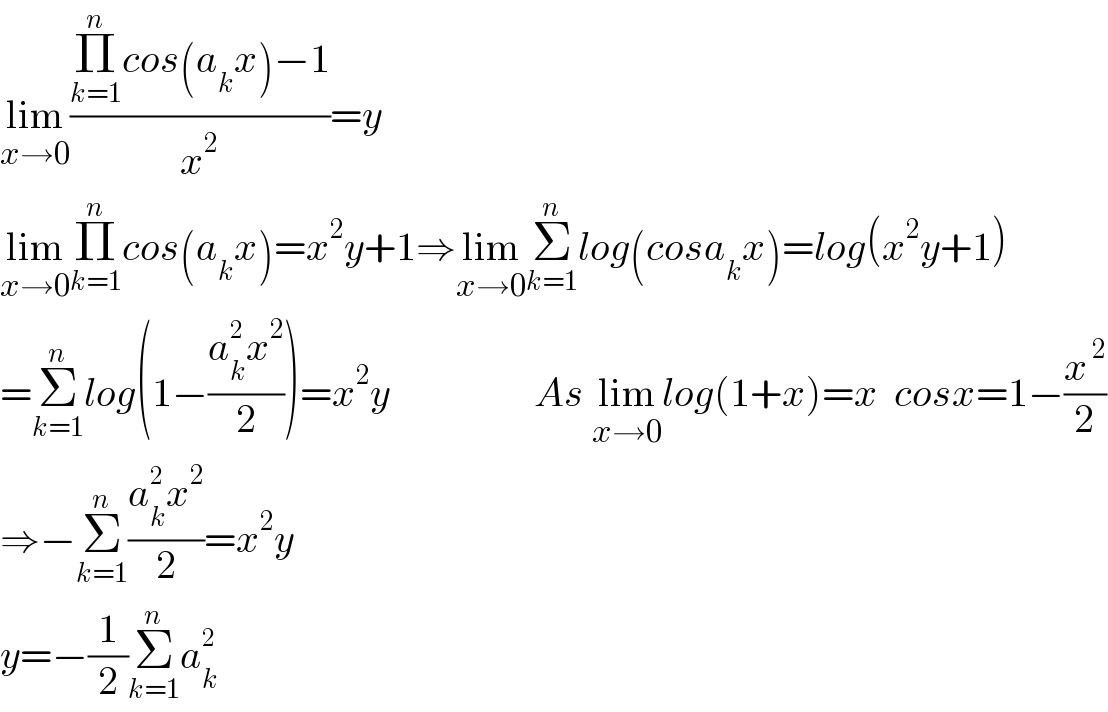
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\prod}}{cos}\left({a}_{{k}} {x}\right)−\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }={y} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\prod}}{cos}\left({a}_{{k}} {x}\right)={x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}+\mathrm{1}\Rightarrow\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}{log}\left({cosa}_{{k}} {x}\right)={log}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}+\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$=\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}{log}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{{a}_{{k}} ^{\mathrm{2}} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\right)={x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{As}\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}{log}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)={x}\:\:{cosx}=\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}^{\:\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow−\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\frac{{a}_{{k}} ^{\mathrm{2}} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}={x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y} \\ $$$${y}=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}{a}_{{k}} ^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
