Question Number 64166 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 14/Jul/19
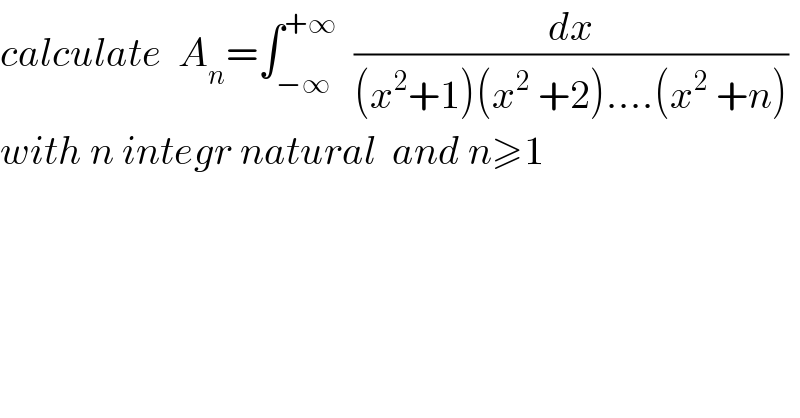
$${calculate}\:\:{A}_{{n}} =\int_{−\infty} ^{+\infty} \:\:\frac{{dx}}{\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\mathrm{2}\right)….\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{n}\right)} \\ $$$${with}\:{n}\:{integr}\:{natural}\:\:{and}\:{n}\geqslant\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Answered by Eminem last updated on 14/Jul/19
![f(z)=(dz/((z^2 +1)......(z^2 +n))) A_n =2iπRe(zk=i(√k),k∈[1..n]) res(f.i(√k))=(1/(2i(√k)Π_(j=1) ^(n,k≠j) (1−j)))=((1−k)/(2i(√k)(−1)^n (n−1)!)) A_n =2iπΣ_(k=2) ^n (((1−k))/(2i(√(k ))(n−1)!))+((2iπ)/(2i(−1)^n (n−1)!))](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q64171.png)
$${f}\left({z}\right)=\frac{{dz}}{\left({z}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\right)……\left({z}^{\mathrm{2}} +{n}\right)} \\ $$$${A}_{{n}} =\mathrm{2}{i}\pi{Re}\left({zk}={i}\sqrt{{k}},{k}\in\left[\mathrm{1}..{n}\right]\right) \\ $$$${res}\left({f}.{i}\sqrt{{k}}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{i}\sqrt{{k}}\underset{{j}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n},{k}\neq{j}} {\prod}}\left(\mathrm{1}−{j}\right)}=\frac{\mathrm{1}−{k}}{\mathrm{2}{i}\sqrt{{k}}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)!} \\ $$$${A}_{{n}} =\mathrm{2}{i}\pi\underset{{k}=\mathrm{2}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\frac{\left(\mathrm{1}−{k}\right)}{\mathrm{2}{i}\sqrt{{k}\:}\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)!}+\frac{\mathrm{2}{i}\pi}{\mathrm{2}{i}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} \left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)!} \\ $$
