Question Number 30356 by soksan last updated on 21/Feb/18
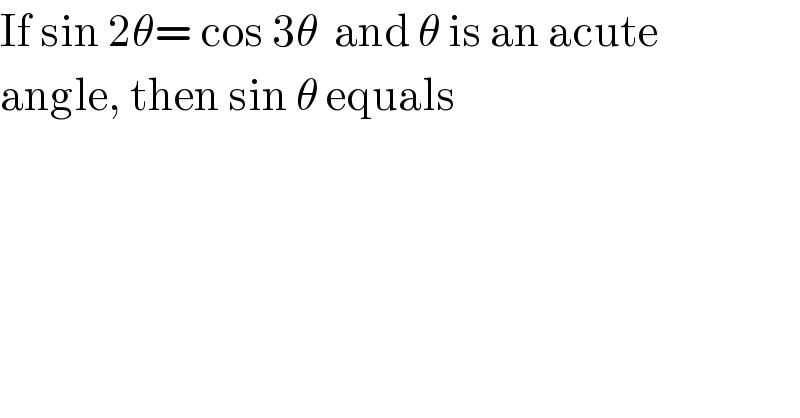
$$\mathrm{If}\:\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}\theta=\:\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{3}\theta\:\:\mathrm{and}\:\theta\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{an}\:\mathrm{acute} \\ $$$$\mathrm{angle},\:\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{sin}\:\theta\:\mathrm{equals} \\ $$
Answered by mrW2 last updated on 21/Feb/18

$$\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}\theta=\:\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{3}\theta \\ $$$$\mathrm{2sin}\:\theta\mathrm{cos}\:\theta=\mathrm{4cos}^{\mathrm{3}} \:\theta−\mathrm{3cos}\:\theta \\ $$$$\mathrm{2sin}\:\theta=\mathrm{4cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\theta−\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2sin}\:\theta=\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\theta\right)−\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\mathrm{4sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\theta+\mathrm{2sin}\:\theta−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{sin}\:\theta=\frac{−\mathrm{2}+\sqrt{\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{16}}}{\mathrm{8}}=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$${or} \\ $$$$\mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}\theta=\:\mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{3}\theta \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{2}\theta+\mathrm{3}\theta=\mathrm{90}° \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\theta=\mathrm{18}° \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{sin}\:\theta=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$
