Question Number 137784 by mathocean1 last updated on 06/Apr/21
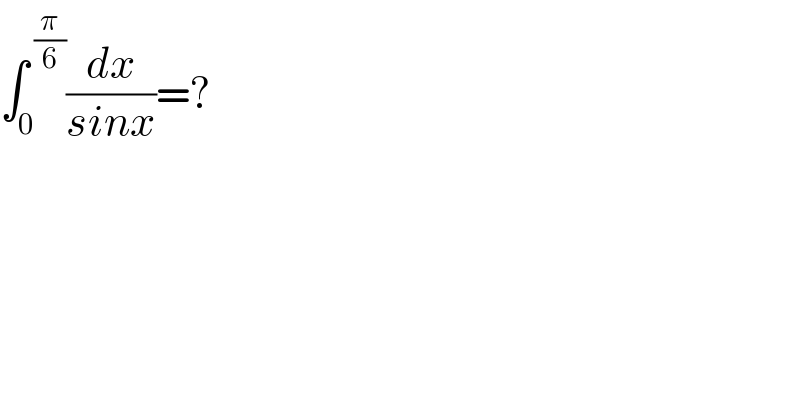
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{6}}} \frac{{dx}}{{sinx}}=? \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by EnterUsername last updated on 06/Apr/21
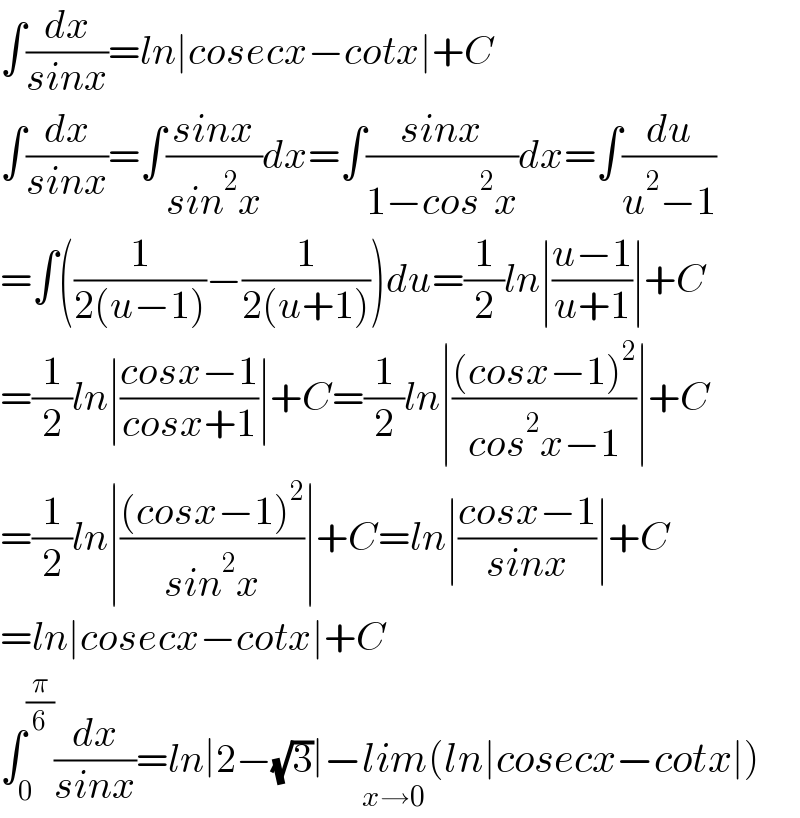
$$\int\frac{{dx}}{{sinx}}={ln}\mid{cosecx}−{cotx}\mid+{C} \\ $$$$\int\frac{{dx}}{{sinx}}=\int\frac{{sinx}}{{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}{dx}=\int\frac{{sinx}}{\mathrm{1}−{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}{dx}=\int\frac{{du}}{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$=\int\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\left({u}−\mathrm{1}\right)}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\left({u}+\mathrm{1}\right)}\right){du}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\mid\frac{{u}−\mathrm{1}}{{u}+\mathrm{1}}\mid+{C} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\mid\frac{{cosx}−\mathrm{1}}{{cosx}+\mathrm{1}}\mid+{C}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\mid\frac{\left({cosx}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}−\mathrm{1}}\mid+{C} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\mid\frac{\left({cosx}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}}\mid+{C}={ln}\mid\frac{{cosx}−\mathrm{1}}{{sinx}}\mid+{C} \\ $$$$={ln}\mid{cosecx}−{cotx}\mid+{C} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{6}}} \frac{{dx}}{{sinx}}={ln}\mid\mathrm{2}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\mid−\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {{lim}}\left({ln}\mid{cosecx}−{cotx}\mid\right) \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 06/Apr/21
![∫_0 ^(π/6) (dx/(sinx))=lim_(ξ→0) ∫_ξ ^(π/6) (dx/(sinx)) we have ∫_ξ ^(π/6) (dx/(sinx)) =_(tan((x/2))=t) ∫_(tan((ξ/2))) ^(2−(√3)) ((2dt)/((1+t^2 )×((2t)/(1+t^2 )))) =∫_(tan((ξ/2))) ^(2−(√3)) (dt/t) =[log∣t∣]_(tan((ξ/2))) ^(2−(√3)) =log(2−(√3))−log∣tan((x/2))∣ ⇒ lim_(ξ→0) ∫_ξ ^(π/6) (dx/(sinx)) =+∞ this integral is divergent !](https://www.tinkutara.com/question/Q137808.png)
$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{6}}} \:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{sinx}}=\mathrm{lim}_{\xi\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\:\int_{\xi} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{6}}} \:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{sinx}}\:\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have} \\ $$$$\int_{\xi} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{6}}} \:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{sinx}}\:=_{\mathrm{tan}\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)=\mathrm{t}} \:\:\:\int_{\mathrm{tan}\left(\frac{\xi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)} ^{\mathrm{2}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{2dt}}{\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)×\frac{\mathrm{2t}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }} \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{tan}\left(\frac{\xi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)} ^{\mathrm{2}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}} \frac{\mathrm{dt}}{\mathrm{t}}\:=\left[\mathrm{log}\mid\mathrm{t}\mid\right]_{\mathrm{tan}\left(\frac{\xi}{\mathrm{2}}\right)} ^{\mathrm{2}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}} \:\:=\mathrm{log}\left(\mathrm{2}−\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\right)−\mathrm{log}\mid\mathrm{tan}\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\mid\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{lim}_{\xi\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \int_{\xi} ^{\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{6}}} \:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{sinx}}\:=+\infty\:\:\:\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{integral}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{divergent}\:! \\ $$
