Question Number 217448 by ArshadS last updated on 14/Mar/25

Commented by Frix last updated on 14/Mar/25

Commented by Hanuda354 last updated on 15/Mar/25
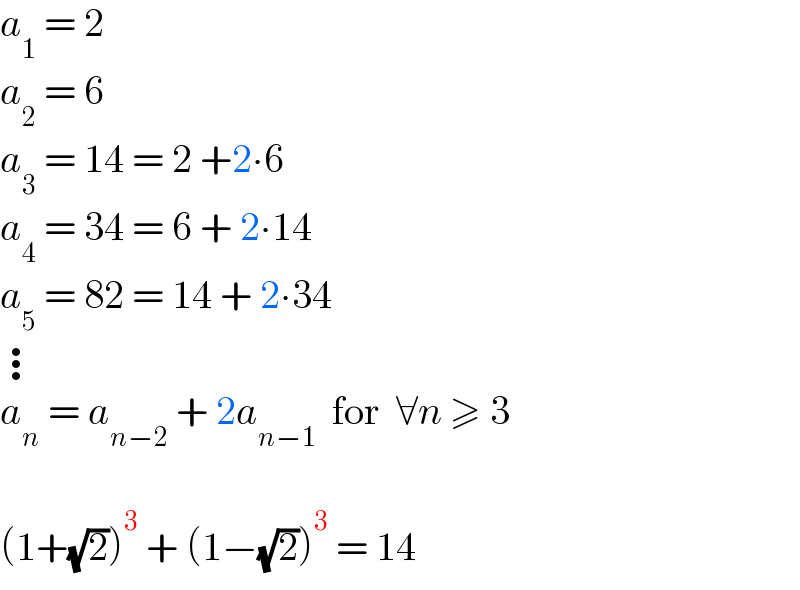
Answered by MrGaster last updated on 14/Mar/25

Answered by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 14/Mar/25
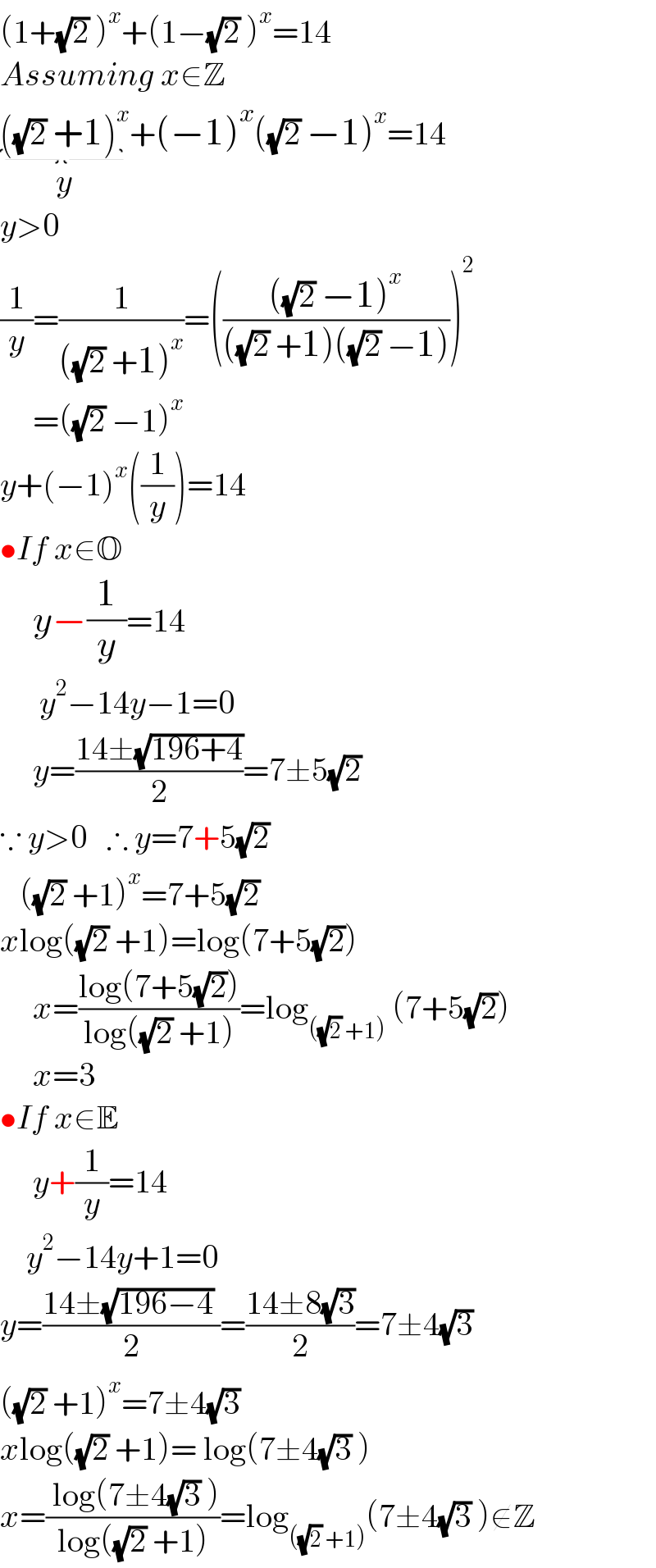
Answered by profcedricjunior last updated on 14/Mar/25

