Question Number 141858 by gsk2684 last updated on 24/May/21

Commented by gsk2684 last updated on 24/May/21

$${solution}\:{please} \\ $$
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 24/May/21
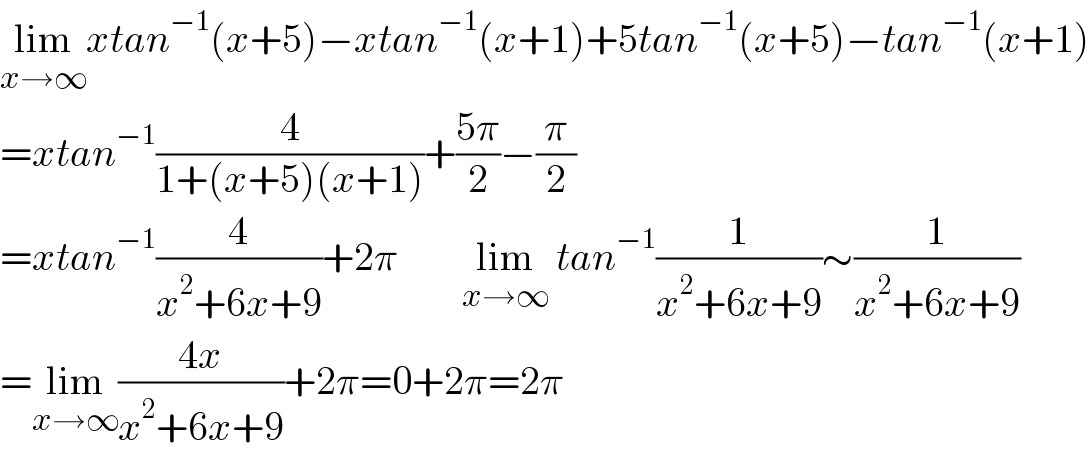
$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}{xtan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({x}+\mathrm{5}\right)−{xtan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)+\mathrm{5}{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({x}+\mathrm{5}\right)−{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$={xtan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{1}+\left({x}+\mathrm{5}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right)}+\frac{\mathrm{5}\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}\:\:\:\:\: \\ $$$$={xtan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{4}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{6}{x}+\mathrm{9}}+\mathrm{2}\pi\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:{tan}^{−\mathrm{1}} \frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{6}{x}+\mathrm{9}}\sim\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{6}{x}+\mathrm{9}} \\ $$$$=\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\mathrm{4}{x}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{6}{x}+\mathrm{9}}+\mathrm{2}\pi=\mathrm{0}+\mathrm{2}\pi=\mathrm{2}\pi \\ $$
Commented by gsk2684 last updated on 24/May/21

$${thank}\:{you}\: \\ $$
