Question Number 77285 by jagoll last updated on 05/Jan/20
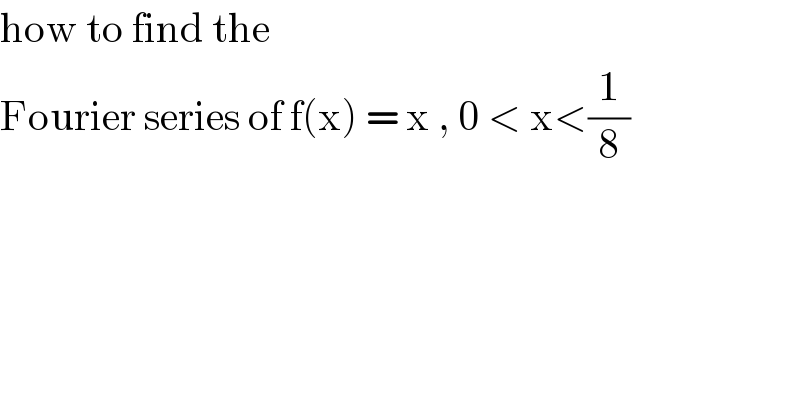
$$\mathrm{how}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{the}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{Fourier}\:\mathrm{series}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{x}\:,\:\mathrm{0}\:<\:\mathrm{x}<\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}} \\ $$
Answered by john santu last updated on 05/Jan/20
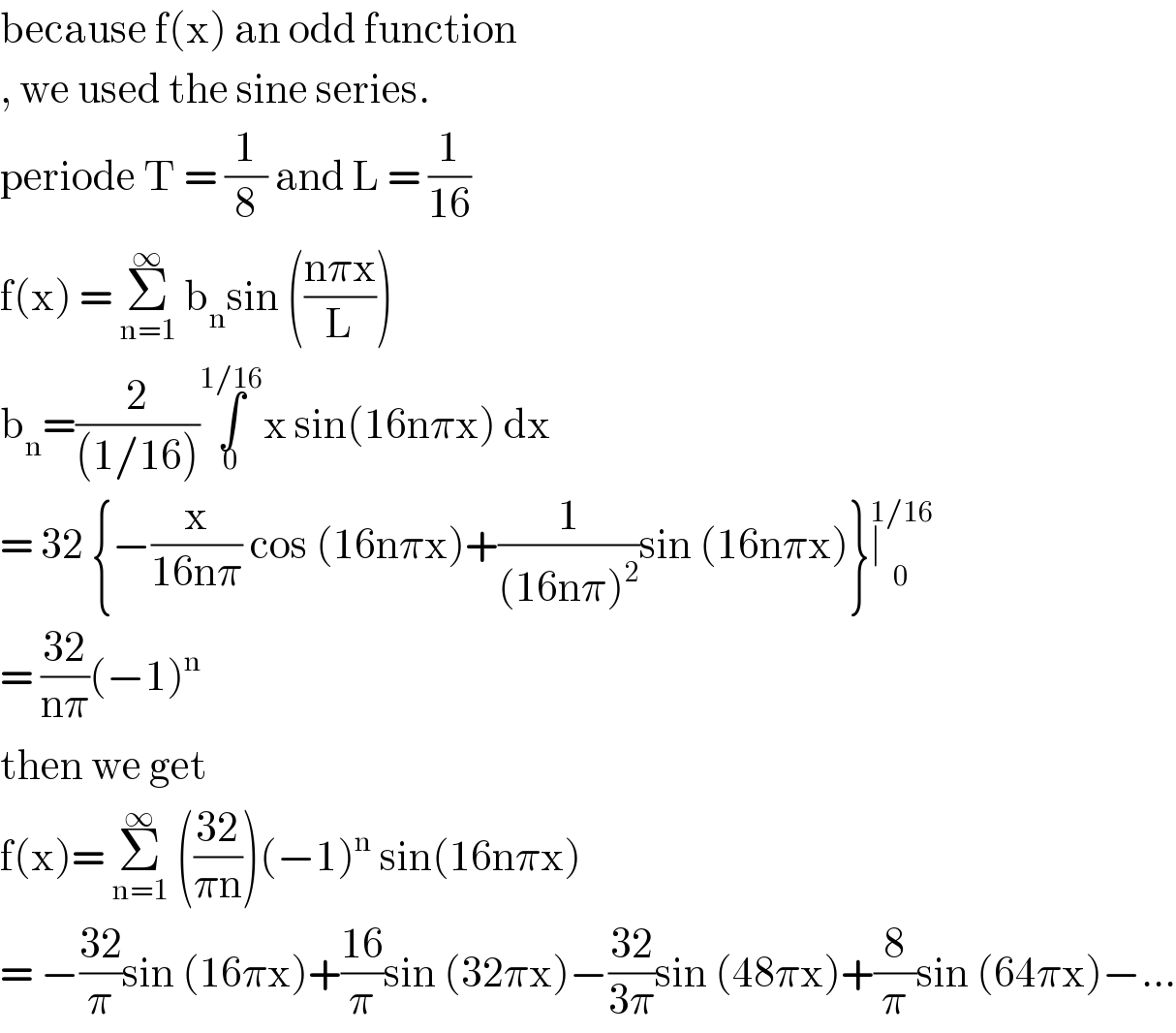
$$\mathrm{because}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:\mathrm{an}\:\mathrm{odd}\:\mathrm{function}\: \\ $$$$,\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{used}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{sine}\:\mathrm{series}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{periode}\:\mathrm{T}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{L}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{16}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\:\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\:\mathrm{b}_{\mathrm{n}} \mathrm{sin}\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{n}\pi\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{L}}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{b}_{\mathrm{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\left(\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{16}\right)}\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{16}} {\int}}\mathrm{x}\:\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{16n}\pi\mathrm{x}\right)\:\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$=\:\mathrm{32}\:\left\{−\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{16n}\pi}\:\mathrm{cos}\:\left(\mathrm{16n}\pi\mathrm{x}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{16n}\pi\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{16n}\pi\mathrm{x}\right)\right\}\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{16}} {\mid}} \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\mathrm{32}}{\mathrm{n}\pi}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{get}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\:\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{32}}{\pi\mathrm{n}}\right)\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{n}} \:\mathrm{sin}\left(\mathrm{16n}\pi\mathrm{x}\right)\: \\ $$$$=\:−\frac{\mathrm{32}}{\pi}\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{16}\pi\mathrm{x}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{16}}{\pi}\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{32}\pi\mathrm{x}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{32}}{\mathrm{3}\pi}\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{48}\pi\mathrm{x}\right)+\frac{\mathrm{8}}{\pi}\mathrm{sin}\:\left(\mathrm{64}\pi\mathrm{x}\right)−… \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 05/Jan/20

$$\mathrm{thanks}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
