Question Number 112 by saidinesh999.sd@gmail.com last updated on 25/Jan/15
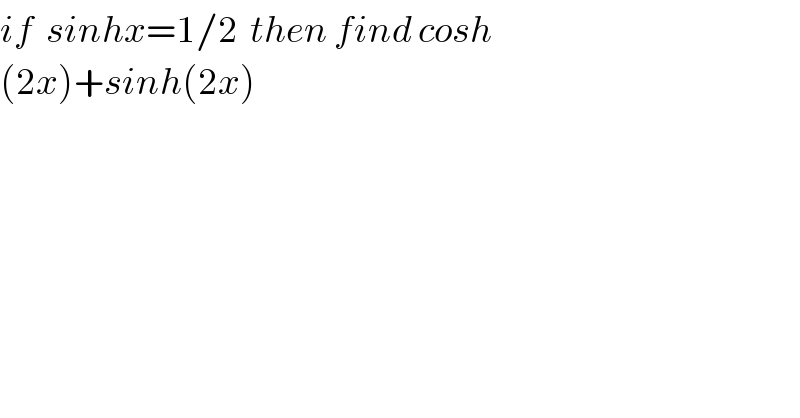
$${if}\:\:{sinhx}=\mathrm{1}/\mathrm{2}\:\:{then}\:{find}\:{cosh} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right)+{sinh}\left(\mathrm{2}{x}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by sagarwal last updated on 04/Dec/14
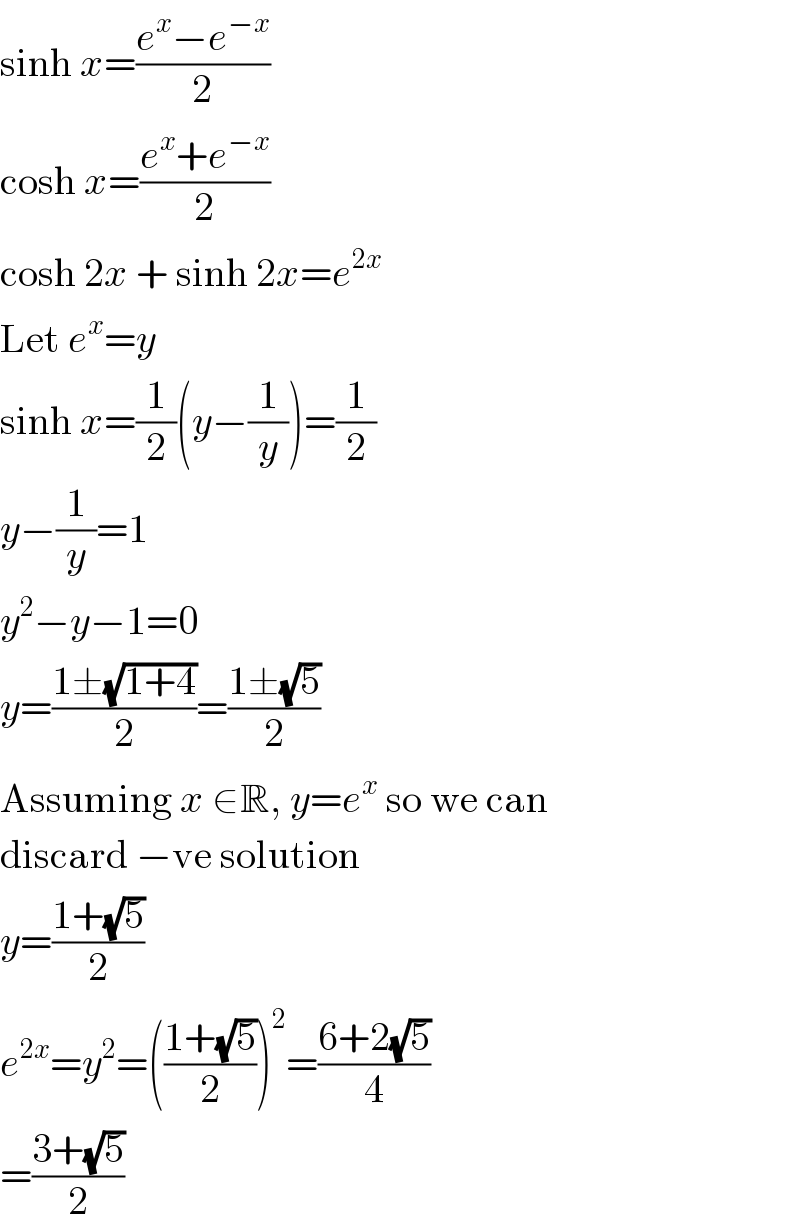
$$\mathrm{sinh}\:{x}=\frac{{e}^{{x}} −{e}^{−{x}} }{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{cosh}\:{x}=\frac{{e}^{{x}} +{e}^{−{x}} }{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{cosh}\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:+\:\mathrm{sinh}\:\mathrm{2}{x}={e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Let}\:{e}^{{x}} ={y} \\ $$$$\mathrm{sinh}\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({y}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{y}}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${y}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{y}}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${y}^{\mathrm{2}} −{y}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{\mathrm{1}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{4}}}{\mathrm{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{1}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Assuming}\:{x}\:\in\mathbb{R},\:{y}={e}^{{x}} \:\mathrm{so}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{can} \\ $$$$\mathrm{discard}\:−\mathrm{ve}\:\mathrm{solution} \\ $$$${y}=\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} ={y}^{\mathrm{2}} =\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{6}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{3}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
