
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 103154 by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 13/Jul/20
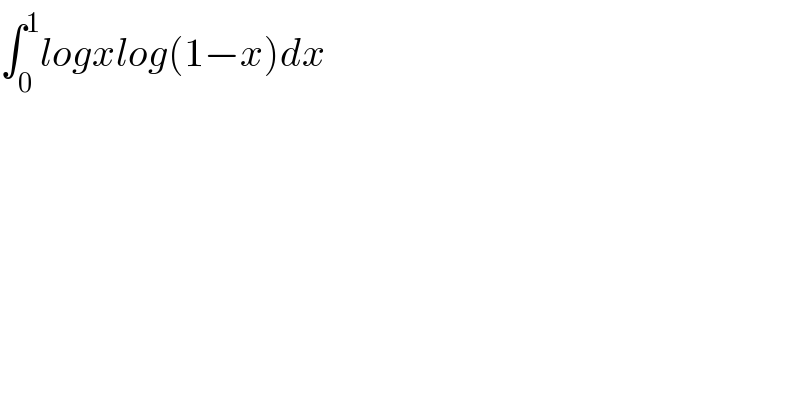
Answered by OlafThorendsen last updated on 13/Jul/20
![I = ∫_0 ^1 lnxln(1−x)dx −(1/(1−x)) = −Σ_(n=0) ^∞ x^n ln(1−x) = −Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (x^(n+1) /(n+1)) = −Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (x^n /n) I = −∫_0 ^1 lnxΣ_(n=1) ^∞ (x^n /n)dx I = −Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (1/n)∫_0 ^1 x^n lnxdx I_n = −∫_0 ^1 x^n lnxdx I_n = −[(x^(n+1) /(n+1))lnx]_0 ^1 +∫_0 ^1 (x^(n+1) /(n+1)).(1/x)dx I_n = 0+∫_0 ^1 (x^n /(n+1))dx = [(x^(n+1) /((n+1)^2 ))]_0 ^1 I_n = (1/((n+1)^2 )) I = Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (1/n)I_n = Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (1/(n(n+1)^2 )) I = Σ_(n=1) ^∞ ((1/n)−(1/(n+1))−(1/((n+1)^2 ))) Σ_(n=1) ^∞ ((1/n)−(1/(n+1))) = (1−(1/2))+((1/2)−(1/3))+... Σ_(n=1) ^∞ ((1/n)−(1/(n+1))) = 1 I = 1−Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (1/((n+1)^2 )) I = 1−Σ_(n=2) ^∞ (1/n^2 ) I = 2−Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (1/n^2 ) I = 2−ζ(2) = 2−(π^2 /6)](Q103174.png)
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 13/Jul/20

Answered by bobhans last updated on 13/Jul/20
![I = ∫_0 ^1 ln(x) ln(1−x) dx by Maclaurin series ln(1−x) = −Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (x^n /n) we obtain I=−∫_0 ^1 ln(x)Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (x^n /n) dx I = −Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (1/n)∫_0 ^1 x^n ln(x) dx [ by parts ] { ((u = ln(x))),((dv = x^n dx )) :} I=−Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (1/n)∣((x^(n+1) /(n+1)) ln(x)−(x^(n+1) /((n+1)^2 )))∣_0 ^1 I= Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (1/(n(n+1)^2 )) [ by L′Hopital rule′s] I= Σ_(n=1) ^∞ ((1/n)−(1/(n+1))−(1/((n+1)^2 ))) the first series Σ_(n=1) ^∞ ((1/n)−(1/(n+1))) is telescoping ⇒ lim_(p→∞) Σ_(n=1) ^p ((1/n)−(1/(n+1))) = lim_(p→∞) (1−(1/(p+1))) = 1 now the second series Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (1/((n+1)^2 )) = Σ_(k=2) ^∞ (1/k^2 ) = −1+Σ_(k=1) ^∞ (1/k^2 ) = −1+(π^2 /6) . therefore I = ∫_0 ^1 ln(x) ln(1−x)dx = 1−(−1+(π^2 /6)) = 2−(π^2 /6) . ★](Q103210.png)
