
Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 100766 by john santu last updated on 28/Jun/20

Answered by Rio Michael last updated on 28/Jun/20
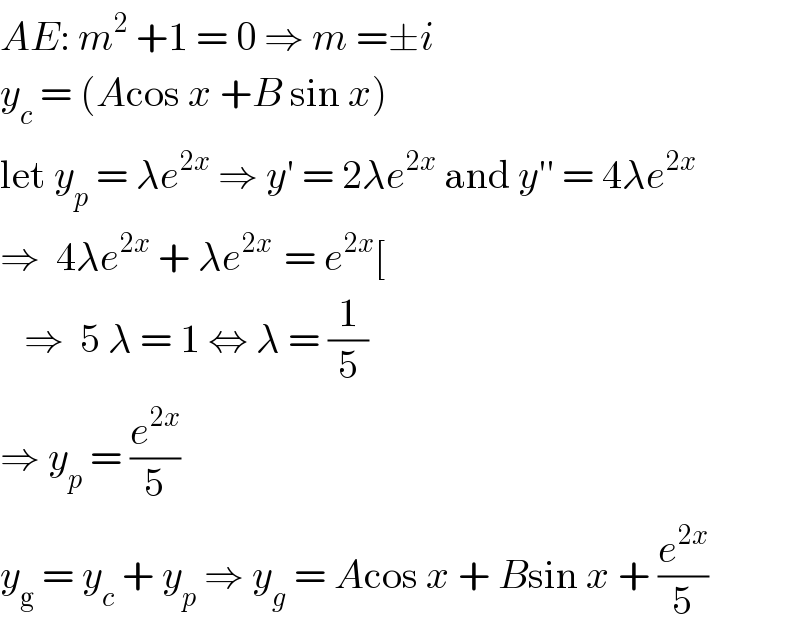
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 28/Jun/20

Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 28/Jun/20
![Laplace method y^(′′) +y =e^(2x) ⇒L(y^(′′) )+L(y) =L(e^(2x) ) ⇒ x^2 L(y)−xy(0)−y^′ (0) +L(y) =L(e^(2x) ) ⇒(x^2 +1)L(y) =xy(0)+y^′ (0)+L(e^(2x) ) we have L(e^(2x) ) =∫_0 ^∞ e^(2t) e^(−xt) dt =∫_0 ^∞ e^((2−x)t) dt =[(1/(2−x)) e^((2−x)t) ]_0 ^(+∞) =−(1/(2−x)) =(1/(x−2)) ⇒(x^2 +1)L(y) =(1/(x−2)) +xy(o) +y^′ (0) ⇒ L(y) =(1/((x−2)(x^2 +1))) +(x/(x^2 +1))y(o) +((y^′ (0))/(x^2 +1)) ⇒ y(x) =L^(−1) ((1/((x−2)(x^2 +1))))+y(o)L^(−1) ((x/(x^2 +1)))+y^′ (o)L^(−1) ((1/(x^2 +1))) we have L^(−1) ((x/(x^2 +1))) =cosx and L^(−1) ((1/(x^2 +1))) =sinx f(x) =(1/((x−2)(x^2 +1))) =(1/((x−2)(x−i)(x+i))) =(a/(x−2)) +(b/(x−i)) +(c/(x+i)) L^(−1) (f(x)) =ae^(2x) +b e^(ix) +ce^(−ix) →ae^(2x) +αcosx +βsinx ⇒ a =(1/5) ⇒y(x) =(1/5)e^(2x) +A cosx +B sinx](Q100780.png)
Answered by john santu last updated on 28/Jun/20

