
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 101888 by bemath last updated on 05/Jul/20
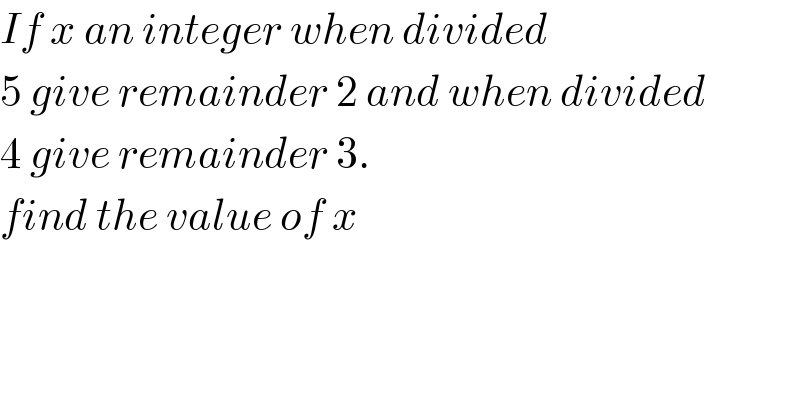
Commented by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 05/Jul/20
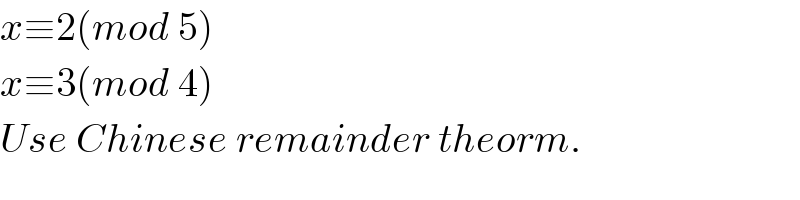
Answered by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 05/Jul/20

Answered by john santu last updated on 05/Jul/20
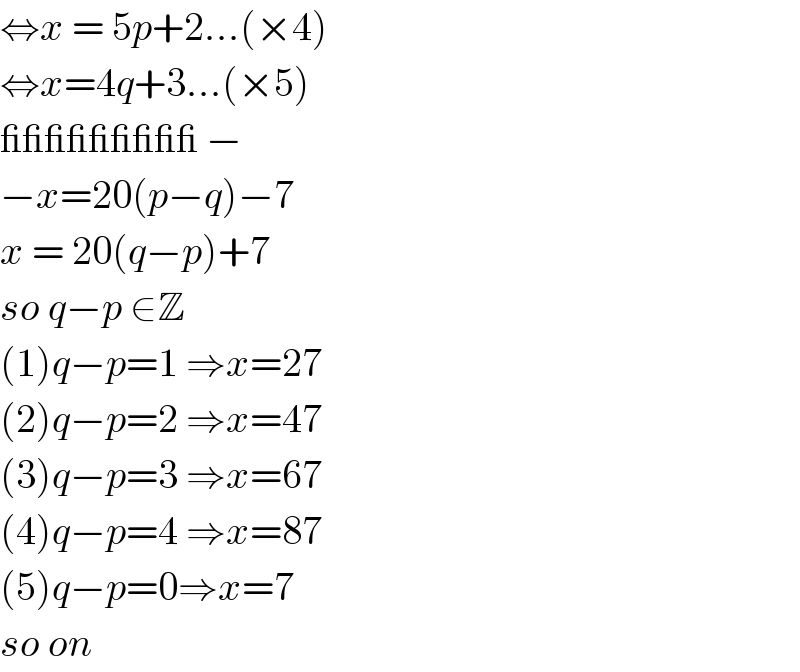
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 05/Jul/20
![x≡2[5] and x ≡3 4] ⇒x =5n +2 and x =4m+3 ⇒ 5n+2 =4m+3 let use congruence modulo 5(prime) ⇒ 2^− =−m^− +3^− ⇒m^− = 3^− −2^− =1^− ⇒m =5q+1 ⇒x =4(5q+1)+3 ⇒x =20q +7](Q101938.png)
