
Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 102716 by Ar Brandon last updated on 10/Jul/20

Answered by bramlex last updated on 10/Jul/20

Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 10/Jul/20
�� Thanks
Commented by bramlex last updated on 10/Jul/20
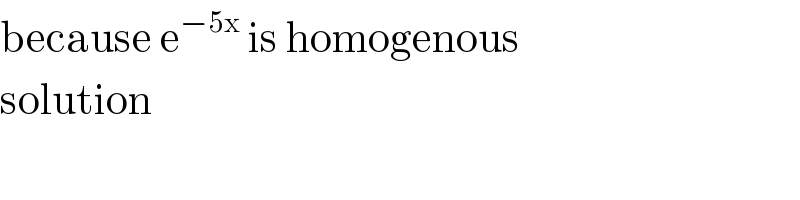
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 10/Jul/20

Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 10/Jul/20

Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 10/Jul/20

Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 10/Jul/20
�� Thanks
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 10/Jul/20
https://www.pdfdrive.com/search?q=jee+mathematics&pagecount=&pubyear=&searchin=
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 10/Jul/20
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 10/Jul/20
Yes bro,�� They're among my ebooks.��
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 10/Jul/20
Oh I am a Indian student also����.Which book do you study?��
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 10/Jul/20
��From your name I could deduce that.
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 10/Jul/20
But actually I just use these JEE Ebooks to help maximise my skills. I noticed it contains questions which push you to the peak of reasoning in every chapter.And I'm also a student.��
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 10/Jul/20
�� I am also.......( understand what I want to mean)
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 10/Jul/20
����
Commented by IRAN_majid last updated on 10/Jul/20

Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 10/Jul/20

Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 10/Jul/20
What's the theory, Sir ? ��
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 10/Jul/20
I understand you may be so busy by now. Please reply whenever you feel it's OK to do so.��
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 10/Jul/20
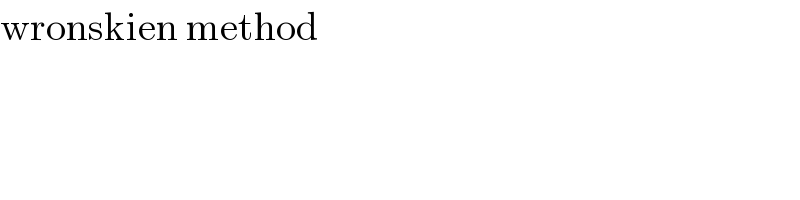
Answered by Aziztisffola last updated on 10/Jul/20

