
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 103623 by Lordose last updated on 16/Jul/20
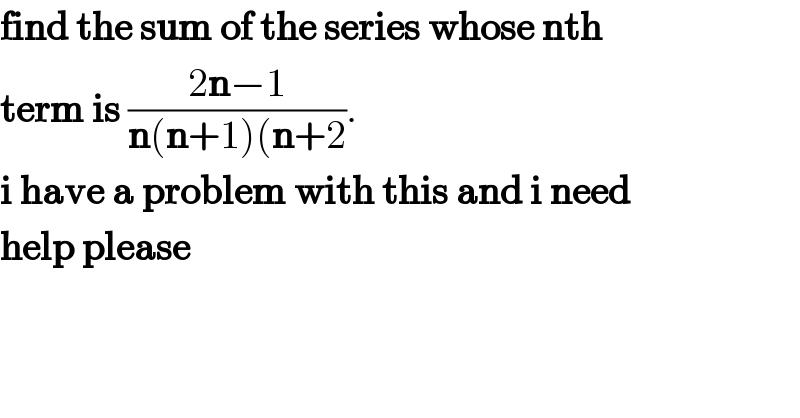
Answered by OlafThorendsen last updated on 16/Jul/20

Commented by Lordose last updated on 16/Jul/20

Answered by bobhans last updated on 16/Jul/20
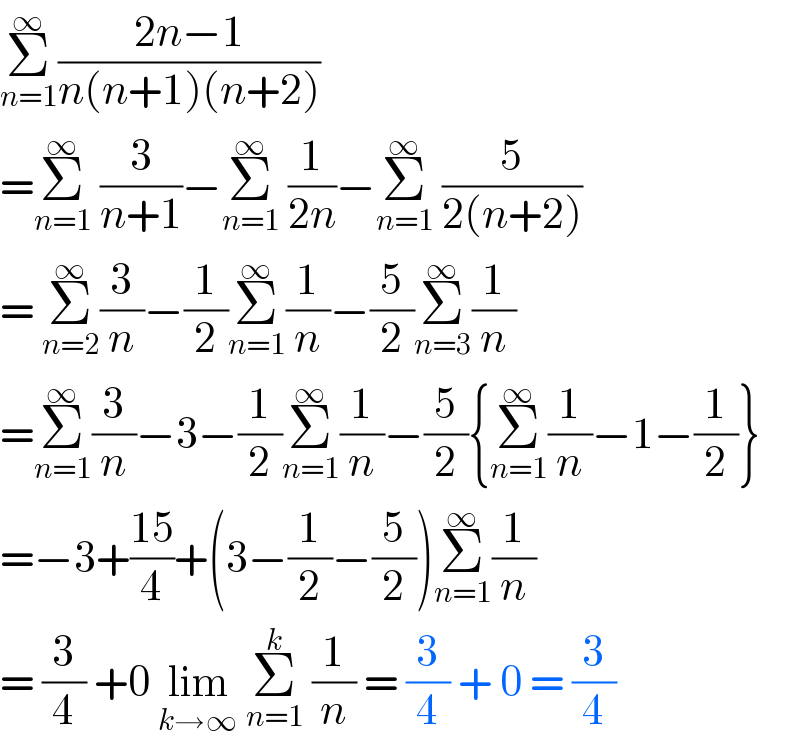
Commented by Lordose last updated on 16/Jul/20

Commented by bobhans last updated on 16/Jul/20

