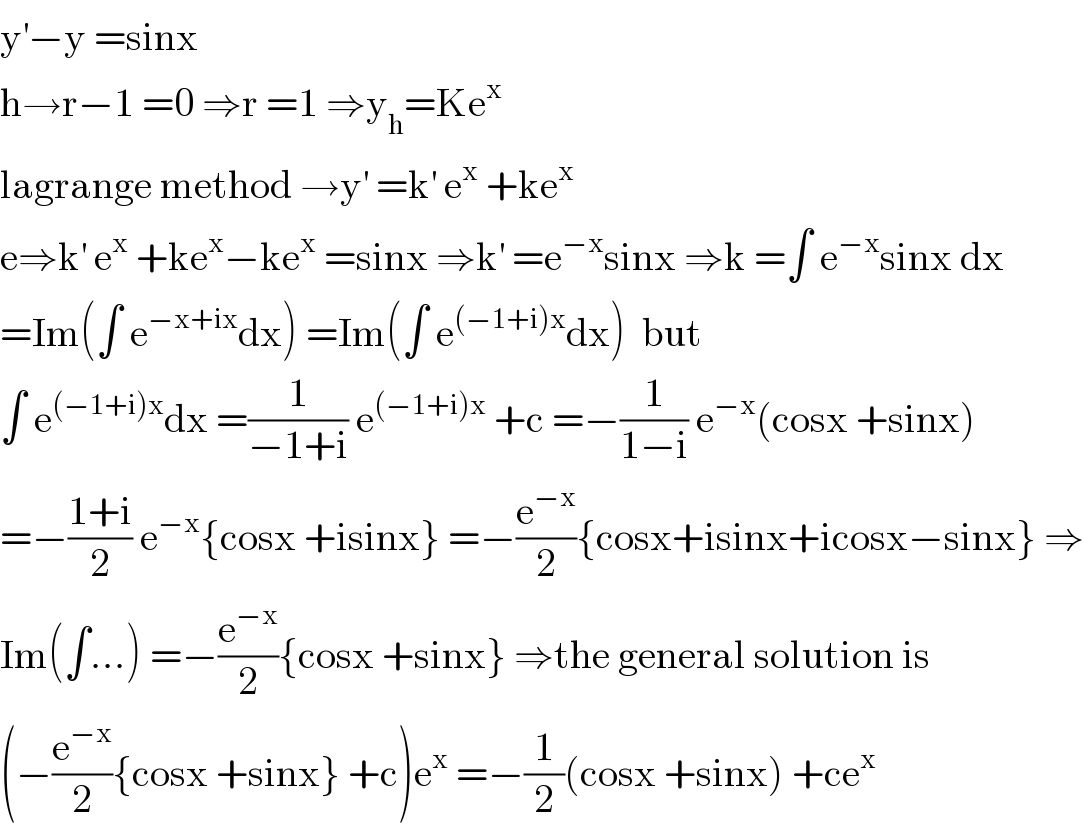Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 104265 by mohammad17 last updated on 20/Jul/20
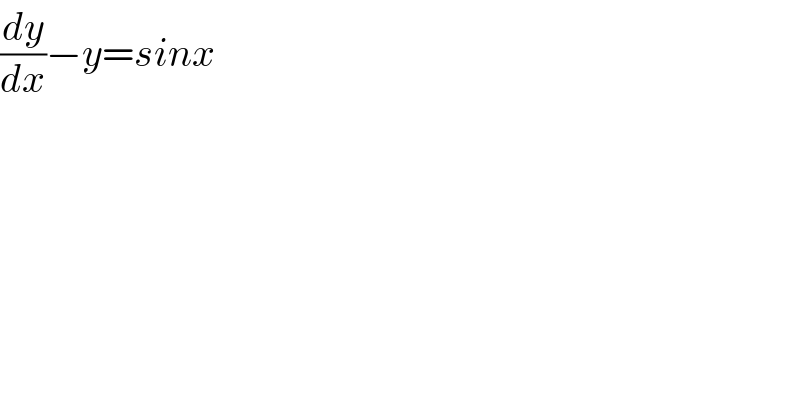
Answered by bemath last updated on 20/Jul/20
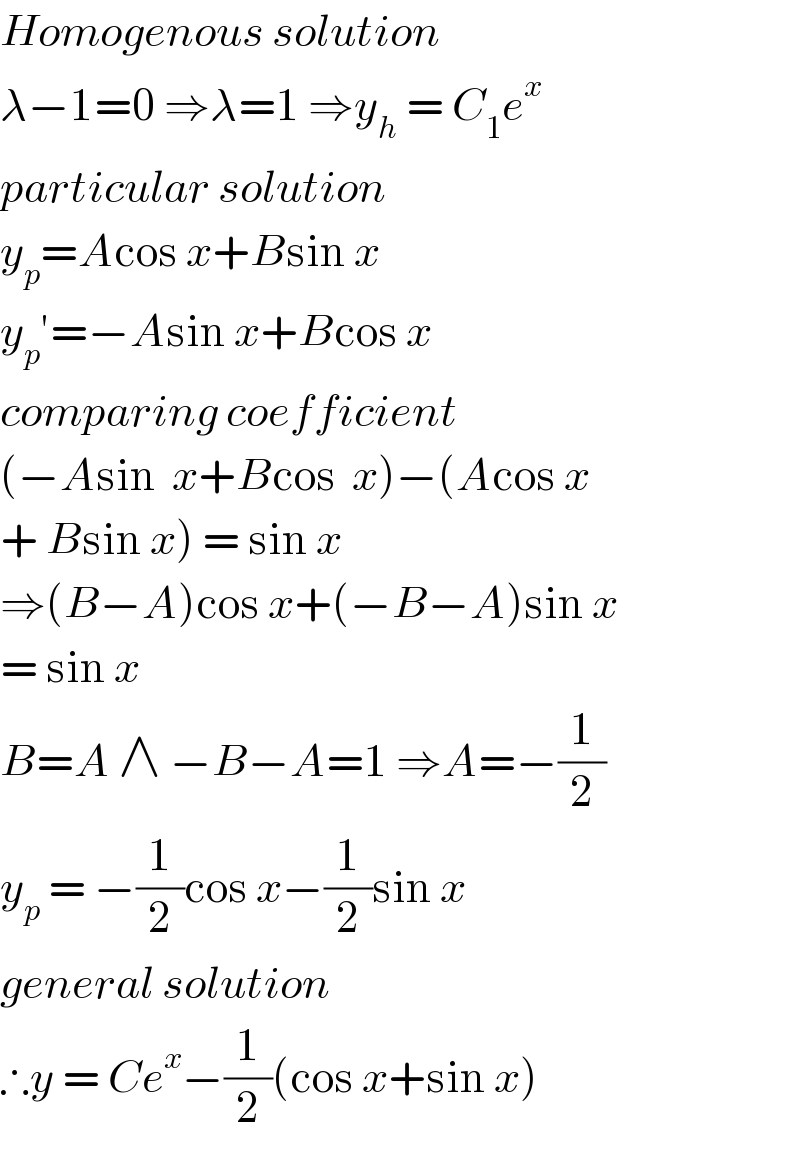
Commented by mohammad17 last updated on 20/Jul/20
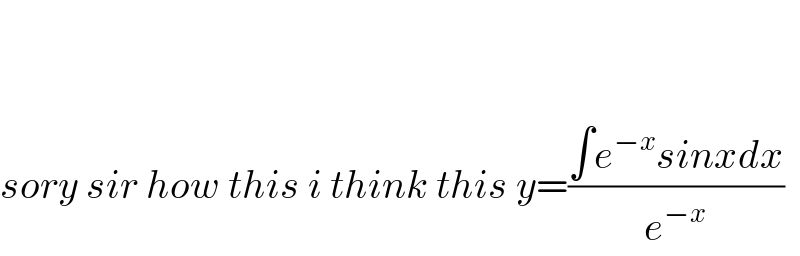
Commented by mohammad17 last updated on 20/Jul/20

Commented by mohammad17 last updated on 20/Jul/20
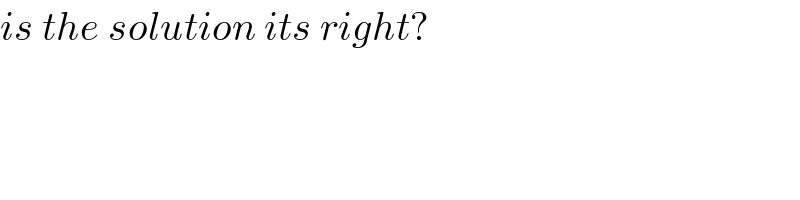
Commented by bemath last updated on 20/Jul/20

Commented by mohammad17 last updated on 20/Jul/20

Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 20/Jul/20
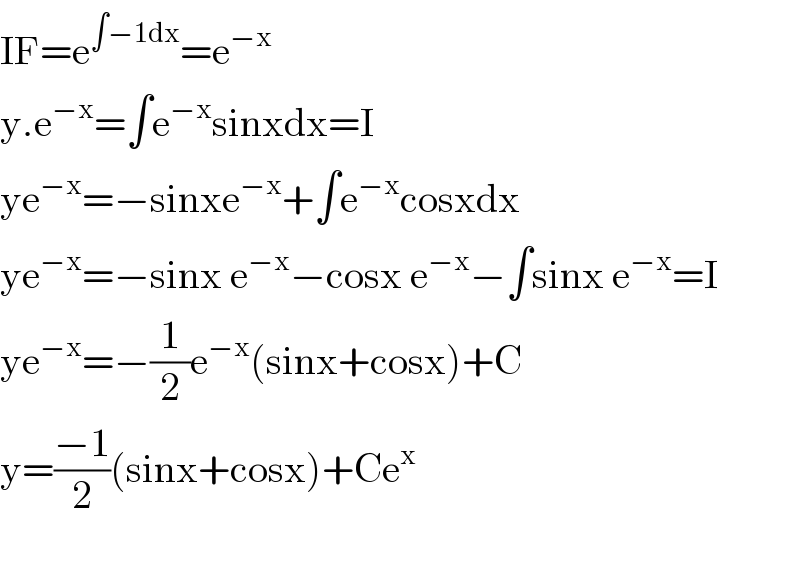
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 20/Jul/20

Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 20/Jul/20