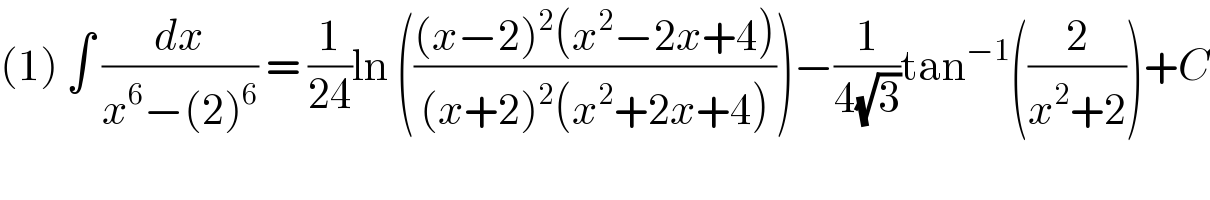Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 105039 by bemath last updated on 25/Jul/20

Answered by bobhans last updated on 25/Jul/20
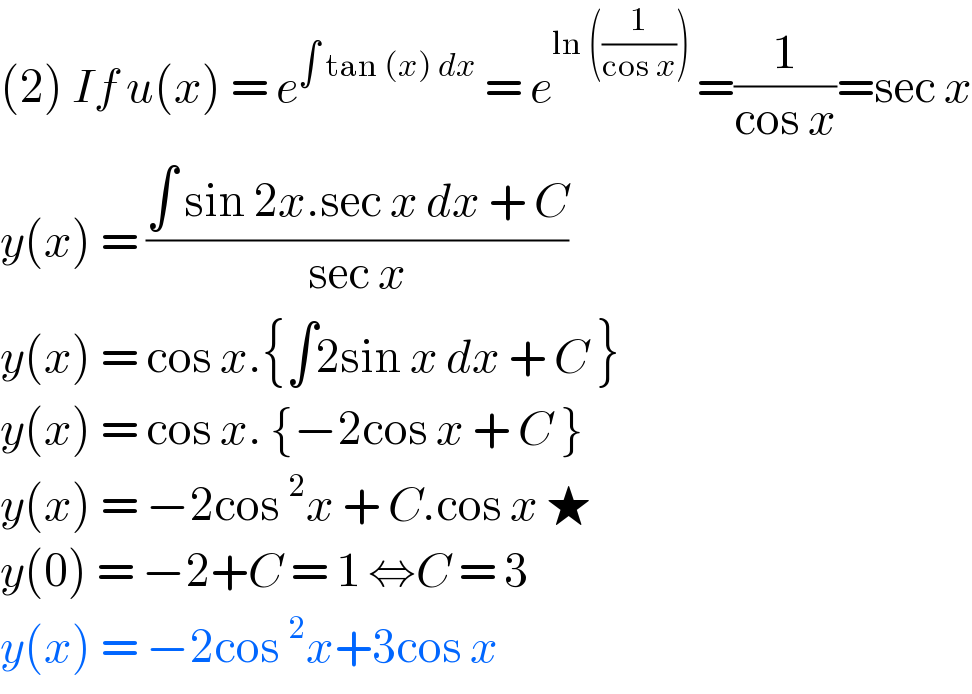
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 25/Jul/20
![1) complex method we decompose F(z) =(1/(z^6 −64)) ⇒ z^6 =64 let z =re^(iθ) so e ⇒r^6 e^(i6θ) =64 e^(i(2kπ)) ⇒r =^6 (√(64)) =2 θ =((kπ)/3) and k∈[[0,5]] so the roots are z_k =2e^(i((kπ)/3)) and 0≤k≤5 ⇒F(z) =(1/(Π_(k=0) ^5 (z−z_k ))) =Σ_(k=0) ^5 (a_k /(z−z_k )) with a_k =(1/(6z_k ^5 )) =(z_k /(6(64))) =(z_k /(384)) ⇒F(z) =(1/(384)) Σ_(k=0) ^5 (z_k /(z−z_k )) ⇒∫ F(z)dz =(1/(384)) Σ_(k=0) ^5 z_k ∫ (dz/(z−2e^((ikπ)/3) )) =(1/(384)) Σ_(k=0) ^5 (2e^((ikπ)/3) )ln(z−2e^((ikπ)/3) ) +C](Q105049.png)
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 25/Jul/20
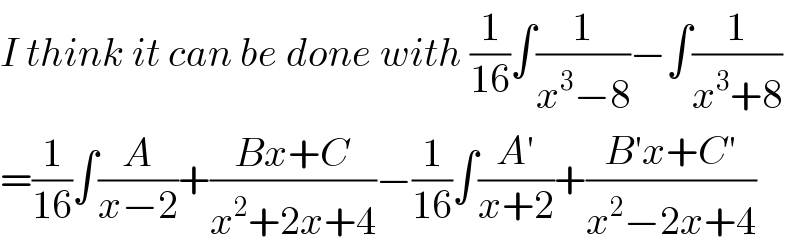
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 26/Jul/20
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 25/Jul/20
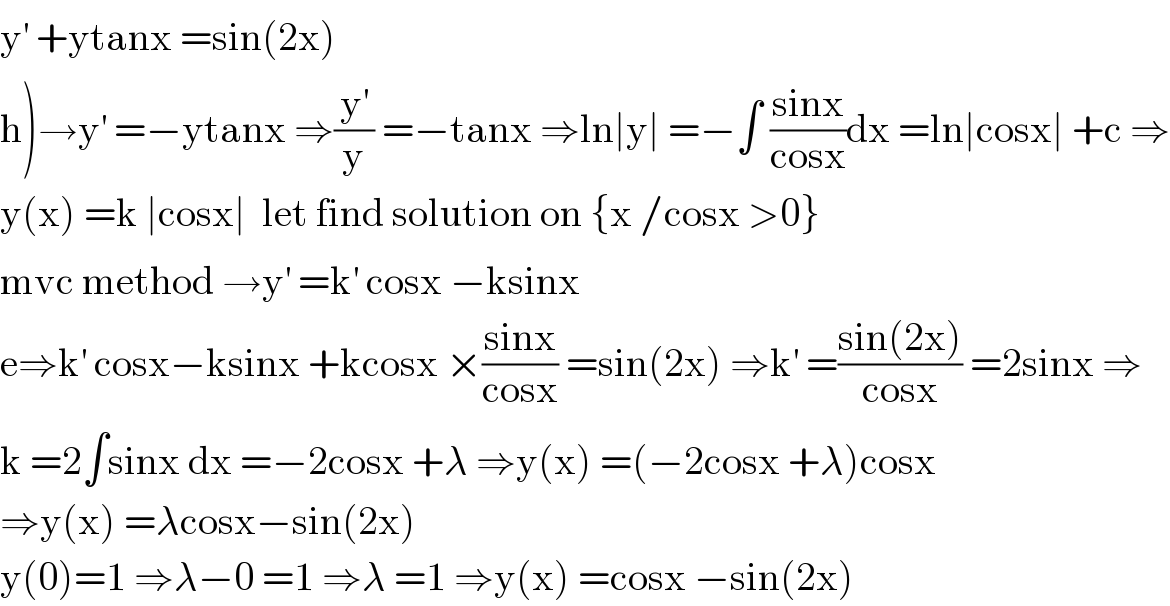
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 25/Jul/20
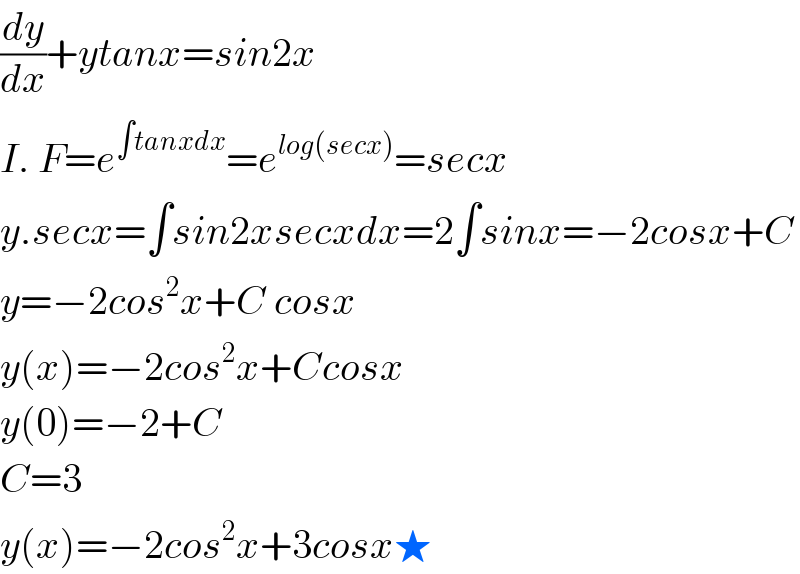
Answered by OlafThorendsen last updated on 25/Jul/20
![(1) R(x) = (1/(x^6 −1)) R(x) = (1/((x−1)(x+1)(x^2 −x+1)(x^2 −x+1))) ∫R(x)dx = ∫((1/(6(x−1)))−(1/(6(x+1)))+((x−2)/(6(x^2 −x+1)))−((x+2)/(6(x^2 +x+1))))dx = (1/6)ln∣((x−1)/(x+1))∣ +(1/(12))∫((2x−1)/(x^2 −x+1))dx−(1/(12))∫((2x+1)/(x^2 +x+1))dx −(1/4)∫(dx/(x^2 −x+1))−(1/4)∫(dx/(x^2 +x+1)) =(1/6)ln∣((x−1)/(x+1))∣+(1/(12))ln∣((x^2 −x+1)/(x^2 +x+1))∣ −(1/3)∫(dx/((4/3)(x−(1/2))^2 +1))−(1/3)∫(dx/((4/3)(x+(1/2))^2 +1)) =(1/6)ln∣((x−1)/(x+1))∣+(1/(12))ln∣((x^2 −x+1)/(x^2 +x+1))∣ −(1/(2(√3)))arctan[(2/(√3))(x−(1/2))]−(1/(2(√3)))arctan[(2/(√3))(x+(1/2))] arctanu+arctanv = arctan((u+v)/(1−uv)) u = (2/(√3))(x−(1/2)) and v = (2/(√3))(x+(1/2)) ((u+v)/(1−uv)) = (((4/(√3))x)/(1−(4/3)(x^2 −(1/4)))) = (((√3)x)/(1−x^2 )) Finally : ∫R(x)dx = (1/6)ln∣((x−1)/(x+1))∣+(1/(12))ln∣((x^2 −x+1)/(x^2 +x+1))∣−(1/(2(√3)))arctan(((√3)x)/(1−x^2 ))+C](Q105067.png)
Commented by bemath last updated on 27/Jul/20
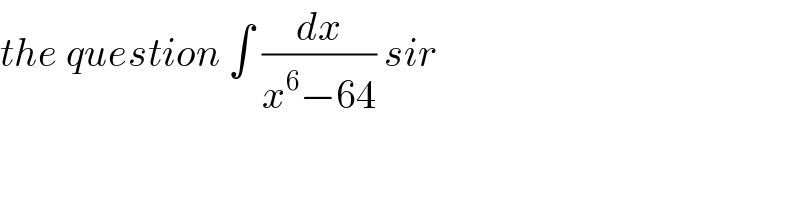
Answered by OlafThorendsen last updated on 25/Jul/20
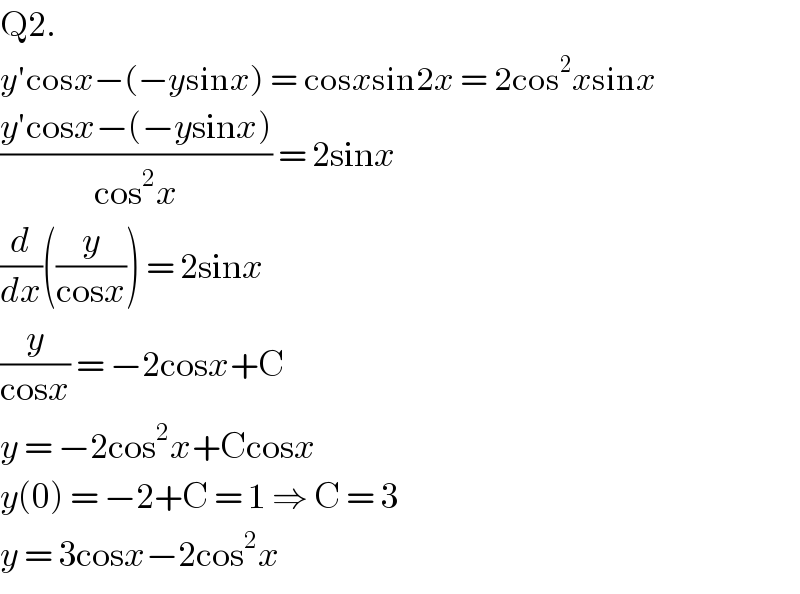
Answered by bramlex last updated on 26/Jul/20