Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 105163 by bemath last updated on 26/Jul/20
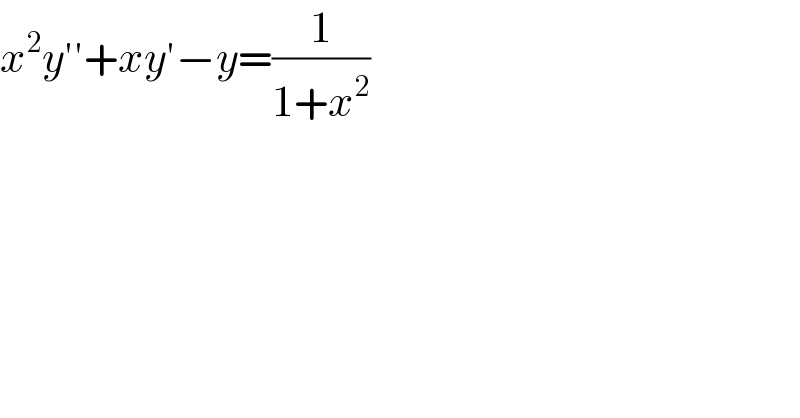
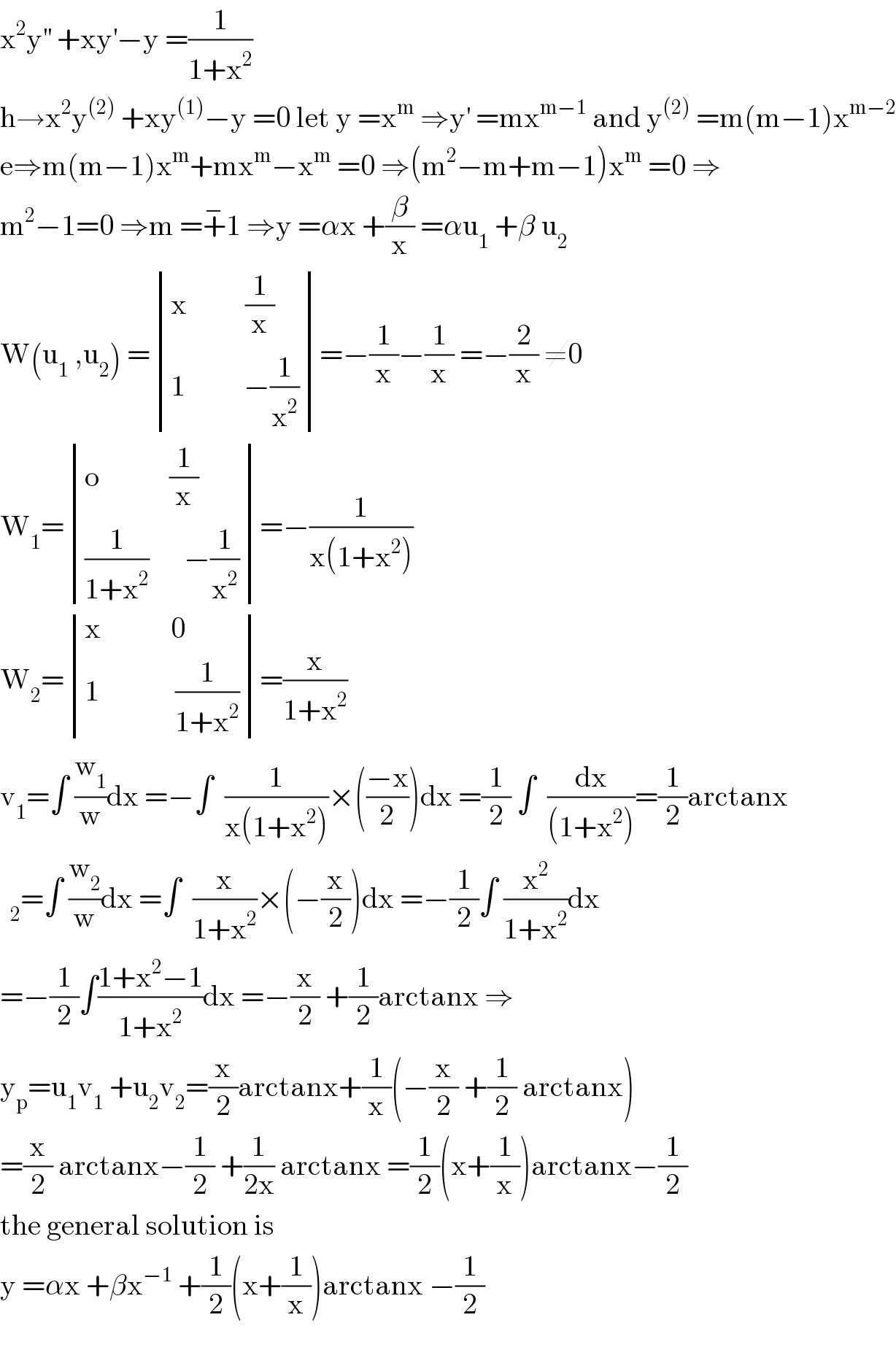
Answered by bramlex last updated on 27/Jul/20
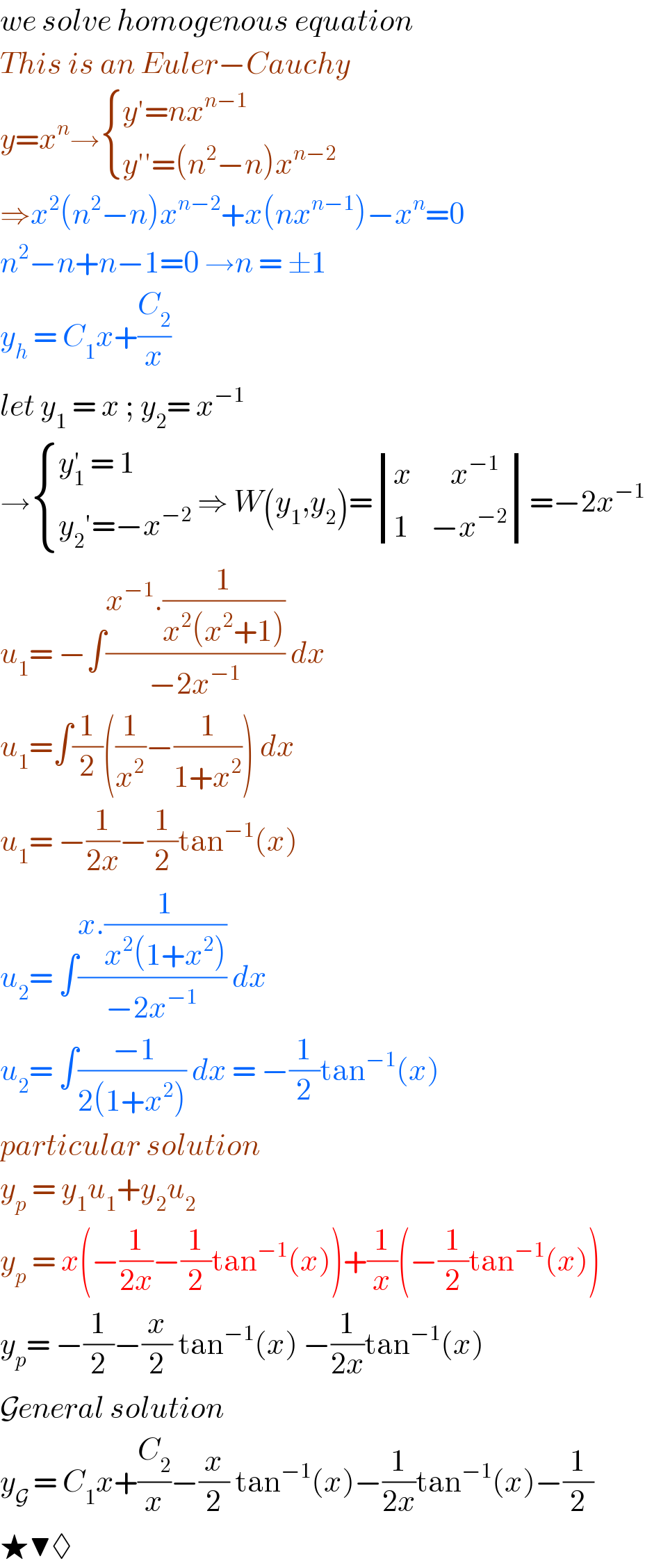
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 26/Jul/20