
Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 105564 by Ar Brandon last updated on 30/Jul/20
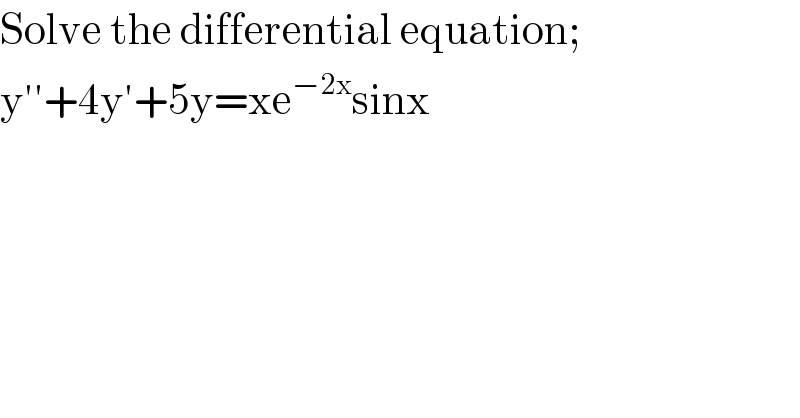
Answered by bobhans last updated on 30/Jul/20
![Homogenous equation υ^2 +4υ+5=0 →υ=((−4±2i)/2)=−2±i y_h =e^(−2x) {C_1 cos x+C_2 sin x} particular solution y_1 =e^(−2x) cos x⇒y_1 ′=−2e^(−2x) cos x−e^(−2x) sinx y_2 =e^(−2x) sin x⇒y_2 ′=−2e^(−2x) sin x+e^(−2x) cosx W= determinant ((( e^(−2x) cos x e^(−2x) sin x)),((e^(−2x) (−2cos x−sin x) e^(−2x) (−2sin x+cos x))) = e^(−4x) (−2sin xcos x+cos^2 x)−e^(−4x) (−2sinx cos x −sin^2 x) = e^(−4x) u_1 =−∫ ((e^(−2x) sin x(xe^(−2x) sin x)dx)/e^(−4x) ) u_1 =−∫ xsin^2 x dx = −∫x((1/2)−(1/2)cos2x)dx u_1 =−[(1/4)x^2 −((1/4)xcos 2x−(1/8)sin 2x)] u_1 =−(1/4)x^2 +(1/4)xcos 2x−(1/8)sin 2x u_2 =∫ ((e^(−2x) cos x(xe^(−2x) sin x)dx)/e^(−4x) ) u_2 = ∫(1/2)xsin 2x dx = −(1/4)xcos 2x+(1/(16))sin2x y_p = y_1 u_1 +y_2 u_2 y_p = e^(−2x) cos x(−(1/4)x^2 +(1/4)xcos 2x−(1/8)sin2x) + e^(−2x) sin x(−(1/4)xcos 2x+(1/(16))sin 2x) General solution y_G = y_b + y_p .★](Q105568.png)
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 30/Jul/20
Thanks, Sir Bobhans. Is this Wronskien's method ?��
Commented by bobhans last updated on 30/Jul/20

Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 30/Jul/20
OK, gracias
