
Question Number 106337 by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 04/Aug/20
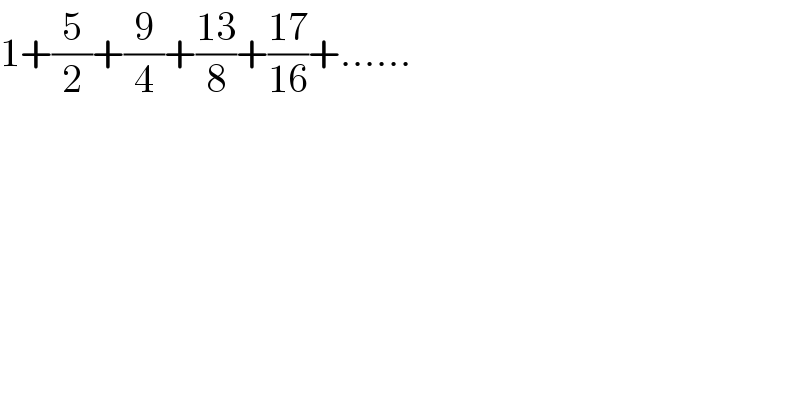
$$\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{\mathrm{13}}{\mathrm{8}}+\frac{\mathrm{17}}{\mathrm{16}}+...... \\ $$
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 04/Aug/20
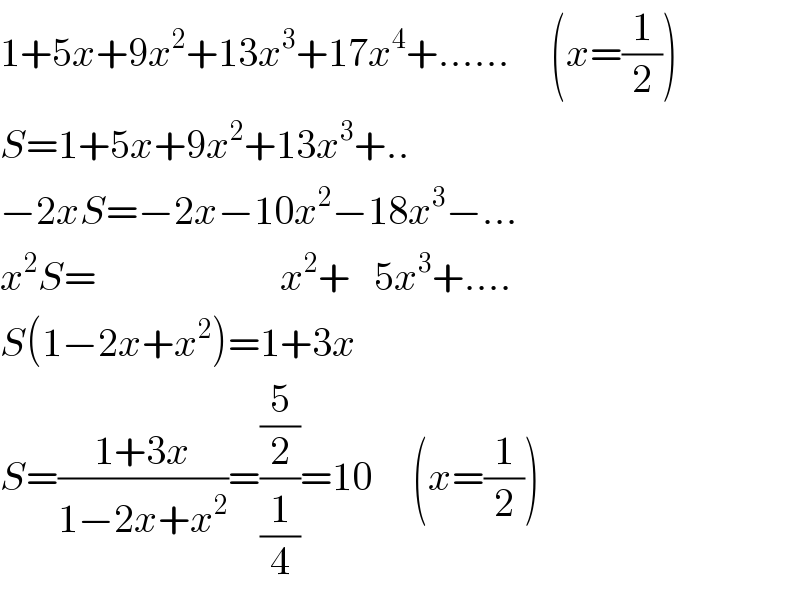
$$\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{5}{x}+\mathrm{9}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{13}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{17}{x}^{\mathrm{4}} +......\:\:\:\:\:\left({x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right) \\ $$$${S}=\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{5}{x}+\mathrm{9}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{13}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +.. \\ $$$$−\mathrm{2}{xS}=−\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{10}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{18}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −... \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} {S}=\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\:\:\:\mathrm{5}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +.... \\ $$$${S}\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2}{x}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)=\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{3}{x} \\ $$$${S}=\frac{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{3}{x}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{2}{x}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}}{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}}=\mathrm{10}\:\:\:\:\:\left({x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right) \\ $$
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 04/Aug/20
Amazing methode��
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 04/Aug/20
I have found this method idea on this book ���� https://drive.google.com/file/d/12J4x021yiK1X38OHkXoomTz_VuBlcIEt/view?usp=drivesdk
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 04/Aug/20
��Thanks bro
Answered by JDamian last updated on 04/Aug/20
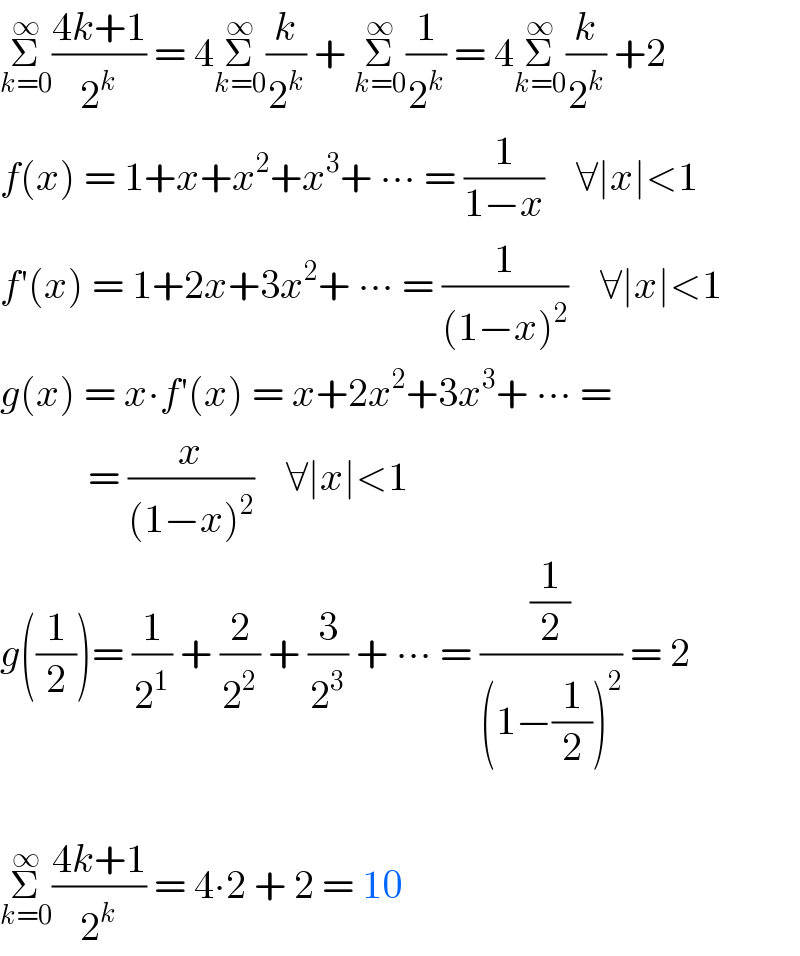
$$\underset{{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{4}{k}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{{k}} }\:=\:\mathrm{4}\underset{{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{k}}{\mathrm{2}^{{k}} }\:+\:\underset{{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{{k}} }\:=\:\mathrm{4}\underset{{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{{k}}{\mathrm{2}^{{k}} }\:+\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{1}+{x}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\:\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−{x}}\:\:\:\:\forall\mid{x}\mid<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${f}'\left({x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{3}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\:\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:\:\:\forall\mid{x}\mid<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${g}\left({x}\right)\:=\:{x}\centerdot{f}'\left({x}\right)\:=\:{x}+\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{3}{x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\:\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot\:= \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\:\frac{{x}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:\:\:\forall\mid{x}\mid<\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${g}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{1}} }\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:+\:\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{3}} }\:+\:\centerdot\centerdot\centerdot\:=\:\frac{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\underset{{k}=\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{4}{k}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{{k}} }\:=\:\mathrm{4}\centerdot\mathrm{2}\:+\:\mathrm{2}\:=\:\mathrm{10} \\ $$
Commented by JDamian last updated on 04/Aug/20
Sigma symbol looks small. How can I get a bigger sigma symbol?
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 04/Aug/20

$$\mathrm{By}\:\mathrm{selecting}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{given}\:\mathrm{symbol}\:\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{touching}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{3}\:\mathrm{small} \\ $$$$\mathrm{dots}\:\mathrm{at}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{bottom}-\mathrm{right}\:\mathrm{corner}.\:\mathrm{There}\:\mathrm{you}'\mathrm{ll}\:\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{A}^{\blacktrinagledown} \:\mathrm{and} \\ $$$$\mathrm{A}^{\blacktriangle} .\:\mathrm{You}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{use}\:\mathrm{them}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{increase}\:\mathrm{or}\:\mathrm{decrease}\:\mathrm{the}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{selected}\:\mathrm{text}. \\ $$
Commented by JDamian last updated on 04/Aug/20
I edited several times the last line of my answer, I increased the size of the sigma symbol and saved... but my answer is unchanged -- it seems to work fine in the editor but the changes are not shown in my answer
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 04/Aug/20
You're right, Sir. I too faced the same problem while trying to demonstrate what I was talking about.
Commented by Tinku Tara last updated on 05/Aug/20

$$\mathrm{There}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{bigger}\:\mathrm{sigma}\:\mathrm{symbol} \\ $$$$\mathrm{press}\:\mathrm{green}\:\mathrm{color}\:\bigstar\:\mathrm{key}\:\mathrm{or} \\ $$$$\mathrm{press}\:\mathrm{green}\:\int\:\mathrm{sign}\:\mathrm{and} \\ $$$$\mathrm{last}\coprod\:\mathrm{key}.\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{Several}\:\mathrm{enhancement}\:\mathrm{were}\:\mathrm{made} \\ $$$$\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{last}\:\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{weeks}\:\mathrm{which}\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{available} \\ $$$$\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{offline}\:\mathrm{editor}\:\mathrm{but}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{forum} \\ $$$$\mathrm{as}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{giving}\:\mathrm{user}\:\mathrm{time}\:\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{update} \\ $$$$\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{latest}\:\mathrm{version}: \\ $$$$\bullet\:\mathrm{Strike}\:\mathrm{thru} \\ $$$$\bullet\:\mathrm{underline} \\ $$$$\bullet\:\mathrm{curly}\:\mathrm{bracket}\:\mathrm{below} \\ $$$$\bullet\:\mathrm{font}\:\mathrm{size}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{every}\:\mathrm{character} \\ $$$$\bullet\:\mathrm{table} \\ $$$$\bullet\:\mathrm{borderless}\:\mathrm{table}\:\left(\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{primarily}\right. \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\mathrm{intented}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{use}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{writing}\:\mathrm{multiple} \\ $$$$\left.\:\:\:\:\mathrm{line}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{drawing}\right) \\ $$
Commented by Tinku Tara last updated on 05/Aug/20

Commented by Tinku Tara last updated on 05/Aug/20

Commented by Tinku Tara last updated on 05/Aug/20

Answered by 1549442205PVT last updated on 04/Aug/20
![The general term of the given sequence is ((4n−3)/2^(n−1) ).We need calculate Σ_(n=1) ^(∞) ((4n−3)/2^(n−1) )=4Σ_(n=1) ^(∞) (n/2^(n−1) )−3Σ_(n=1) ^(∞) (1/2^(n−1) ) Set S_k =Σ_(n=1) ^k (n/2^(n−1) )=(1/1)+(2/2)+(3/2^2 )+(4/2^3 )+...+(k/2^(k−1) ) (1/2)S_k =(1/2)+(2/2^2 )+(3/2^3 )+(4/2^4 )+....+((k−1)/2^(k−1) )+(k/2^k ) Substrating two above equalities we get 0.5S_k =1+(1/2)+(1/2^2 )+(1/2^3 )+...+(1/2^(k−1) )−(k/2^k ) =((1−((1/2))^(k+1) )/(1/2))−(k/2^k )⇒S_k =4(1−((1/2))^(k+1) )−(k/2^(k−1) ) ⇒Σ_(n=1) ^(∞) (n/2^(n−1) )=lim_(k→∞) S_k =lim_(k→∞) [4(1−((1/2))^(k+1) )−(k/2^(k−1) )]=4 Σ(1/2^(n−1) )=(1/1)+(1/2)+(1/2^2 )+...=lim_(n→∞) ((1/1)+(1/2)+(1/2^2 )+...+(1/2^n ))= lim_(n→∞) (((1−((1/2))^(n+1) ))/(1−(1/2)))=lim_(n→∞) [2(1−((1/2))^(n+1) )]=2 Hence, Σ_(n=1) ^(∞) ((4n−3)/2^(n−1) )=4Σ_(n=1) ^(∞) (n/2^(n−1) )−3Σ_(n=1) ^(∞) (1/2^(n−1) ) =4.4−3.2=10](Q106341.png)
$$\mathrm{The}\:\mathrm{general}\:\mathrm{term}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{given}\:\mathrm{sequence}\:\mathrm{is}\: \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{4n}−\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} }.\mathrm{We}\:\mathrm{need}\:\mathrm{calculate}\:\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\Sigma}}\frac{\mathrm{4n}−\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} }=\mathrm{4}\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\Sigma}}\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} }−\mathrm{3}\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\Sigma}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{Set}\:\mathrm{S}_{\mathrm{k}} =\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{k}} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} }=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{3}} }+...+\frac{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{k}−\mathrm{1}} } \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\mathrm{S}_{\mathrm{k}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{3}} }+\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{4}} }+....+\frac{\mathrm{k}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{k}−\mathrm{1}} }+\frac{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{k}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{Substrating}\:\mathrm{two}\:\mathrm{above}\:\mathrm{equalities}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{get} \\ $$$$\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5S}_{\mathrm{k}} =\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{3}} }+...+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{k}−\mathrm{1}} }−\frac{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{k}} } \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}−\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{1}} }{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}}−\frac{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{k}} }\Rightarrow\mathrm{S}_{\mathrm{k}} =\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{1}−\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{1}} \right)−\frac{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{k}−\mathrm{1}} } \\ $$$$\:\Rightarrow\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\Sigma}}\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} }=\underset{\mathrm{k}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\mathrm{S}_{\mathrm{k}} =\underset{\mathrm{k}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[\mathrm{4}\left(\mathrm{1}−\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{k}+\mathrm{1}} \right)−\frac{\mathrm{k}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{k}−\mathrm{1}} }\right]=\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\Sigma\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} }=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}} }+...=\underset{\mathrm{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{2}} }+...+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}} }\right)= \\ $$$$\underset{\mathrm{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\frac{\left(\mathrm{1}−\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} \right)}{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}}=\underset{\mathrm{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\left[\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{1}−\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{n}+\mathrm{1}} \right)\right]=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Hence},\:\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\Sigma}}\frac{\mathrm{4n}−\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} }=\mathrm{4}\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\Sigma}}\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} }−\mathrm{3}\underset{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\Sigma}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} } \\ $$$$=\mathrm{4}.\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{3}.\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{10} \\ $$
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 04/Aug/20
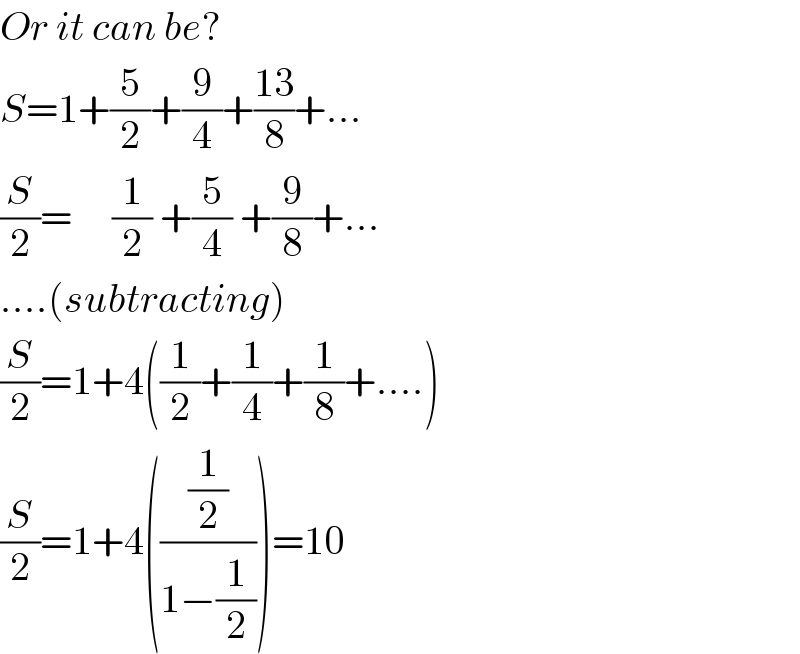
$${Or}\:{it}\:{can}\:{be}? \\ $$$${S}=\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{\mathrm{13}}{\mathrm{8}}+... \\ $$$$\frac{{S}}{\mathrm{2}}=\:\:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{4}}\:+\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{8}}+... \\ $$$$....\left({subtracting}\right) \\ $$$$\frac{{S}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{4}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{8}}+....\right) \\ $$$$\frac{{S}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{4}\left(\frac{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}}{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}}\right)=\mathrm{10} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 04/Aug/20
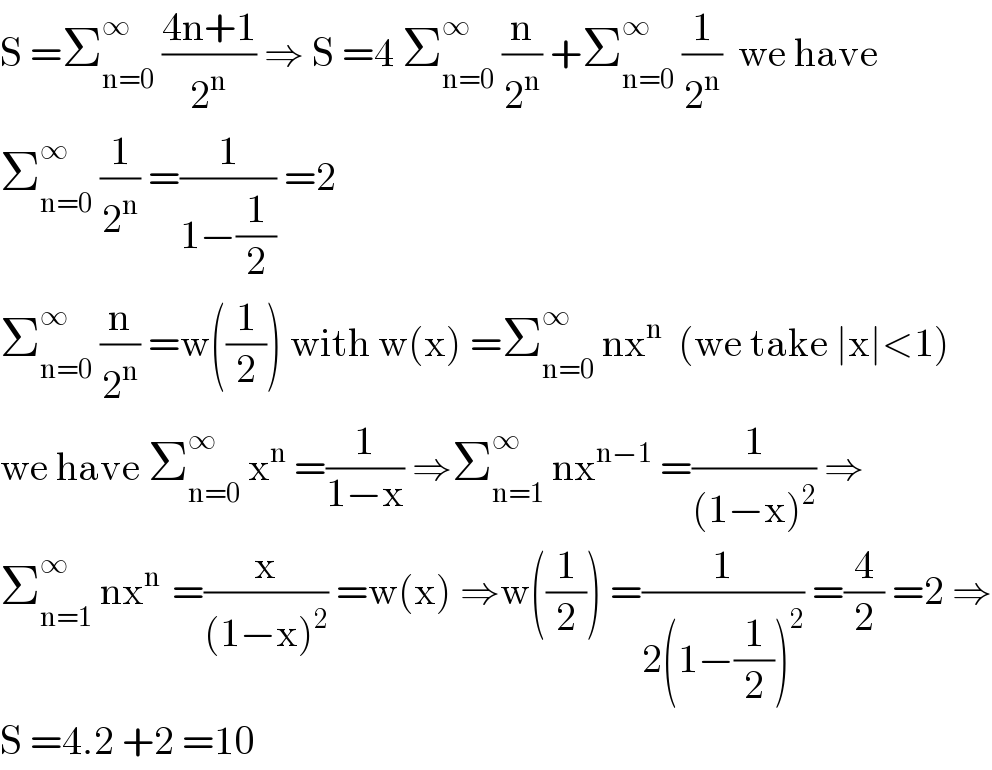
$$\mathrm{S}\:=\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{4n}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}} }\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{S}\:=\mathrm{4}\:\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}} }\:+\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}} }\:\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have} \\ $$$$\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}} }\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}}\:=\mathrm{2}\:\: \\ $$$$\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{2}^{\mathrm{n}} }\:=\mathrm{w}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\:\mathrm{with}\:\mathrm{w}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\mathrm{nx}^{\mathrm{n}} \:\:\left(\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{take}\:\mid\mathrm{x}\mid<\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have}\:\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{n}} \:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{x}}\:\Rightarrow\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\mathrm{nx}^{\mathrm{n}−\mathrm{1}} \:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\sum_{\mathrm{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\mathrm{nx}^{\mathrm{n}\:} \:=\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\left(\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\mathrm{w}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{w}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\frac{\mathrm{4}}{\mathrm{2}}\:=\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{S}\:=\mathrm{4}.\mathrm{2}\:+\mathrm{2}\:=\mathrm{10} \\ $$
