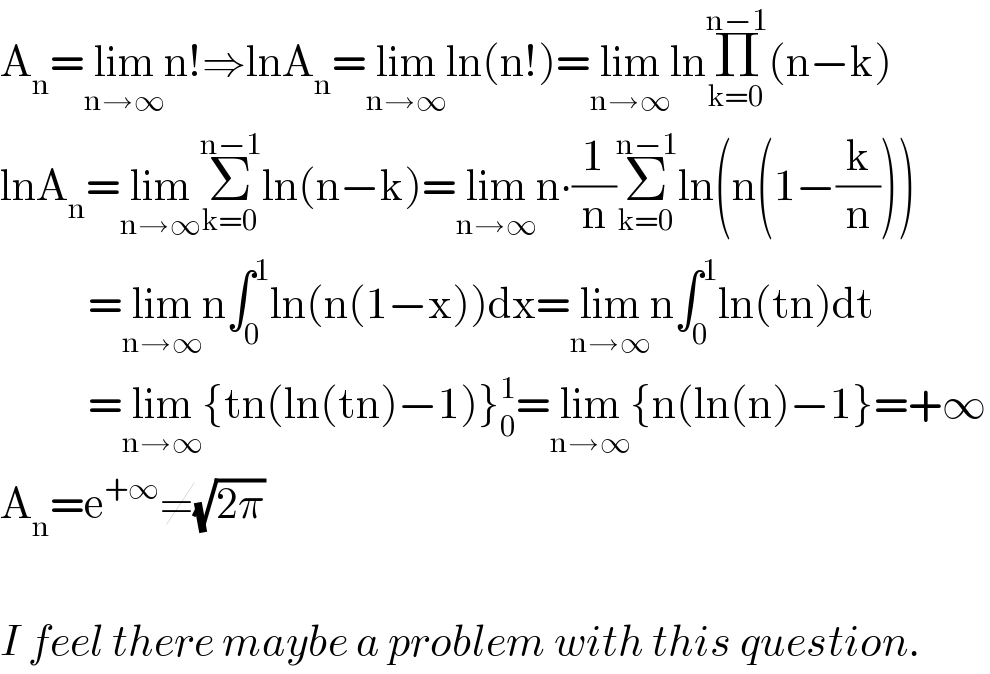Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 106591 by mathdave last updated on 06/Aug/20

Commented by Her_Majesty last updated on 06/Aug/20

Commented by mathdave last updated on 06/Aug/20

Commented by Her_Majesty last updated on 06/Aug/20
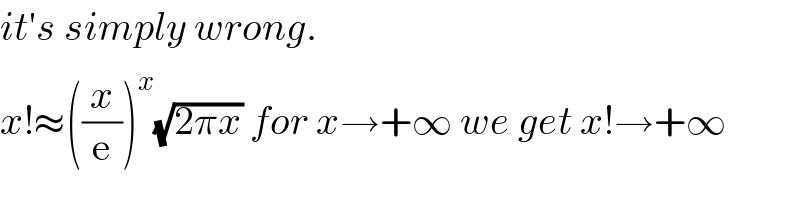
Commented by Her_Majesty last updated on 07/Aug/20

Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 07/Aug/20
Lol, don't bother yourself Sir. I know you wouldn't like to draw the others' attention��
Commented by Her_Majesty last updated on 07/Aug/20

Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 07/Aug/20
Deleted��
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 06/Aug/20