
Question Number 10671 by Saham last updated on 22/Feb/17

$$\underset{\mathrm{n}\:=\:\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\mathrm{5}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)^{\mathrm{n}\:−\:\mathrm{1}} \\ $$
Answered by FilupS last updated on 22/Feb/17
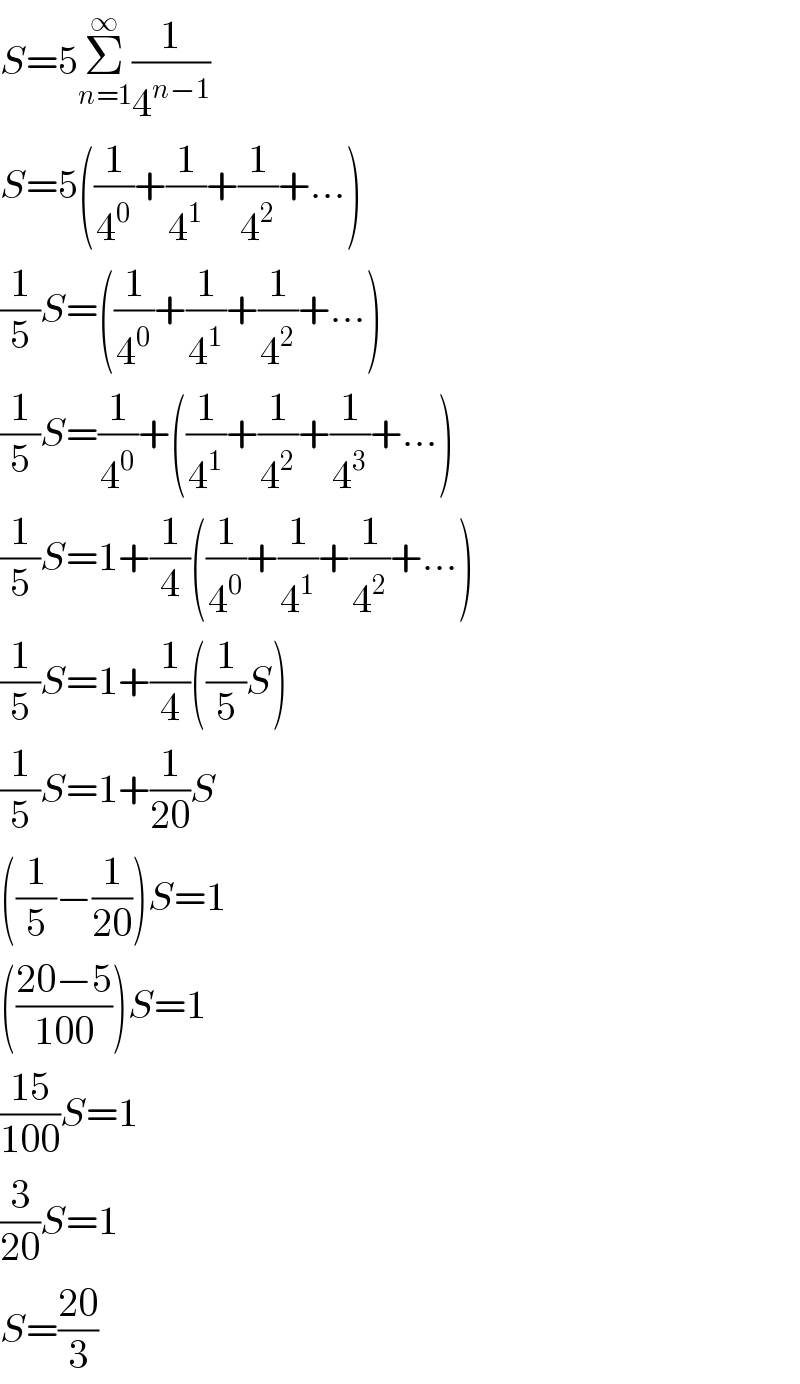
$${S}=\mathrm{5}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}^{{n}−\mathrm{1}} } \\ $$$${S}=\mathrm{5}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{0}} }+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{1}} }+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{2}} }+...\right) \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}{S}=\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{0}} }+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{1}} }+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{2}} }+...\right) \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}{S}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{0}} }+\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{1}} }+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{3}} }+...\right) \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}{S}=\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{0}} }+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{1}} }+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}^{\mathrm{2}} }+...\right) \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}{S}=\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}{S}\right) \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}{S}=\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{20}}{S} \\ $$$$\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{5}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{20}}\right){S}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\left(\frac{\mathrm{20}−\mathrm{5}}{\mathrm{100}}\right){S}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{15}}{\mathrm{100}}{S}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{20}}{S}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${S}=\frac{\mathrm{20}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
Commented by Saham last updated on 22/Feb/17

$$\mathrm{wow},\:\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{really}\:\mathrm{appreciate}. \\ $$
Commented by Saham last updated on 22/Feb/17

$$\mathrm{God}\:\mathrm{bless}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{sir}. \\ $$
Answered by mrW1 last updated on 22/Feb/17
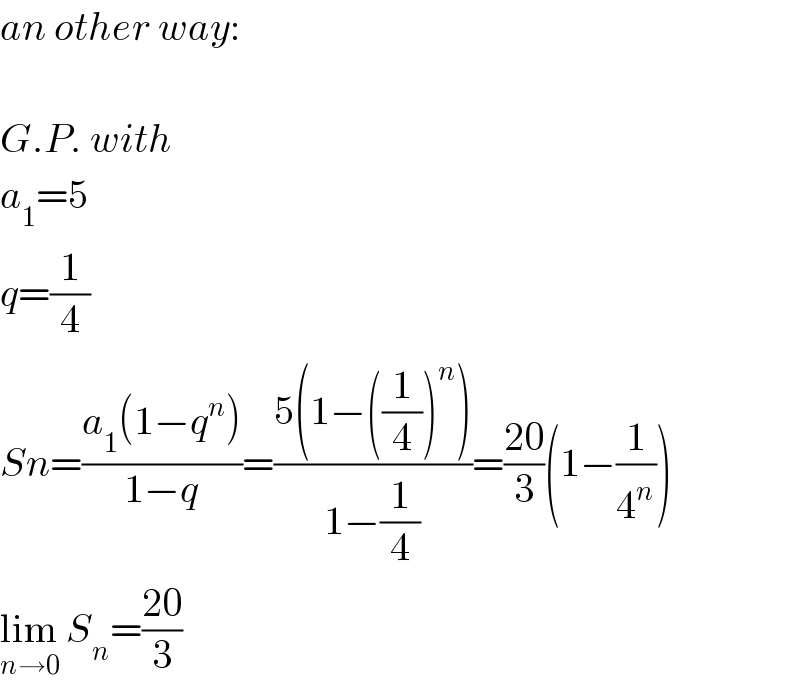
$${an}\:{other}\:{way}: \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${G}.{P}.\:{with} \\ $$$${a}_{\mathrm{1}} =\mathrm{5} \\ $$$${q}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$${Sn}=\frac{{a}_{\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{1}−{q}^{{n}} \right)}{\mathrm{1}−{q}}=\frac{\mathrm{5}\left(\mathrm{1}−\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)^{{n}} \right)}{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}}}=\frac{\mathrm{20}}{\mathrm{3}}\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{4}^{{n}} }\right) \\ $$$$\underset{{n}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:{S}_{{n}} =\frac{\mathrm{20}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
Commented by Saham last updated on 22/Feb/17

$$\mathrm{Great},\:\mathrm{God}\:\mathrm{bless}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{sir}. \\ $$
Commented by Saham last updated on 22/Feb/17

$$\mathrm{Thanks}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{your}\:\mathrm{help}. \\ $$
