
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 107534 by bemath last updated on 11/Aug/20

Commented by hgrocks last updated on 11/Aug/20
7 and 16 both my favorite numbers ����
Commented by bemath last updated on 11/Aug/20

Answered by Rio Michael last updated on 11/Aug/20
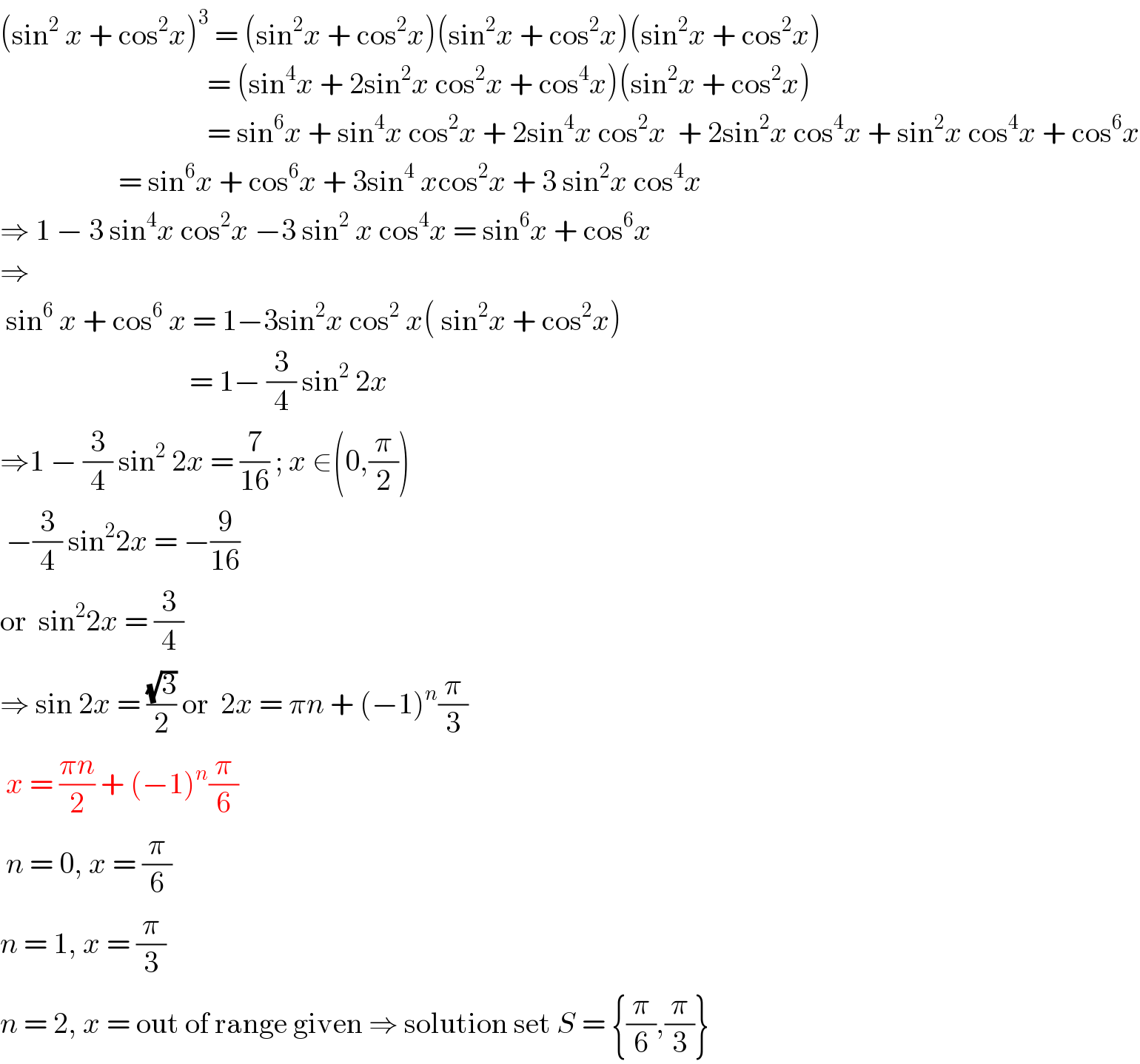
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 11/Aug/20
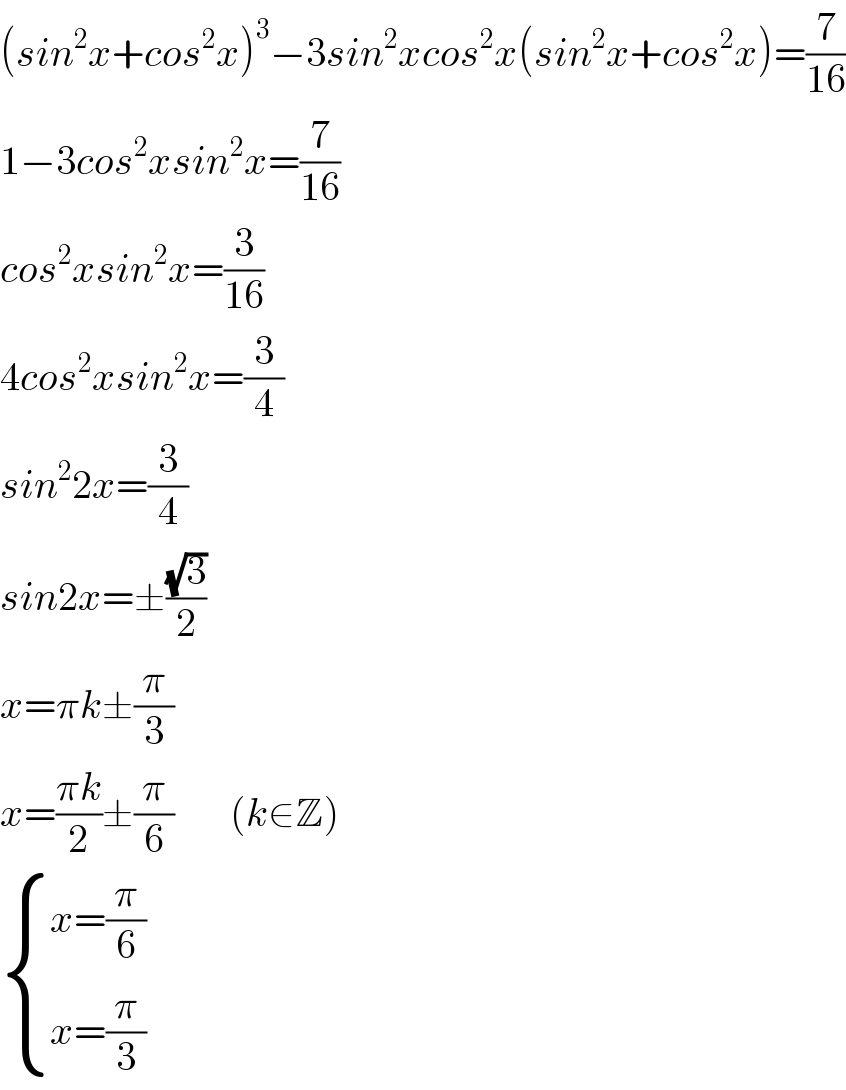
Answered by Sarah85 last updated on 11/Aug/20

Answered by john santu last updated on 11/Aug/20
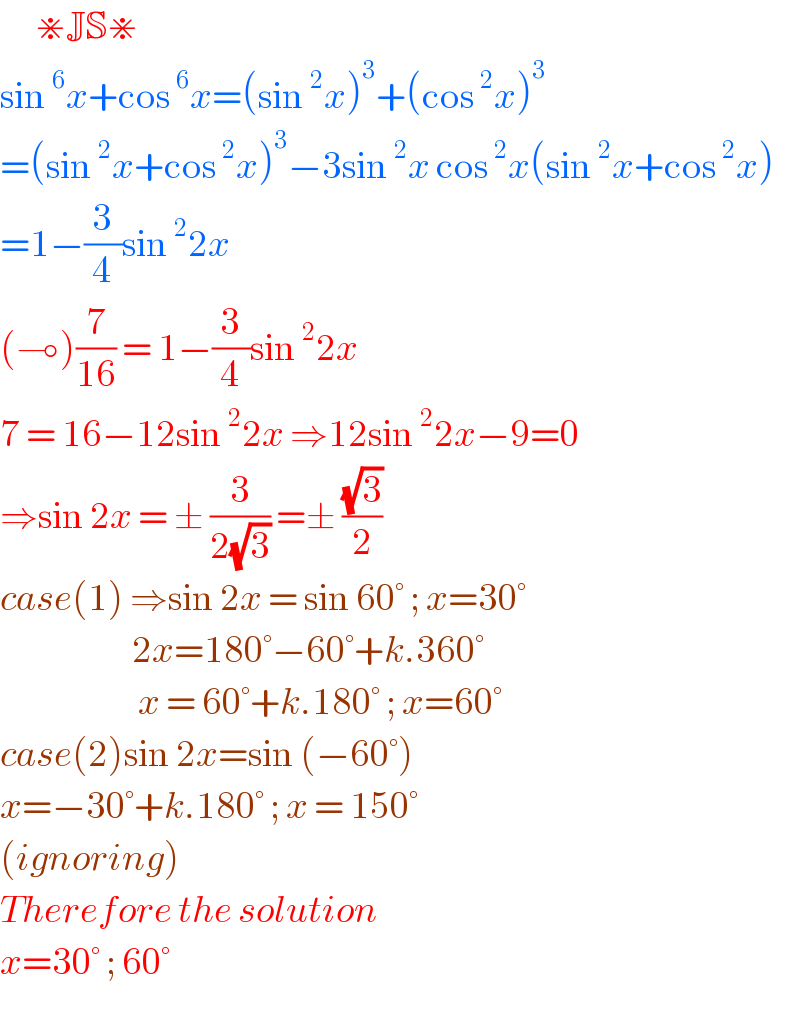
Answered by Her_Majesty last updated on 11/Aug/20

