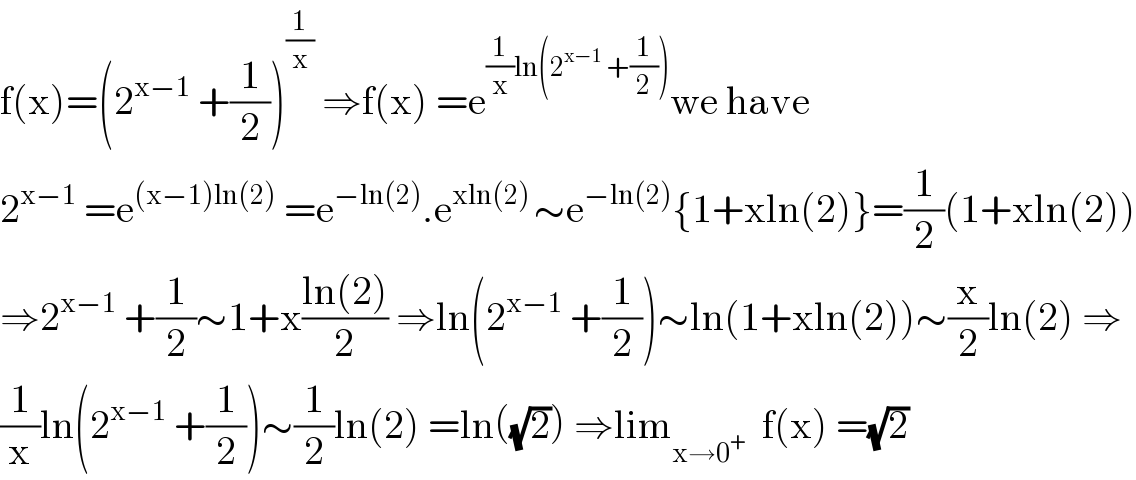Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 107550 by ajfour last updated on 11/Aug/20
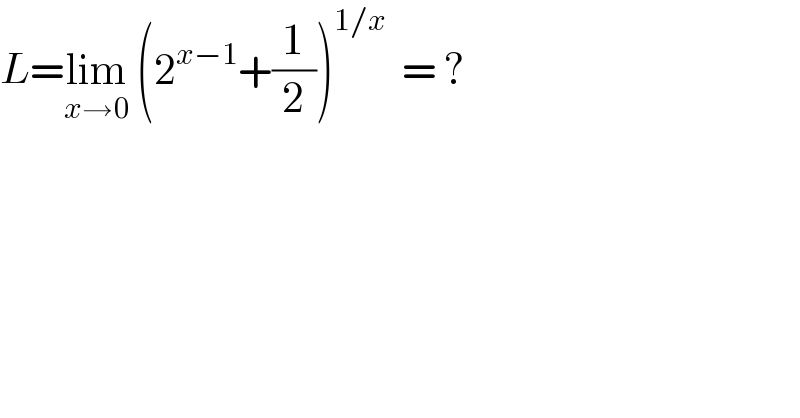
Answered by hgrocks last updated on 11/Aug/20

Commented by ajfour last updated on 11/Aug/20
Answered by john santu last updated on 11/Aug/20
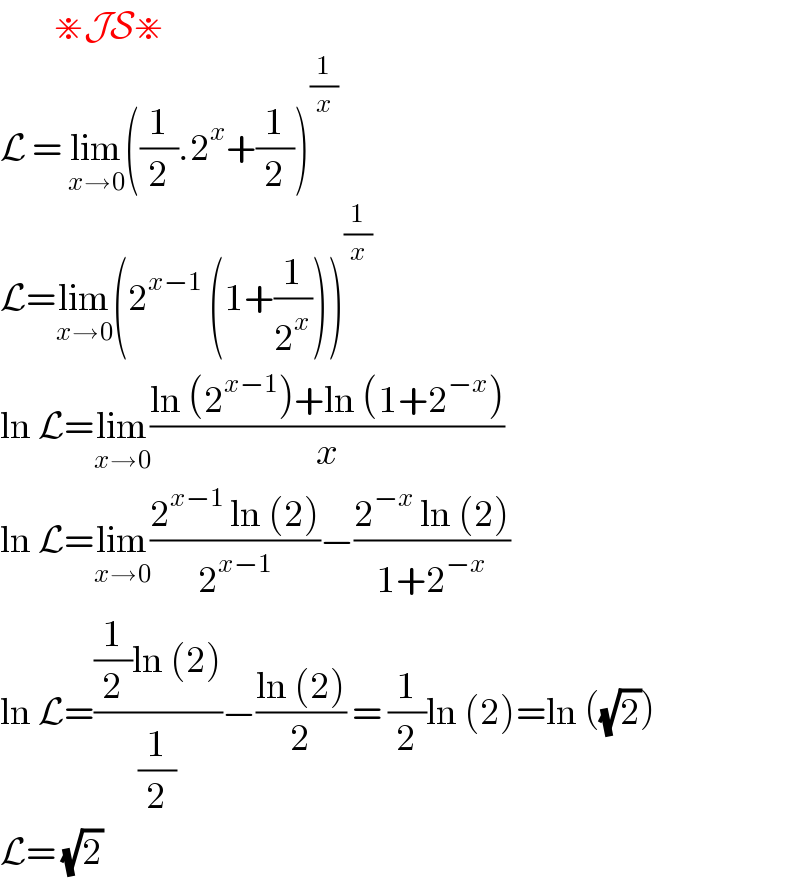
Commented by ajfour last updated on 11/Aug/20

Commented by john santu last updated on 11/Aug/20
no problem. up to you
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 11/Aug/20

Commented by ajfour last updated on 11/Aug/20

Answered by ajfour last updated on 11/Aug/20
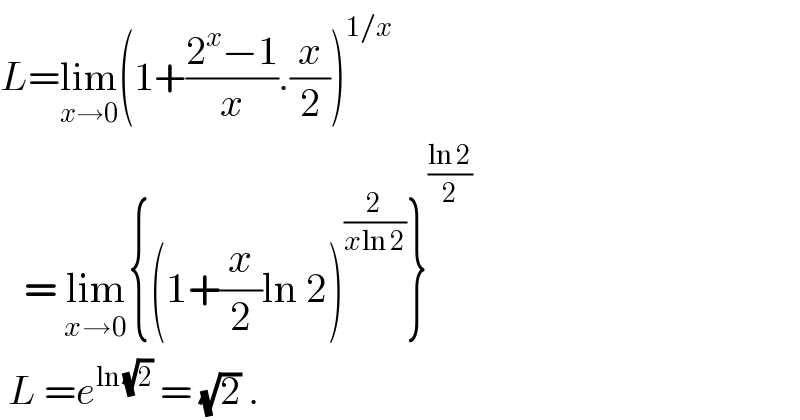
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 11/Aug/20