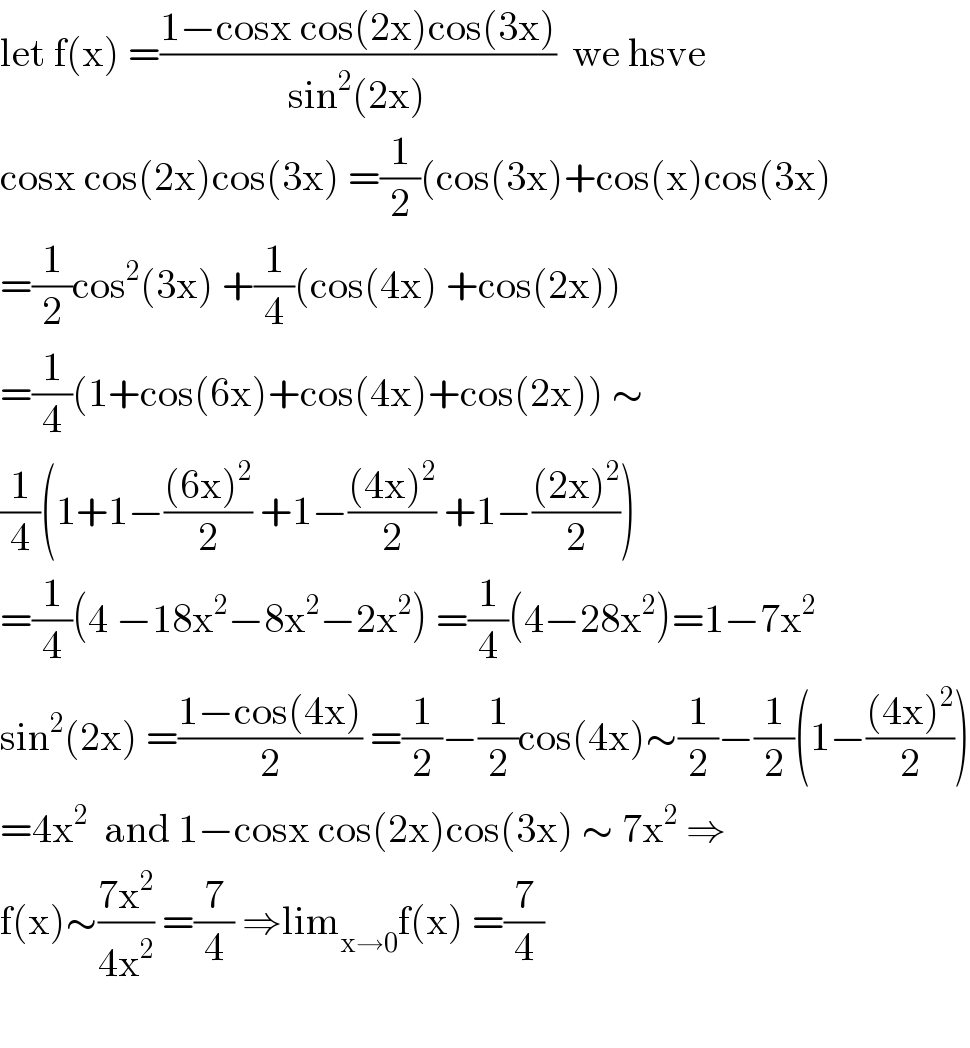Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 107747 by ajfour last updated on 12/Aug/20
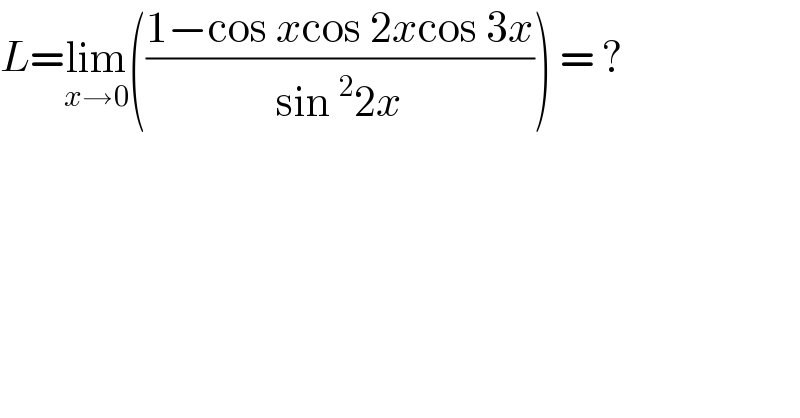
Answered by bobhans last updated on 12/Aug/20
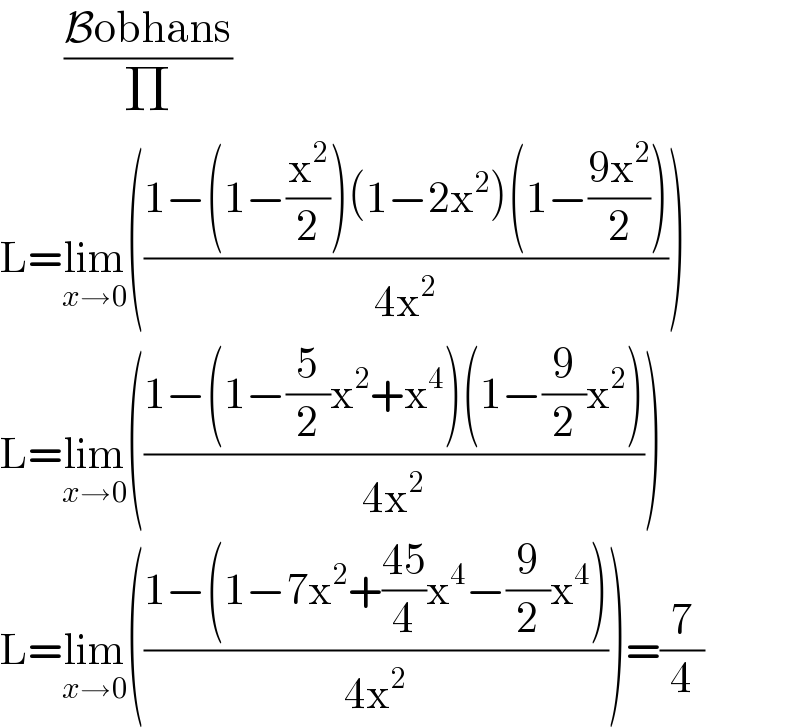
Commented by ajfour last updated on 12/Aug/20
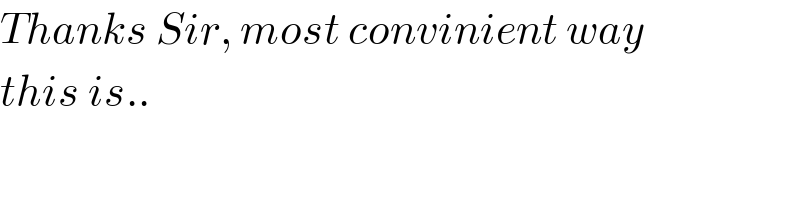
Commented by malwaan last updated on 12/Aug/20
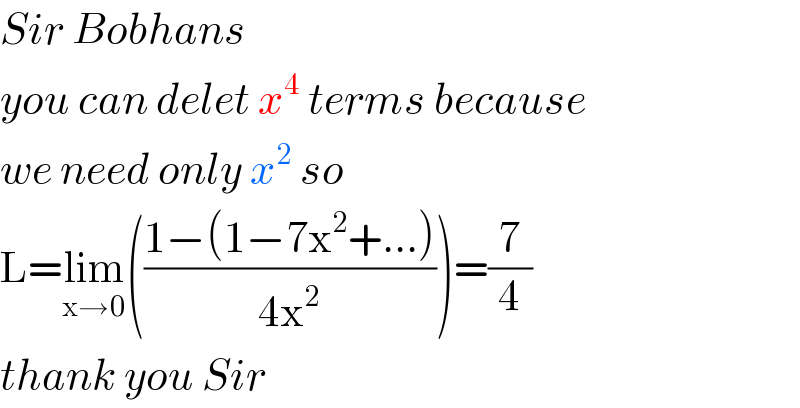
Answered by john santu last updated on 12/Aug/20
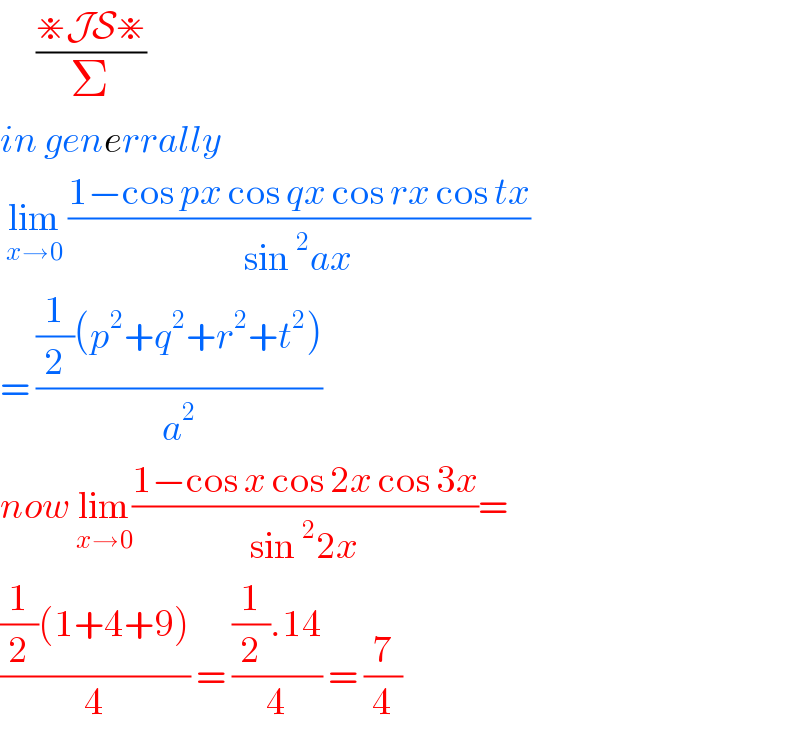
Commented by bemath last updated on 12/Aug/20

Commented by ajfour last updated on 12/Aug/20
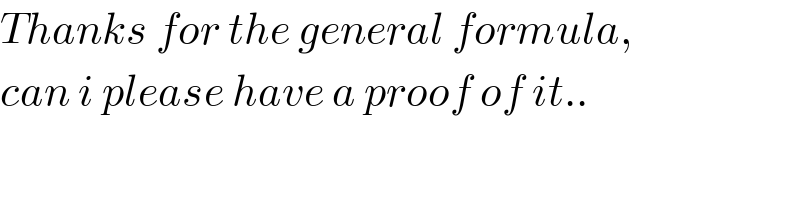
Commented by malwaan last updated on 12/Aug/20

Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 12/Aug/20