
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 108921 by Ar Brandon last updated on 20/Aug/20
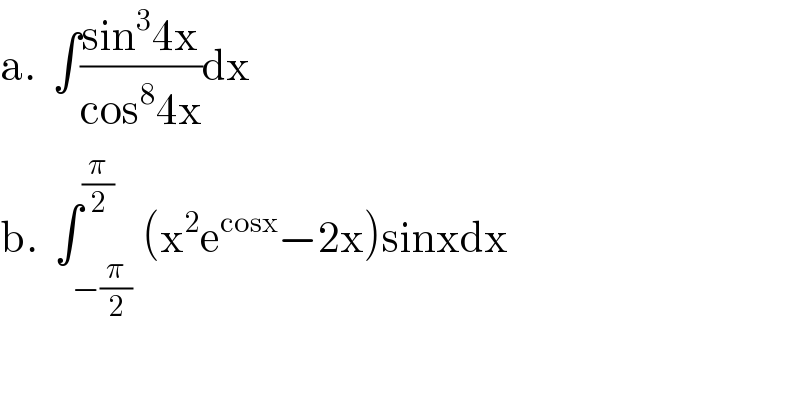
Answered by bobhans last updated on 20/Aug/20
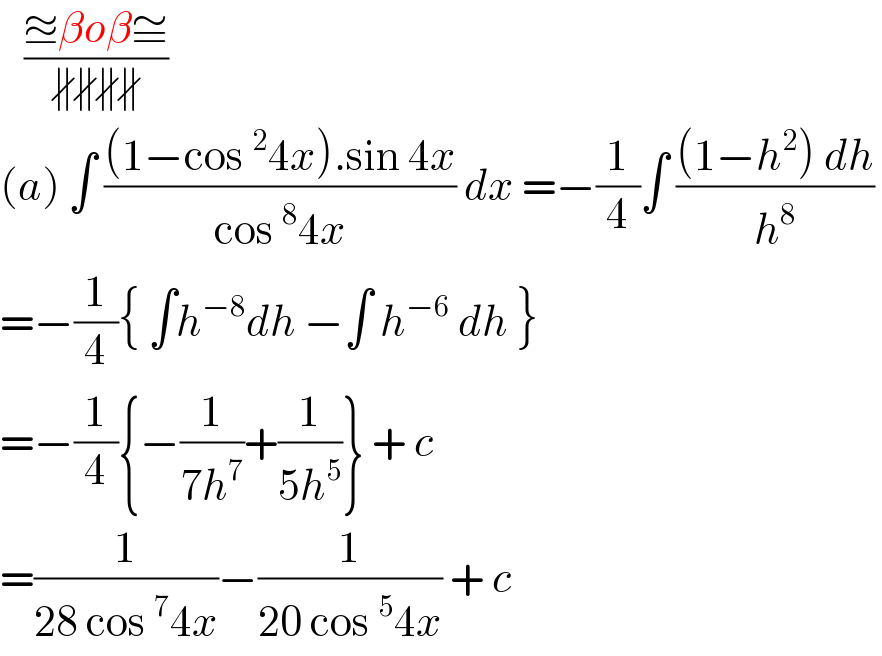
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 20/Aug/20
thanks
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 20/Aug/20
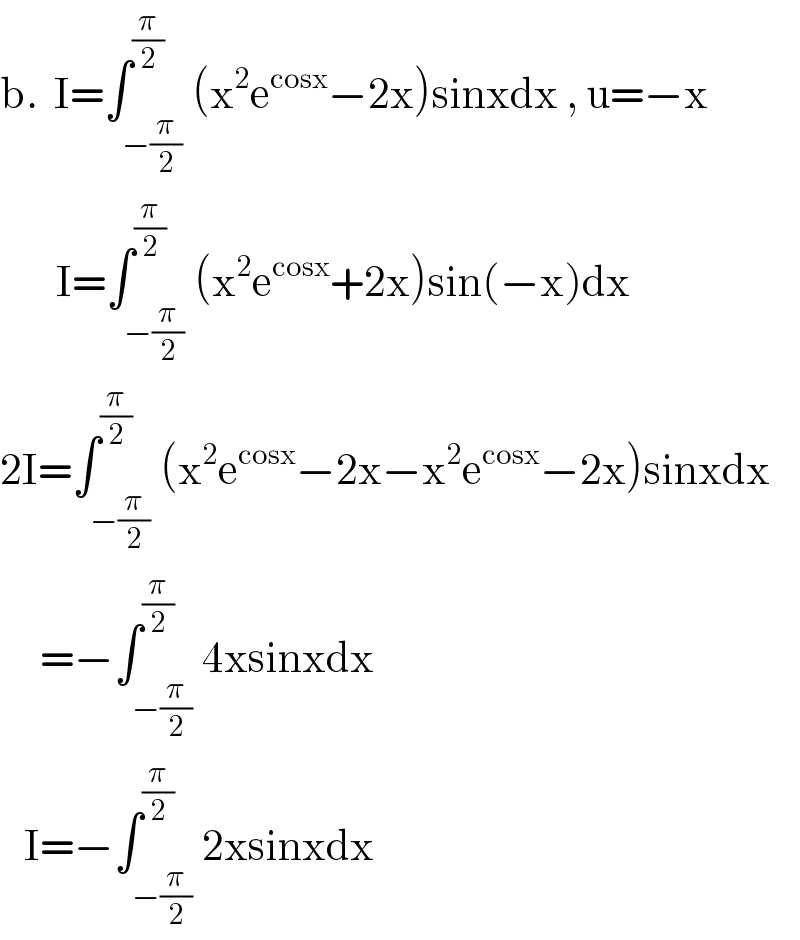
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 20/Aug/20
![∫_(−(π/2)) ^(π/2) (x^2 e^(cosx) −2x)sinxdx=∫_(−(π/2)) ^(π/2) −(x^2 e^(cosx) −2x)sinxdx=I 2I=∫_(−(π/2)) ^(π/2) −4xsinxdx −(I/4)=∫_0 ^(π/2) xsinxdx −(I/4)=−[xcosx]_0 ^(π/2) +[sinx]_0 ^(π/2) I=−4](Q108944.png)
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 20/Aug/20
Cool !
Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 20/Aug/20
Hey bro, what do you think of Q108491 ? ��
