
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 111008 by Khanacademy last updated on 01/Sep/20
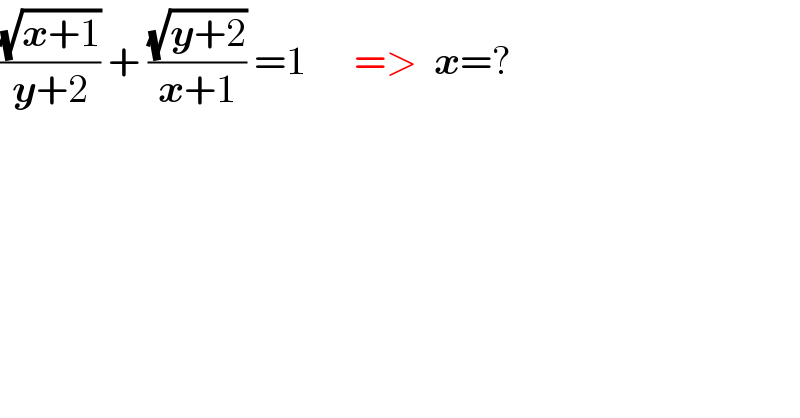
Commented byRasheed.Sindhi last updated on 01/Sep/20

Commented byKhanacademy last updated on 01/Sep/20

Commented byHer_Majesty last updated on 01/Sep/20

| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 111008 by Khanacademy last updated on 01/Sep/20 | ||
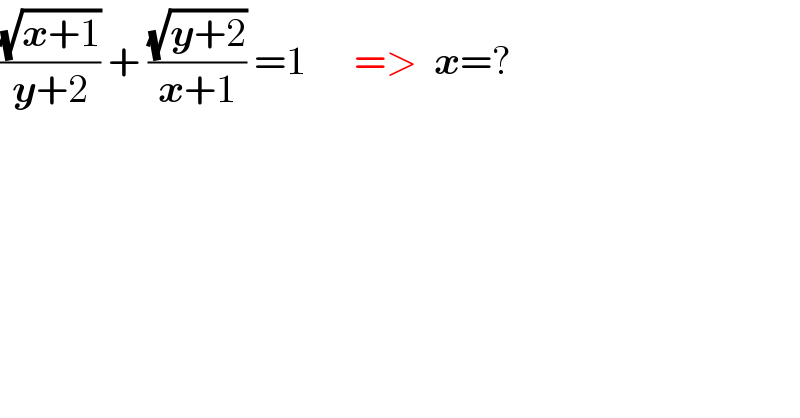 | ||
Commented byRasheed.Sindhi last updated on 01/Sep/20 | ||
 | ||
Commented byKhanacademy last updated on 01/Sep/20 | ||
 | ||
Commented byHer_Majesty last updated on 01/Sep/20 | ||
 | ||