
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 112583 by mohammad17 last updated on 08/Sep/20

Commented by Aziztisffola last updated on 08/Sep/20
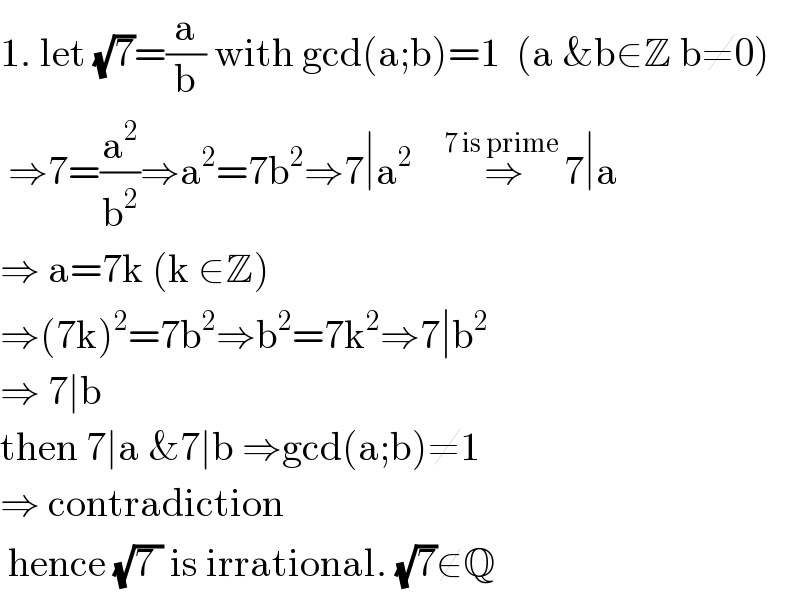
Commented by mohammad17 last updated on 08/Sep/20
Commented by Aziztisffola last updated on 08/Sep/20
![2. ]0;1[⊂R Suppose we can list all number in ]0;1[ x_1 =0.x_(11) x_(12) x_(13) ... x_2 =0.x_(21) x_(22) x_(23) ... x_3 =0.x_(31) x_(32) x_(33) ... ..... x_(ij) =0,...9 Consider a=0.x_(11) x_(22) x_(33) .... construct the number x=0.a_1 a_2 a_3 ... with a_i ≠x_(ii) (and a_i ≠9) then x≠x_1 ; x≠x_2 .... then x is not in the list hence R is uncountable.](Q112596.png)
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 09/Sep/20
![nature of Σ_(n=2) ^∞ ((sin(n))/(n(n+1))) we have ∣((sin(n))/(n(n+1)))∣≤(1/(n(n+1)))≤(1/n^2 ) the serie Σ (1/n^2 ) converges ⇒this serie converges nsture of Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (1/(n+(√n))) let f(x) =(1/(x+(√x))) with x≥1 we hsve f^′ (x) =−((1+(1/(2(√x))))/((x+(√x))^2 )) <0 ⇒f is decreazing so this serie hsve nature of ∫_1 ^(+∞) (dx/(x+(√x))) changement (√x)=t give ∫_1 ^(+∞) (dx/(x+(√x))) =∫_1 ^(+∞) ((2tdt)/(t^2 +t)) =2 ∫_1 ^(+∞) (dt/(t+1)) =2lim_(a→+∞) ∫_1 ^a (dt/(t+1)) =2lim_(a→+∞) [ln(t+1)]_1 ^a =2lim_(a→+∞) ln(a+1)−ln2 =+∞ ⇒ this serie is divergent](Q112623.png)
