
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 114422 by Aina Samuel Temidayo last updated on 19/Sep/20
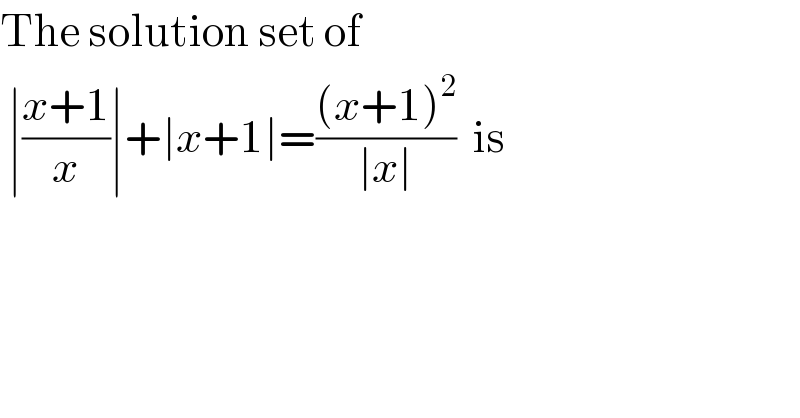
Commented by bemath last updated on 19/Sep/20
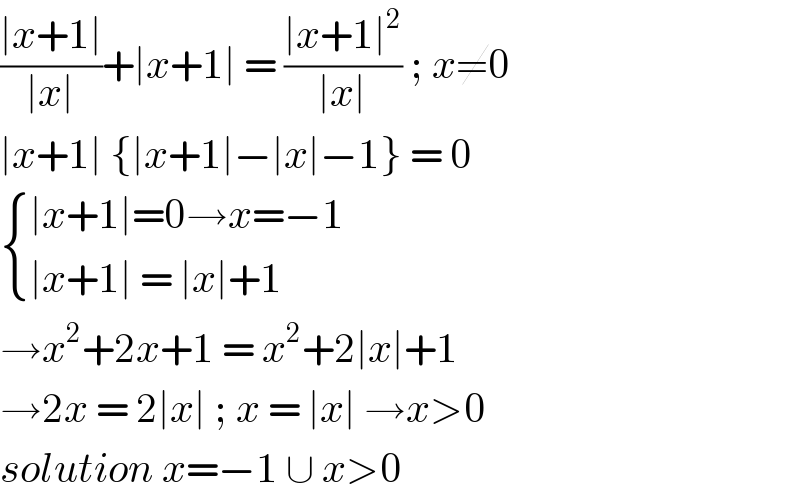
Commented by Aina Samuel Temidayo last updated on 19/Sep/20

Commented by bemath last updated on 19/Sep/20

Answered by 1549442205PVT last updated on 19/Sep/20

Answered by Aina Samuel Temidayo last updated on 19/Sep/20
![= ((∣x+1∣)/(∣x∣))+∣x+1∣ = (((x+1)^2 )/(∣x∣)), x≠0 CASE I: when x+1≥0 and x≥0 x≥−1 and x≥0 Finding their intersections ⇒ x≥0 but x≠0 ⇒ x>0 ⇒ ∣((x+1)/x)∣+∣x+1∣=(((x+1)^2 )/(∣x∣)) = ((x+1)/x)+x+1= ((x^2 +2x+1)/x) ⇒ x+1+x^2 +x= x^2 +2x+1 ⇒ 0=0 ⇒ x∈R Recall x>0 ⇒ x>0 CASE II: when x+1<0 and x<0 ⇒ x<−1 and x<0 ⇒ x<−1 ∣((x+1)/x)∣+∣x+1∣=(((x+1)^2 )/(∣x∣)) =((−(x+1))/(−(x)))+(−(x+1))= ((x^2 +2x+1)/(−(x))) ⇒−x−1+(−x(−(x+1)))=x^2 +2x+1 ⇒−x−1+(−x(−x−1))=x^2 +2x+1 ⇒−x−1+x^2 +x=x^2 +2x+1 ⇒x=−1 since x<−1 ⇒ x∈φ CASE III: when x+1<0 and x≥0 ⇒ x<−1 and x≥0 Finding their intersections ⇒ x∈φ CASE IV: when x+1≥0 and x<0 ⇒ x≥−1 and x<0 ⇒ x∈ [−1,0) ⇒∣((x+1)/x)∣+∣x+1∣=(((x+1)^2 )/(∣x∣)) ⇒((x+1)/(−x))+x+1=((x^2 +2x+1)/(−x)) ⇒(x+1)−x(x+1)=x^2 +2x+1 ⇒ x+1−x^2 −x=x^2 +2x+1 ⇒ 2x^2 +2x=0 ⇒x(x+1)=0 ⇒x=0 or x=−1 since x∈[−1,0) ⇒ x=−1 Combining Cases I,II,III and IV ⇒ x∈ (0,+∞) ∪ [−1] ⇒ x∈ {−1} ∪ (0,+∞)](Q114426.png)
Commented by ruwedkabeh last updated on 19/Sep/20

Commented by Aina Samuel Temidayo last updated on 19/Sep/20
Commented by Aina Samuel Temidayo last updated on 19/Sep/20
Answered by mnjuly1970 last updated on 19/Sep/20
![solution::(x+1)^2 =∣x+1∣^2 ∣x+1∣((1/(∣x∣))+1−((∣x+1∣)/(∣x∣)))=0 x=−1 ✓ or (1/(∣x∣))+1−((∣x+1∣)/(∣x∣))=0 if x<−1 ⇒−(1/x)+1+[((x+1)/x)=1+(1/x)]=0 2=0 impossible if −1≤x≤0 ⇒ −(1/x)+1−1−(1/x)=0⇒((−2)/x)=0 again it is impossible. x>0⇒ (1/x)+1−1−(1/x)=0 ✓✓ ans {−1}∪ x>0 ✓](Q114523.png)
