
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 115664 by bemath last updated on 27/Sep/20
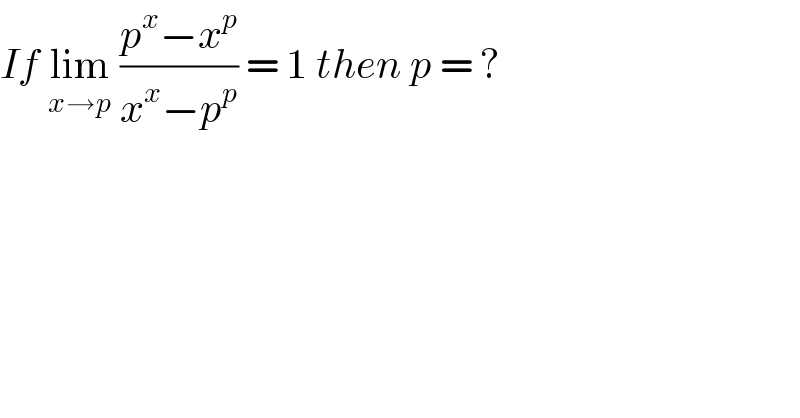
Answered by Olaf last updated on 27/Sep/20
![x = p+u lim_(x→p) ((e^(xlnp) −e^(plnx) )/(e^(xlnx) −e^(plnp) )) lim_(x→p) ((e^((xlnp+plnx)/2) (e^((xlnp−plnx)/2) −e^(−((xlnp−plnx)/2)) ))/(e^((xlnx+plnp)/2) (e^((xlnx−plnp)/2) −e^(−((xlnx−plnp)/2)) ))) lim_(x→p) e^((xln(p/x)+pln(x/p))/2) [((sinh(((xlnp−plnx)/2)))/(sinh(((xlnx−plnp)/2))))] lim_(x→p) 1×[((sinh(((xlnp−plnx)/2)))/(sinh(((xlnx−plnp)/2))))] lim_(x→p) [(((((lnp−(p/x))/2))cosh(((xlnp−plnx)/2)))/((((lnx+1)/2))cosh(((xlnx−plnp)/2))))] = ((lnp−1)/(lnp+1)) = ((ln((p/e)))/(ln(ep))) ((ln((p/e)))/(ln(ep))) = 1 ⇒ (p/e) = ep ? I′m surely wrong.](Q115672.png)
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 27/Sep/20
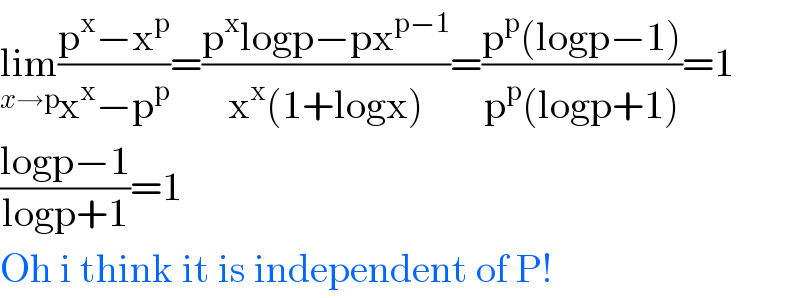
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 115664 by bemath last updated on 27/Sep/20 | ||
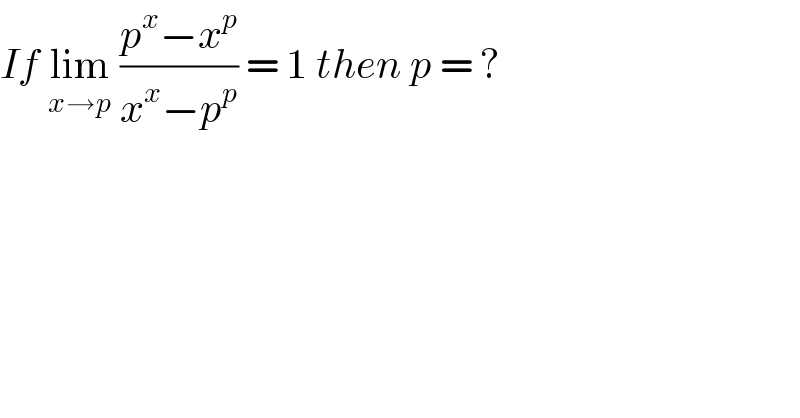 | ||
Answered by Olaf last updated on 27/Sep/20 | ||
![x = p+u lim_(x→p) ((e^(xlnp) −e^(plnx) )/(e^(xlnx) −e^(plnp) )) lim_(x→p) ((e^((xlnp+plnx)/2) (e^((xlnp−plnx)/2) −e^(−((xlnp−plnx)/2)) ))/(e^((xlnx+plnp)/2) (e^((xlnx−plnp)/2) −e^(−((xlnx−plnp)/2)) ))) lim_(x→p) e^((xln(p/x)+pln(x/p))/2) [((sinh(((xlnp−plnx)/2)))/(sinh(((xlnx−plnp)/2))))] lim_(x→p) 1×[((sinh(((xlnp−plnx)/2)))/(sinh(((xlnx−plnp)/2))))] lim_(x→p) [(((((lnp−(p/x))/2))cosh(((xlnp−plnx)/2)))/((((lnx+1)/2))cosh(((xlnx−plnp)/2))))] = ((lnp−1)/(lnp+1)) = ((ln((p/e)))/(ln(ep))) ((ln((p/e)))/(ln(ep))) = 1 ⇒ (p/e) = ep ? I′m surely wrong.](Q115672.png) | ||
| ||
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 27/Sep/20 | ||
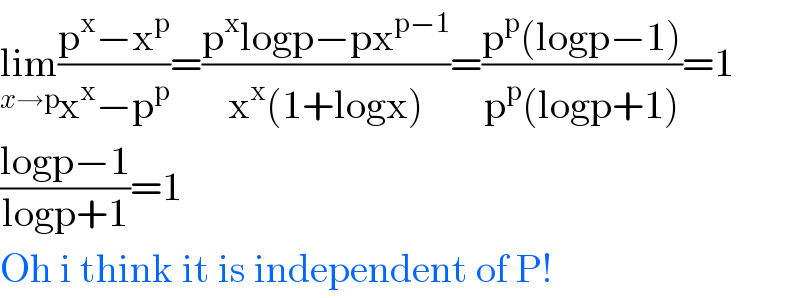 | ||
| ||