
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 115858 by bemath last updated on 29/Sep/20

Answered by floor(10²Eta[1]) last updated on 29/Sep/20
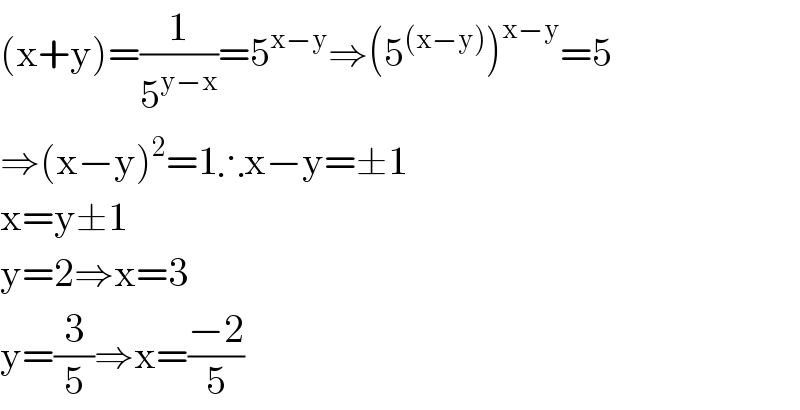
Answered by bobhans last updated on 29/Sep/20
![⇔ (x+y) = 5^(x−y) ∧ (x+y)^(x−y) = 5 ⇒ [ (x+y)^(x−y) ]^(x−y) = 5^(x−y) ⇒ (x+y)^((x−y)^2 ) = (x+y)⇒ (x−y)^2 =1 → { ((x=y+1 )),((x=y−1)) :} case(1) →x=y+1 (2y+1)^1 = 5 ⇒y = 2 ∧x=3 case(2)→x=y−1 (2y−1)^(−1) = 5 ⇒2y−1=(1/5) y = (3/5) ∧ x=−(2/5) solution : (−(2/5),(3/5)) and (3,2)](Q115868.png)
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 115858 by bemath last updated on 29/Sep/20 | ||
 | ||
Answered by floor(10²Eta[1]) last updated on 29/Sep/20 | ||
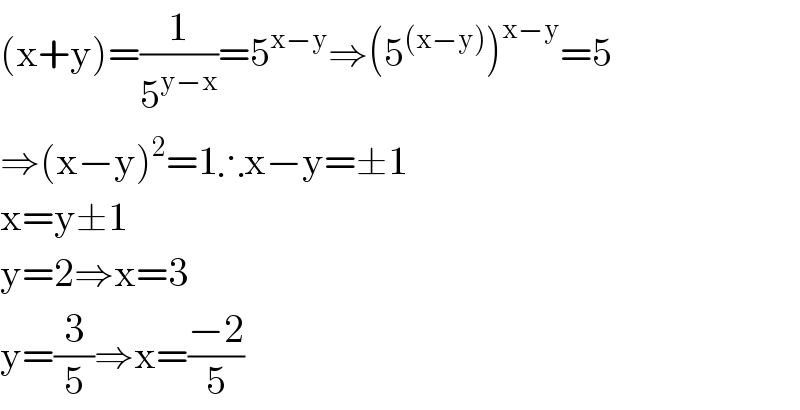 | ||
| ||
Answered by bobhans last updated on 29/Sep/20 | ||
![⇔ (x+y) = 5^(x−y) ∧ (x+y)^(x−y) = 5 ⇒ [ (x+y)^(x−y) ]^(x−y) = 5^(x−y) ⇒ (x+y)^((x−y)^2 ) = (x+y)⇒ (x−y)^2 =1 → { ((x=y+1 )),((x=y−1)) :} case(1) →x=y+1 (2y+1)^1 = 5 ⇒y = 2 ∧x=3 case(2)→x=y−1 (2y−1)^(−1) = 5 ⇒2y−1=(1/5) y = (3/5) ∧ x=−(2/5) solution : (−(2/5),(3/5)) and (3,2)](Q115868.png) | ||
| ||