
Question Number 116738 by Eric002 last updated on 06/Oct/20
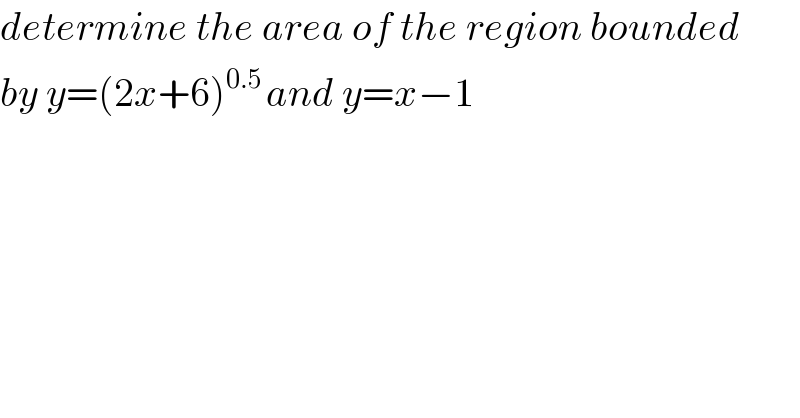
$${determine}\:{the}\:{area}\:{of}\:{the}\:{region}\:{bounded} \\ $$$${by}\:{y}=\left(\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{6}\right)^{\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}\:} {and}\:{y}={x}−\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by bobhans last updated on 06/Oct/20

Answered by 1549442205PVT last updated on 06/Oct/20
![Question should be:Calculate the area of region bounded by curve y=(√(2x+6)) ,the line y=x−1 and the Ox We find the intersection of line(d): y=x−1 and the curve C: y=(√(2x+6)) x−1=(√(2x+6))⇔2x+6=x^2 −2x+1(x≥1) ⇔x^2 −4x−5=0 ⇔(x+1)(x−5)=0 ⇔x=5⇒y=4.⇒C∩d=B(5;4) C∩Ox=A(−3;0),d∩Ox=C(1;0).Hence The area of region bounded by C,d and the asix Ox equal to S=∫_(−3) ^( 5) (√(2x+6))dx−∫_1 ^( 5) (x−1)dx Put (√(2x+6))=u⇒2x+6=u^2 ⇒dx=udu ∫(√(2x+6))dx=∫u^2 du=(u^3 /3) ⇒S=(((2x+6)(√(2x+6)))/3)∣_(−3) ^5 −[(x^2 /2)−x]_1 ^5 = =((64)/3)−7.5−0.5=((64)/3)−8=((40)/3) S=((40)/3)](Q116754.png)
$$\mathrm{Question}\:\mathrm{should}\:\mathrm{be}:\mathrm{Calculate}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{area} \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{region}\:\mathrm{bounded}\:\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{curve}\:\mathrm{y}=\sqrt{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$$,\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{line}\:\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{Ox} \\ $$$$\mathrm{We}\:\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{intersection}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{line}\left(\mathrm{d}\right): \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{curve}\:\mathrm{C}:\:\mathrm{y}=\sqrt{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{6}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}=\sqrt{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{6}}\Leftrightarrow\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{6}=\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{1}\left(\mathrm{x}\geqslant\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4x}−\mathrm{5}=\mathrm{0}\:\Leftrightarrow\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{5}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Leftrightarrow\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{5}\Rightarrow\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{4}.\Rightarrow\mathrm{C}\cap\mathrm{d}=\mathrm{B}\left(\mathrm{5};\mathrm{4}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{C}\cap\mathrm{Ox}=\mathrm{A}\left(−\mathrm{3};\mathrm{0}\right),\mathrm{d}\cap\mathrm{Ox}=\mathrm{C}\left(\mathrm{1};\mathrm{0}\right).\mathrm{Hence} \\ $$$$\mathrm{The}\:\mathrm{area}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{region}\:\mathrm{bounded}\:\mathrm{by}\:\mathrm{C},\mathrm{d}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{asix}\:\mathrm{Ox}\:\mathrm{equal}\:\mathrm{to} \\ $$$$\mathrm{S}=\int_{−\mathrm{3}} ^{\:\mathrm{5}} \sqrt{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{6}}\mathrm{dx}−\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\:\mathrm{5}} \left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Put}\:\sqrt{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{6}}=\mathrm{u}\Rightarrow\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{6}=\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{dx}=\mathrm{udu}\:\int\sqrt{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{6}}\mathrm{dx}=\int\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{du}=\frac{\mathrm{u}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{S}=\frac{\left(\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{6}\right)\sqrt{\mathrm{2x}+\mathrm{6}}}{\mathrm{3}}\mid_{−\mathrm{3}} ^{\mathrm{5}} −\left[\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{x}\right]_{\mathrm{1}} ^{\mathrm{5}} = \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{64}}{\mathrm{3}}−\mathrm{7}.\mathrm{5}−\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}=\frac{\mathrm{64}}{\mathrm{3}}−\mathrm{8}=\frac{\mathrm{40}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{S}=\frac{\mathrm{40}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
