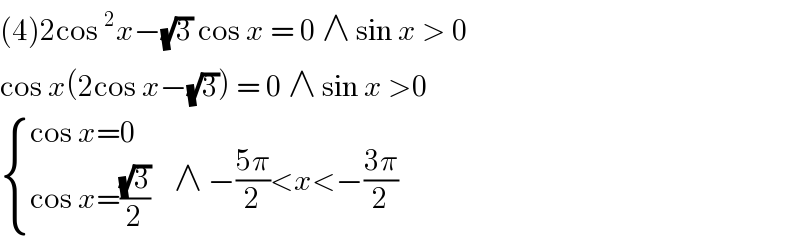Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 117938 by bemath last updated on 14/Oct/20
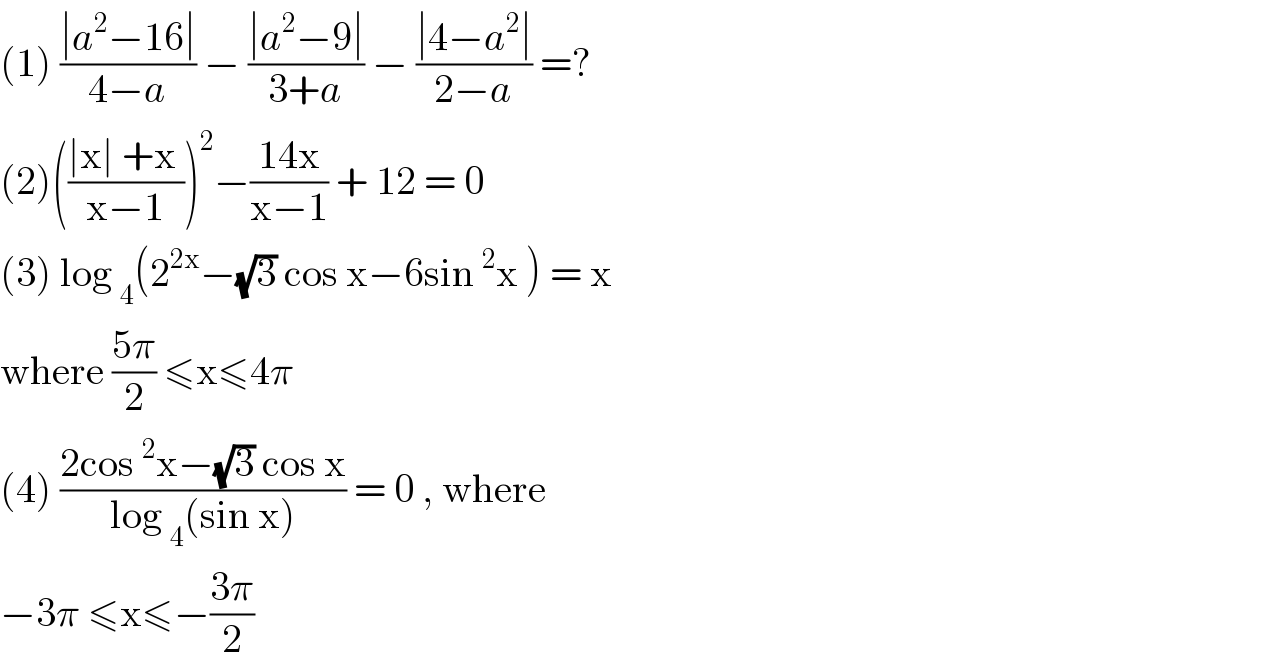
Answered by john santu last updated on 14/Oct/20
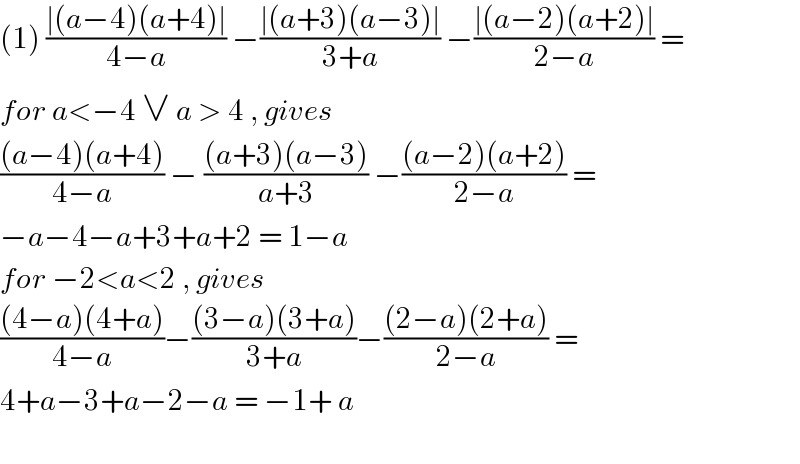
Answered by john santu last updated on 14/Oct/20
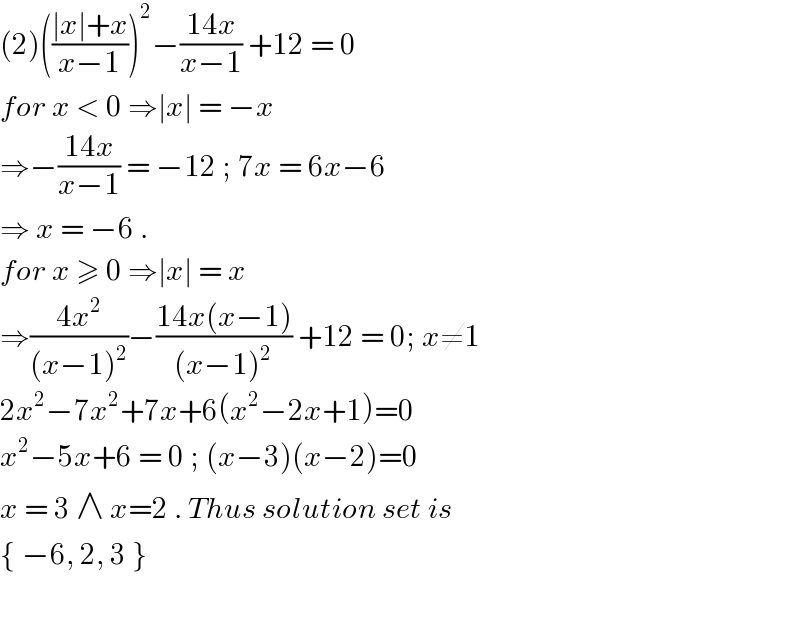
Answered by john santu last updated on 14/Oct/20
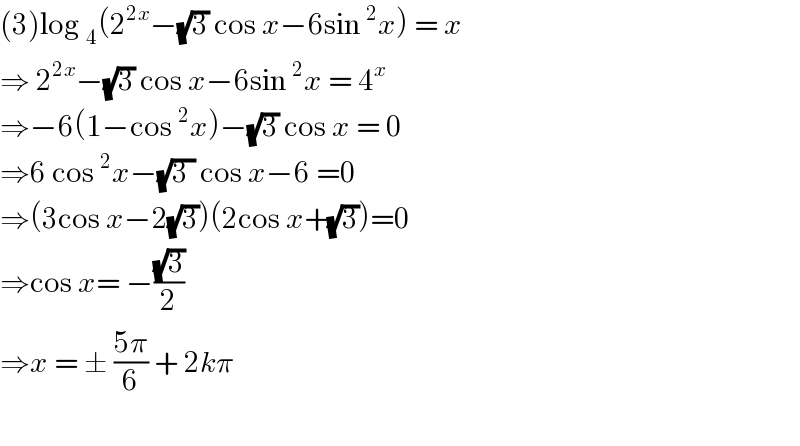
Answered by Lordose last updated on 14/Oct/20
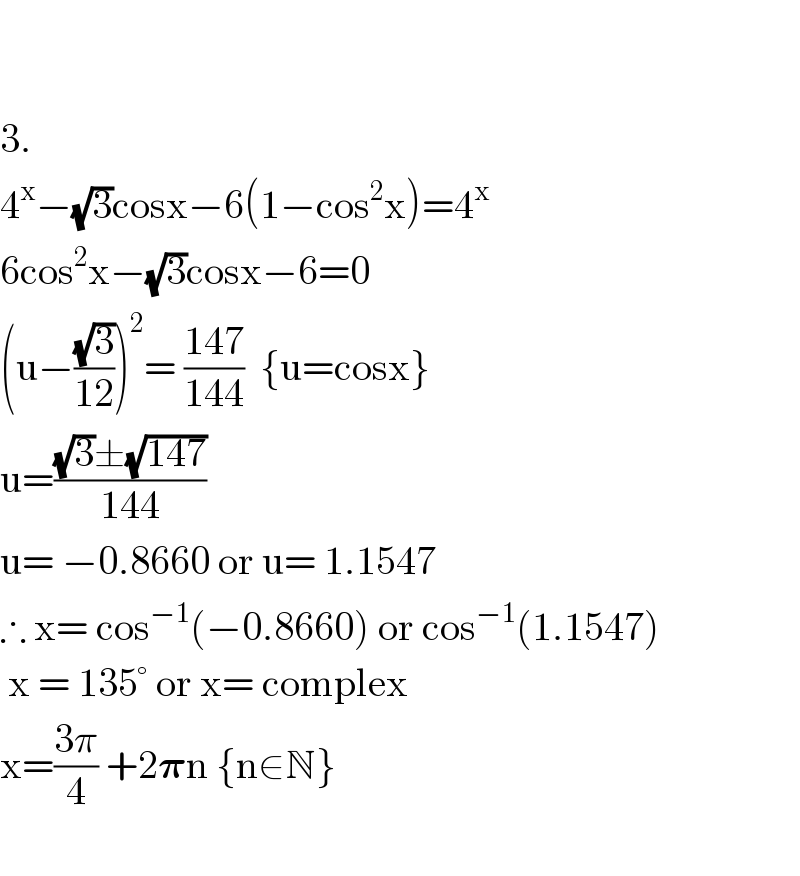
Commented by bemath last updated on 14/Oct/20
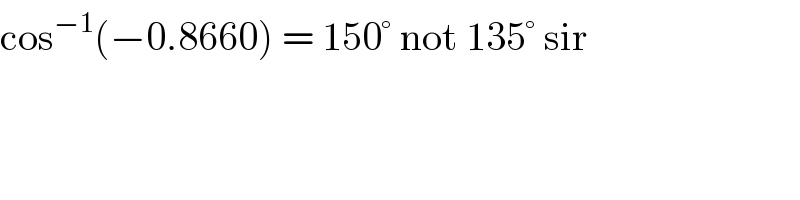
Commented by Lordose last updated on 14/Oct/20

Answered by john santu last updated on 14/Oct/20