
Question Number 118188 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 16/Oct/20

Commented by MJS_new last updated on 16/Oct/20
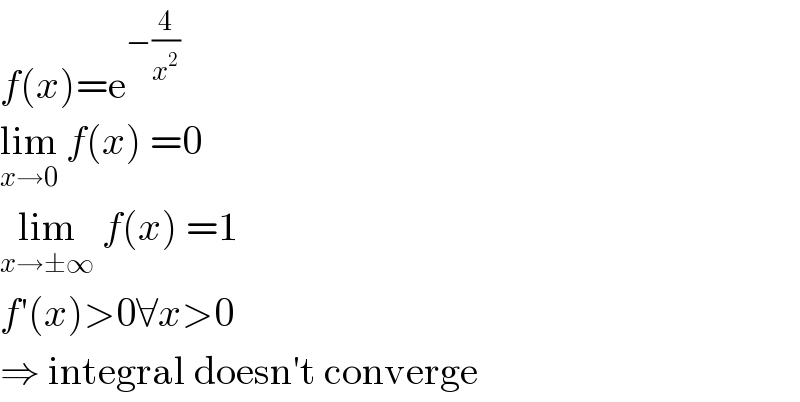
$${f}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{4}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\underset{{x}\rightarrow\pm\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${f}'\left({x}\right)>\mathrm{0}\forall{x}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{integral}\:\mathrm{doesn}'\mathrm{t}\:\mathrm{converge} \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 16/Oct/20
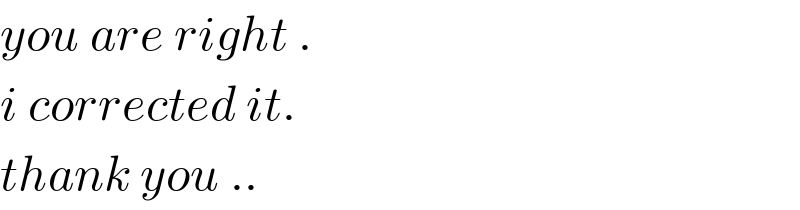
$${you}\:{are}\:{right}\:. \\ $$$${i}\:{corrected}\:{it}. \\ $$$${thank}\:{you}\:.. \\ $$
Answered by aleks041103 last updated on 16/Oct/20
![u=(1/x) ⇒ x=(1/u) ⇒ dx = −(1/u^2 )du ⇒ ∫e^(−1/x^2 ) dx=−∫e^(−u^2 ) (du/u^2 )=∫e^(−u^2 ) d((1/u)) IBP ∫e^(−u^2 ) d((1/u))=(e^(−u^2 ) /u)−∫(1/u)d(e^(−u^2 ) )= =(e^(−u^2 ) /u)+∫2ue^(−u^2 ) (1/u)du= =(√π) erf(u)+(e^(−u^2 ) /u)=(√π)erf(1/x)+xe^(−1/x^2 ) ⇒∫e^(−1/x^2 ) dx=(√π)erf(1/x)+xe^(−1/x^2 ) ∫e^(−(a/x)^2 ) dx=a∫e^(−(1/(x/a))^2 ) d(x/a)= =[a(√π)erf((a/x))+xe^(−(a/x)^2 ) ] ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−(a/x)^2 ) dx=−[a(√π)erf((a/x))+xe^(−(a/x)^2 ) ]_∞ ^0 = =−a(√π)+lim_(x→∞) xe^(−(a/x)^2 ) Ω=∫_0 ^∞ (e^(−(4/x^2 )) −e^(−(9/x^2 )) )dx= =∫_0 ^∞ e^(−(2/x)^2 ) dx−∫_0 ^∞ e^(−(3/x)^2 ) dx= =−2(√π)+3(√π)−lim_(x→∞) [x(e^(−(3/x)^2 ) −e^(−(2/x)^2 ) )]= =(√π)−lim_(x→∞) [x((1−(9/x^2 ))−(1−(4/x^2 )))] =(√π)+5lim_(x→∞) ((1/x))=(√π) Ω=(√π)](Q118199.png)
$${u}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\:\Rightarrow\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}}\:\Rightarrow\:{dx}\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }{du} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\int{e}^{−\mathrm{1}/{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {dx}=−\int{e}^{−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} } \frac{{du}}{{u}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\int{e}^{−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} } {d}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}}\right) \\ $$$${IBP} \\ $$$$\int{e}^{−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} } {d}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}}\right)=\frac{{e}^{−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} } }{{u}}−\int\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}}{d}\left({e}^{−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} } \right)= \\ $$$$=\frac{{e}^{−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} } }{{u}}+\int\mathrm{2}{ue}^{−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} } \frac{\mathrm{1}}{{u}}{du}= \\ $$$$=\sqrt{\pi}\:{erf}\left({u}\right)+\frac{{e}^{−{u}^{\mathrm{2}} } }{{u}}=\sqrt{\pi}{erf}\left(\mathrm{1}/{x}\right)+{xe}^{−\mathrm{1}/{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\int{e}^{−\mathrm{1}/{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } {dx}=\sqrt{\pi}{erf}\left(\mathrm{1}/{x}\right)+{xe}^{−\mathrm{1}/{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\int{e}^{−\left({a}/{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } {dx}={a}\int{e}^{−\left(\mathrm{1}/\left({x}/{a}\right)\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } {d}\left({x}/{a}\right)= \\ $$$$=\left[{a}\sqrt{\pi}{erf}\left(\frac{{a}}{{x}}\right)+{xe}^{−\left({a}/{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \right] \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−\left({a}/{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } {dx}=−\left[{a}\sqrt{\pi}{erf}\left(\frac{{a}}{{x}}\right)+{xe}^{−\left({a}/{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \right]_{\infty} ^{\mathrm{0}} = \\ $$$$=−{a}\sqrt{\pi}+\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {{lim}xe}^{−\left({a}/{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\Omega=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \left({e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{4}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }} −{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{9}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }} \right){dx}= \\ $$$$=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−\left(\mathrm{2}/{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } {dx}−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−\left(\mathrm{3}/{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } {dx}= \\ $$$$=−\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\pi}+\mathrm{3}\sqrt{\pi}−\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {{lim}}\left[{x}\left({e}^{−\left(\mathrm{3}/{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } −{e}^{−\left(\mathrm{2}/{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \right)\right]= \\ $$$$=\sqrt{\pi}−\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {{lim}}\left[{x}\left(\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{9}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)−\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{4}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\right)\right)\right] \\ $$$$=\sqrt{\pi}+\mathrm{5}\underset{{x}\rightarrow\infty} {{lim}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\right)=\sqrt{\pi} \\ $$$$\Omega=\sqrt{\pi} \\ $$
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 16/Oct/20
$${bravo} \\ $$$${thank}\:{you}\:{so}\:{much}.. \\ $$
