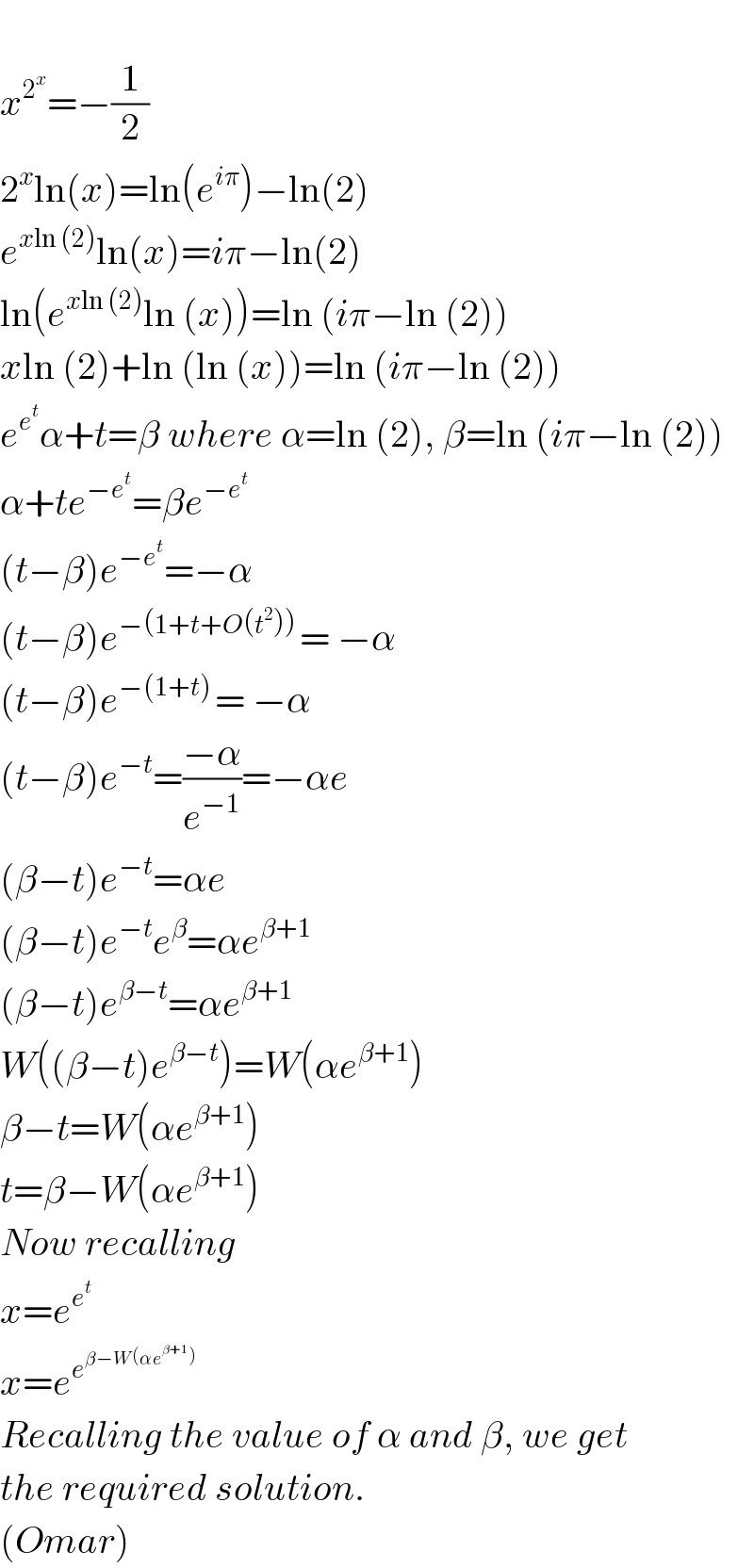Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 120780 by mathace last updated on 02/Nov/20
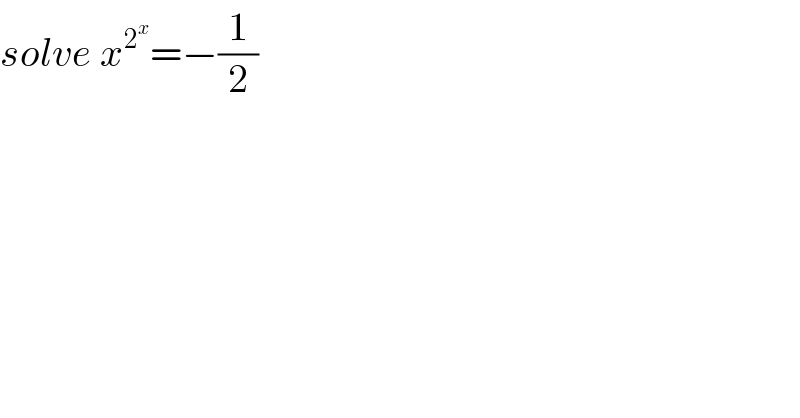
Commented by Anuragkar last updated on 02/Nov/20
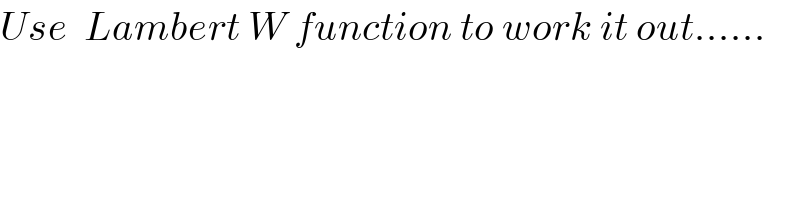
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 02/Nov/20

Answered by Anuragkar last updated on 14/Nov/20
![2^x ln(x)=ln(e^(iπ) )−ln(2) xln(x)ln(2)=ln(iπ−ln(2)) ln(x)e^(ln(x)) =ln(iπ−ln(2))/ln(2) Now use lambert W function W(ln(x)e^(ln(x)) )=ln(x)=W[ln{iπ−ln(2)}/ln(2)] x=e^(W[ln{iπ−ln(2)}/ln(2)]) .....this is the final answer....calculstw it using Wolframalpha](Q122046.png)
Commented by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 13/Nov/20
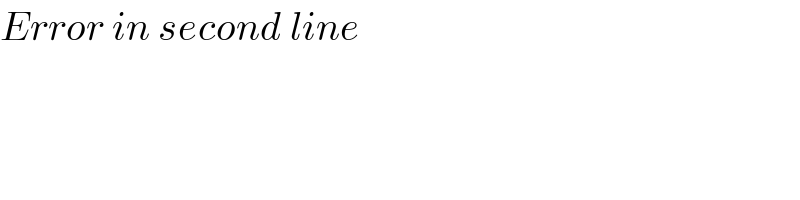
Answered by mathace last updated on 18/Nov/20