
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 121046 by bounhome last updated on 05/Nov/20
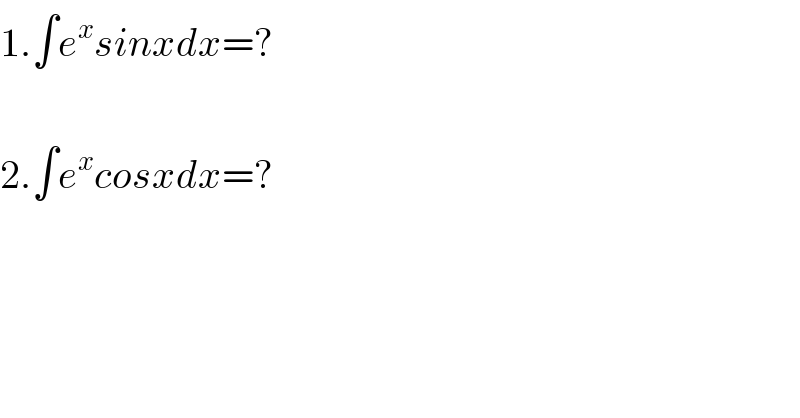
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 05/Nov/20
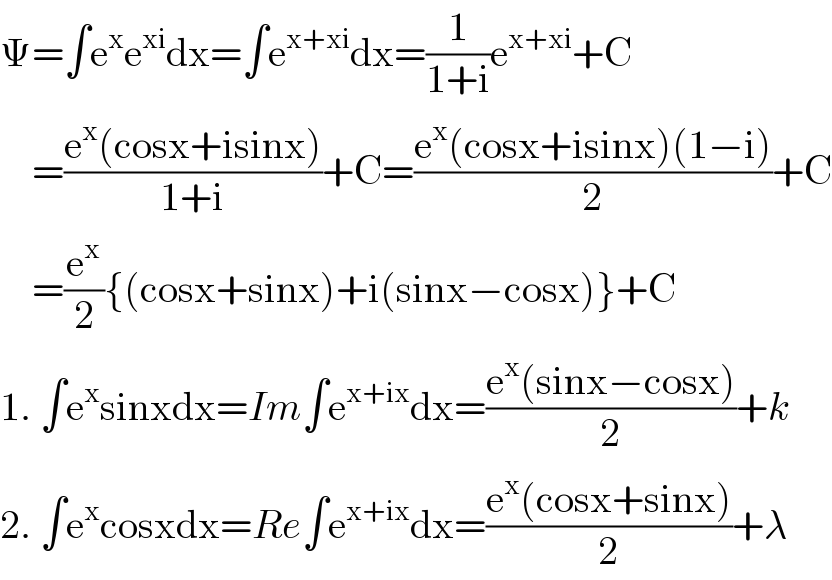
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 05/Nov/20
![1. I=∫e^x sinxdx=sinx∫e^x dx−∫{((dsinx)/dx)∙∫e^x }dx =e^x sinx−∫e^x cosxdx=e^x sinx−[e^x cosx+∫e^x sinxdx] =((e^x (sinx−cosx))/2)+k](Q121048.png)
Answered by ebi last updated on 05/Nov/20
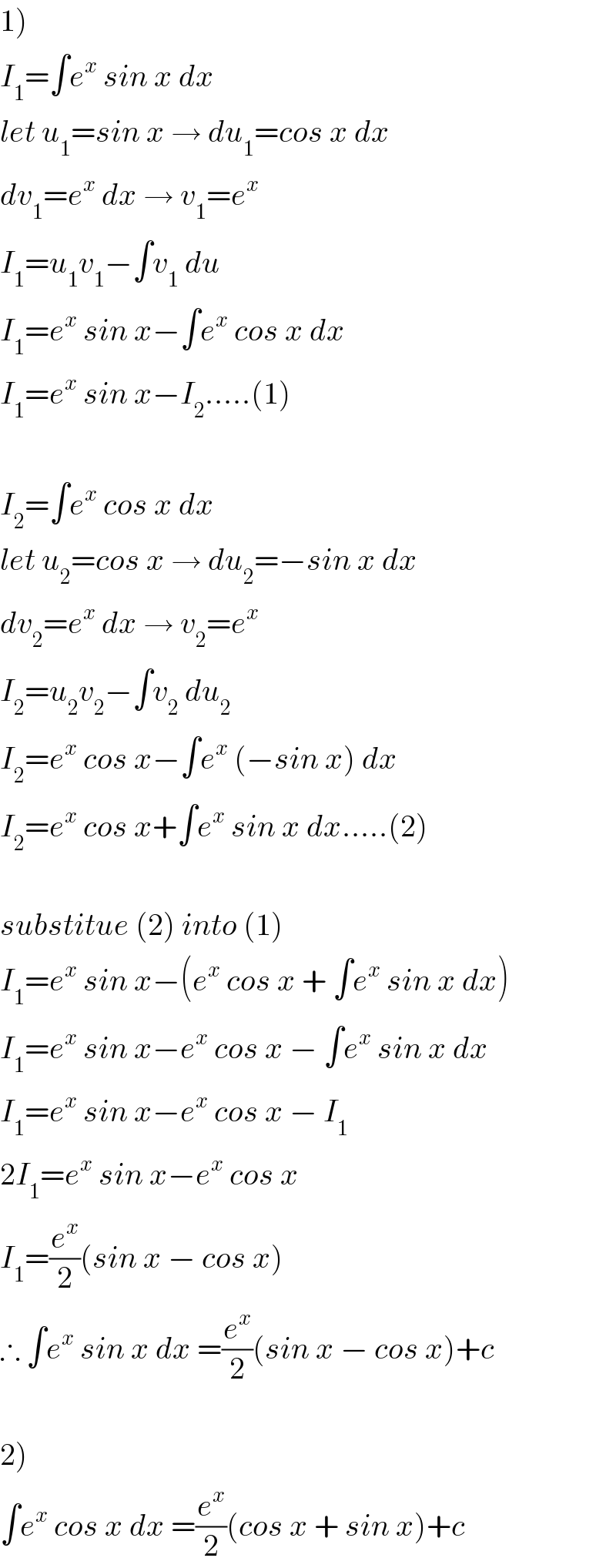
Answered by n0y0n last updated on 05/Nov/20

