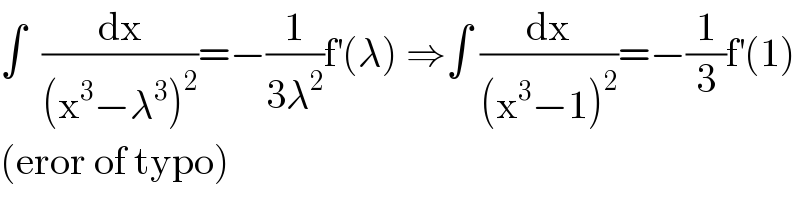Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 125114 by bramlexs22 last updated on 08/Dec/20
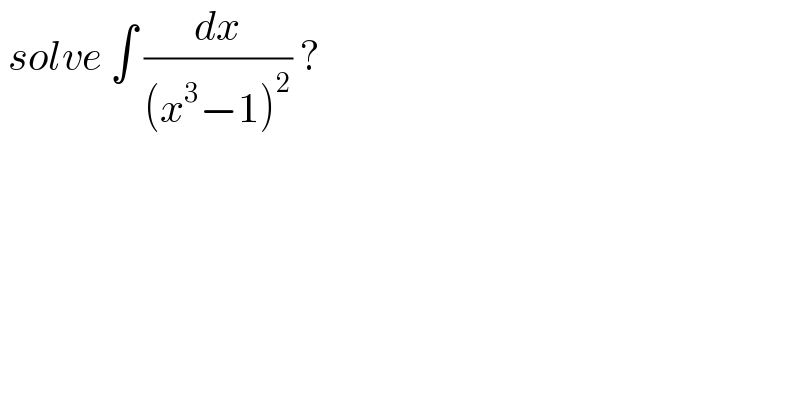
Commented by liberty last updated on 08/Dec/20

Answered by liberty last updated on 08/Dec/20
![equation has the form ∫ (dx/((x^3 −1)^2 )) = ((ax^2 +bx+c)/(x^3 −1))+∫ ((ex^2 +fx+g)/(x^3 −1)) dx differentiating both side we have (1/((x^3 −1)^2 )) = (((x^3 −1)(2ax+b)−(ax^2 +bx+c)3x^2 )/((x^3 −1)^2 )) + ((ex^2 +fx+g)/(x^3 −1)) equating the coefficients gives e = 0 , a=0 , c=0 , b=−(1/3) , f=0 , g=−(2/3) I= ∫(dx/((x^3 −1)^2 )) = ((−(1/3)x)/(x^3 −1)) + ∫ (((−2)/3)/(x^3 −1)) dx = ((−x)/(3(x^3 −1)))+ ∫ [ ((−(2/9))/(x−1)) + (((2/9)x+(4/9))/(x^2 +x+1)) ]dx = −(x/(3(x^3 −1)))−(2/9)ln ∣x−1∣ + (1/9)ln ∣x^2 +x+1∣ + ((2(√3))/9) arc tan (((2x+1)/( (√3)))) + c](Q125118.png)
Commented by bramlexs22 last updated on 08/Dec/20

Commented by MJS_new last updated on 08/Dec/20

Commented by bramlexs22 last updated on 08/Dec/20
does anyone have a pdf file about this method
Commented by MJS_new last updated on 08/Dec/20

Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 08/Dec/20
well detailed��
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 08/Dec/20

Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 08/Dec/20