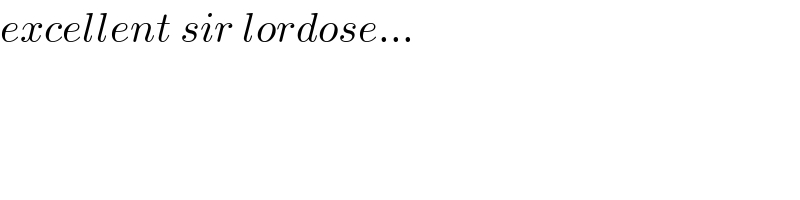Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 126003 by mnjuly1970 last updated on 16/Dec/20

Answered by Olaf last updated on 16/Dec/20
![φ = ∫_0 ^(π/2) tanxln(cosx)ln(sinx)dx φ = −∫_0 ^(π/2) [−tanxln(cosx)]ln(sinx)dx φ = −[(1/2)ln^2 (cosx)ln(sinx)]_0 ^(π/2) +∫_0 ^(π/2) [(1/2)ln^2 (cosx)]cotxdx φ = (1/2)∫_0 ^(π/2) cotx.ln^2 (cosx)dx Let u = cosx du = −sinxdx = −(√(1−u^2 ))dx φ = (1/2)∫_1 ^0 (u/( (√(1−u^2 ))))ln^2 u(−(du/( (√(1−u^2 ))))) φ = (1/2)∫_0 ^1 (u/( 1−u^2 ))ln^2 udu φ = (1/2)∫_0 ^1 u.ln^2 uΣ_(n=0) ^∞ u^(2n) du φ = (1/2)Σ_(n=0) ^∞ ∫_0 ^1 u^(2n+1) ln^2 udu φ = (1/2)Σ_(n=0) ^∞ {[(u^(2n+2) /(2n+2))ln^2 u]_0 ^1 −∫_0 ^1 (u^(2n+2) /(2n+2))(2((lnu)/u))du} φ = (1/2)Σ_(n=0) ^∞ {−∫_0 ^1 (u^(2n+2) /(2n+2))(2((lnu)/u))du} φ = −Σ_(n=0) ^∞ ∫_0 ^1 (u^(2n+1) /(2n+2))lnudu φ = −Σ_(n=0) ^∞ {[(u^(2n+2) /((2n+2)^2 ))lnu]_0 ^1 −∫_0 ^1 (u^(2n+2) /((2n+2)^2 )).(du/u)} φ = Σ_(n=0) ^∞ ∫_0 ^1 (u^(2n+2) /((2n+2)^2 )).(du/u) φ = Σ_(n=0) ^∞ ∫_0 ^1 (u^(2n+1) /((2n+2)^2 )).du φ = Σ_(n=0) ^∞ [(u^(2n+2) /((2n+2)^3 ))]_0 ^1 φ = Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (1/((2n+2)^3 )) φ = (1/8)Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (1/((n+1)^3 )) φ = (1/8)Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (1/n^3 ) φ = ((ζ(3))/8)](Q126050.png)
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 16/Dec/20
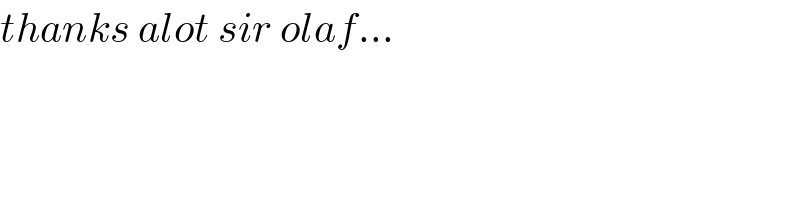
Answered by Lordose last updated on 16/Dec/20
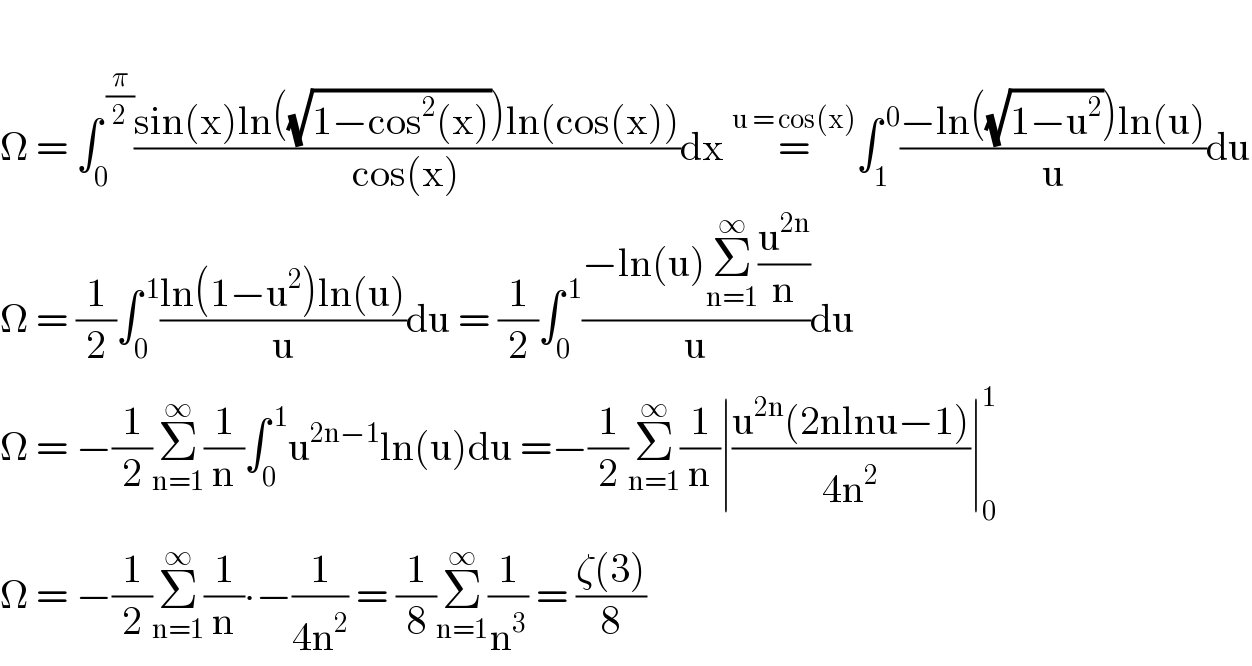
Commented by mnjuly1970 last updated on 16/Dec/20