
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 126056 by TITA last updated on 16/Dec/20

Commented by TITA last updated on 16/Dec/20

Answered by Olaf last updated on 16/Dec/20

Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 16/Dec/20
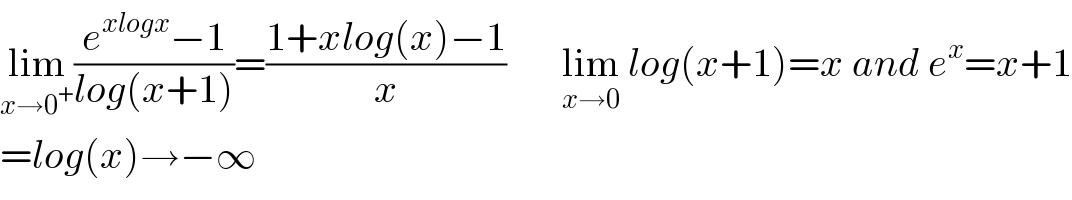
Answered by 676597498 last updated on 17/Dec/20

