
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 129287 by math178 last updated on 14/Jan/21

Commented by math178 last updated on 14/Jan/21
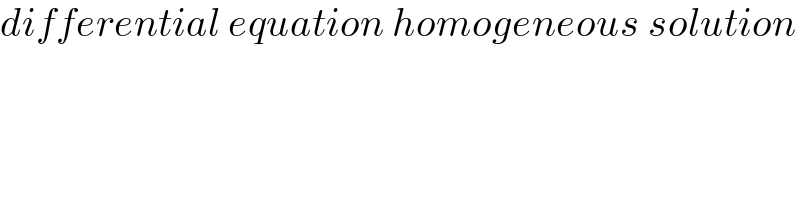
$${differential}\:{equation}\:{homogeneous}\:{solution} \\ $$
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 15/Jan/21
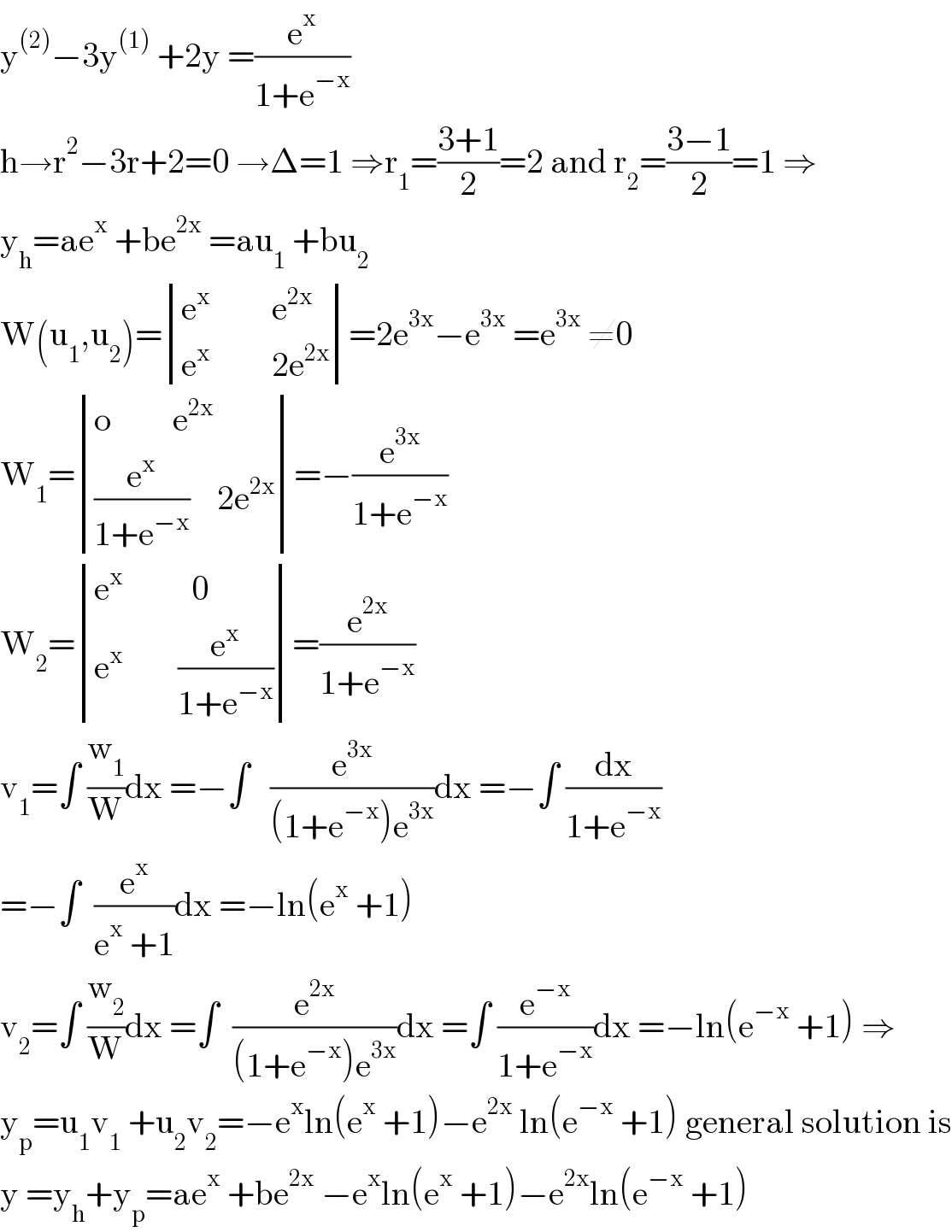
$$\mathrm{y}^{\left(\mathrm{2}\right)} −\mathrm{3y}^{\left(\mathrm{1}\right)} \:+\mathrm{2y}\:=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{h}\rightarrow\mathrm{r}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3r}+\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{0}\:\rightarrow\Delta=\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{r}_{\mathrm{1}} =\frac{\mathrm{3}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{r}_{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{\mathrm{3}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{h}} =\mathrm{ae}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{be}^{\mathrm{2x}} \:=\mathrm{au}_{\mathrm{1}} \:+\mathrm{bu}_{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{W}\left(\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{1}} ,\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{2}} \right)=\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} }\\{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{2e}^{\mathrm{2x}} }\end{vmatrix}=\mathrm{2e}^{\mathrm{3x}} −\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3x}} \:=\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3x}} \:\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{1}} =\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{o}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} }\\{\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }\:\:\:\:\mathrm{2e}^{\mathrm{2x}} }\end{vmatrix}=−\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3x}} }{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{2}} =\begin{vmatrix}{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{0}}\\{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }}\end{vmatrix}=\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} }{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{1}} =\int\:\frac{\mathrm{w}_{\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{W}}\mathrm{dx}\:=−\int\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3x}} }{\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \right)\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3x}} }\mathrm{dx}\:=−\int\:\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} } \\ $$$$=−\int\:\:\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{1}}\mathrm{dx}\:=−\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{2}} =\int\:\frac{\mathrm{w}_{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{W}}\mathrm{dx}\:=\int\:\:\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} }{\left(\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \right)\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{3x}} }\mathrm{dx}\:=\int\:\frac{\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} }\mathrm{dx}\:=−\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{p}} =\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{1}} \:+\mathrm{u}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{v}_{\mathrm{2}} =−\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} \:\mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)\:\mathrm{general}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\mathrm{is} \\ $$$$\mathrm{y}\:=\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{h}} +\mathrm{y}_{\mathrm{p}} =\mathrm{ae}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{be}^{\mathrm{2x}} \:−\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{2x}} \mathrm{ln}\left(\mathrm{e}^{−\mathrm{x}} \:+\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$
