
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 129839 by liberty last updated on 20/Jan/21

Answered by EDWIN88 last updated on 20/Jan/21
![J=∫_( 0) ^( π/2) ((3(√(cos x)))/(((√(cos x)) +(√(sin x)) )^5 )) dx let x=(π/2)−t ⇒J=∫_(π/2) ^( 0) ((3(√(sin t)))/(((√(sin t)) +(√(cos t)))^5 ))(−dt) or J = ∫_0 ^(π/2) ((3(√(sin x)))/(((√(sin x)) +(√(cos x)) )^5 )) dx we get 2J = ∫_0 ^( π/2) ((3((√(sin x)) +(√(cos x)) ))/(((√(sin x)) +(√(cos x)) )^5 )) dx 2J = ∫_0 ^( π/2) ((3 dx)/(((√(cos x)) (1+(√(tan x)) ))^4 )) 2J= 3∫_0 ^( π/2) ((sec^2 x)/((1+(√(tan x)))^4 )) dx 2J = 3∫_0 ^( ∞) (dj/((1+(√j) )^4 )) 2J=3∫_1 ^( ∞) (z^(−3) −z^(−4) )dz ; with z=1+(√j) J=(3/2)lim_(q→∞) [ −(z^(−2) /2)+(z^(−3) /3) ]_1 ^q = (1/2)](Q129840.png)
Answered by Lordose last updated on 20/Jan/21
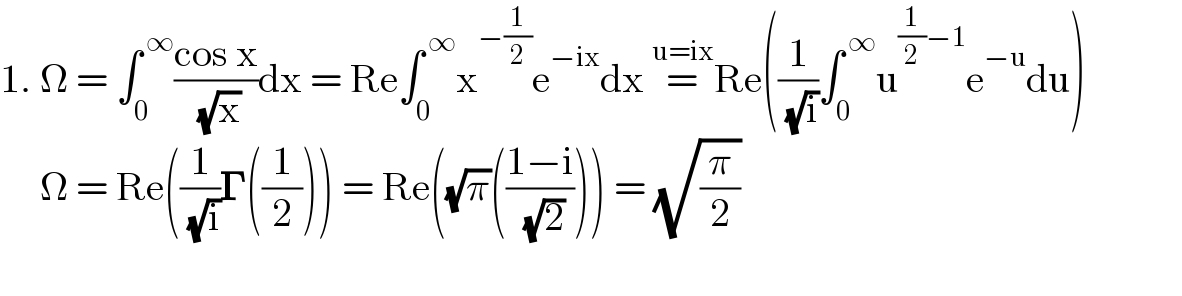
Answered by Lordose last updated on 20/Jan/21
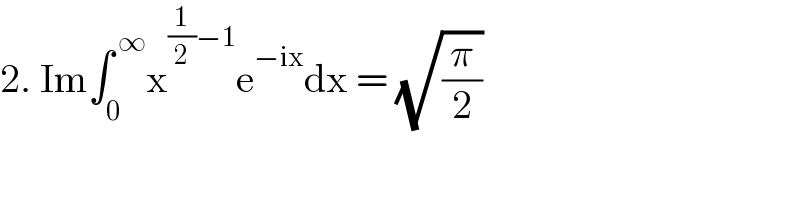
Answered by Olaf last updated on 20/Jan/21
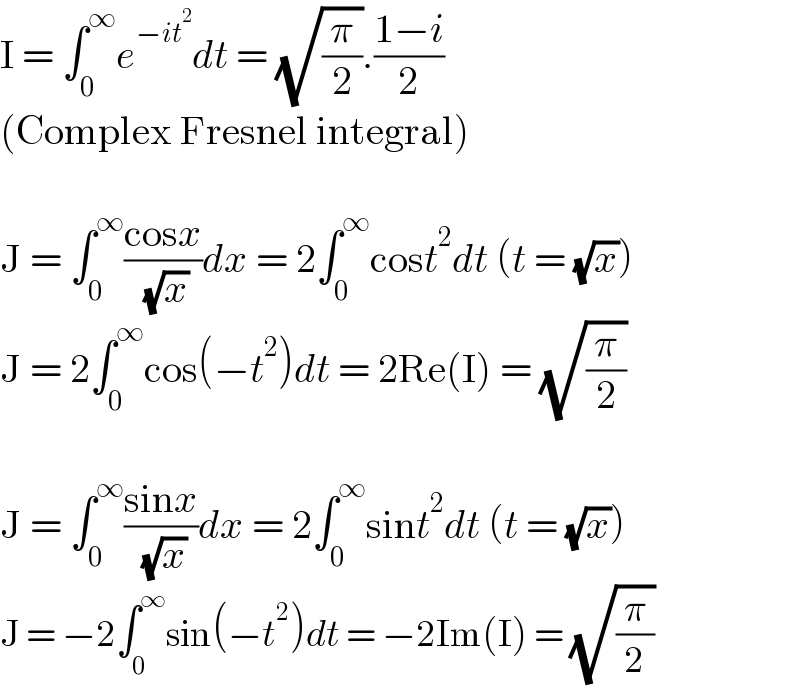
Answered by EDWIN88 last updated on 20/Jan/21
![one approach to solving this would be to use the Gaussian Integral ∫_0 ^( ∞) e^(−t^2 ) dt = ((√π)/2) let t =y(√x) where x is constant (2/( (√π)))∫_0 ^( ∞) e^(−xy^2 ) dy = (1/( (√x))) I=∫_0 ^( ∞) cos x (2/( (√π))) ∫_0 ^( ∞) e^(−xy^2 ) dydx = (2/( (√π))) ∫_0 ^∞ ∫_0 ^( ∞) e^(−xy^2 ) cos x dx dy = (2/( (√π))) ∫_0 ^( ∞) L(cos t)∣_(s=y^2 ) dy = (2/( (√π))) ∫_0 ^( ∞) (y^2 /(y^4 +1)) dy similarly to J=∫_0 ^( ∞) ((sin x)/( (√x))) dx = (2/( (√π))) ∫_0 ^( ∞) (dy/(y^4 +1)) I=J ⇒2I=(2/( (√π))) ∫_0 ^( ∞) ((y^2 +1)/(y^4 +1)) dy 2I= (2/( (√π))) ∫_(−∞) ^( ∞) (1/(u^2 +2)) du [ with u = y−(1/y) ] 2I=(2/( (√π))).(1/( (√2))) (arctan ((u/( (√2)))) )∣_(−∞) ^∞ I= (√(π/2)) → { ((∫_0 ^∞ ((cos x)/( (√x))) dx = (√(π/2)))),((∫_0 ^( ∞) ((sin x)/( (√x))) dx = (√(π/2)))) :}](Q129850.png)
Answered by Bird last updated on 20/Jan/21
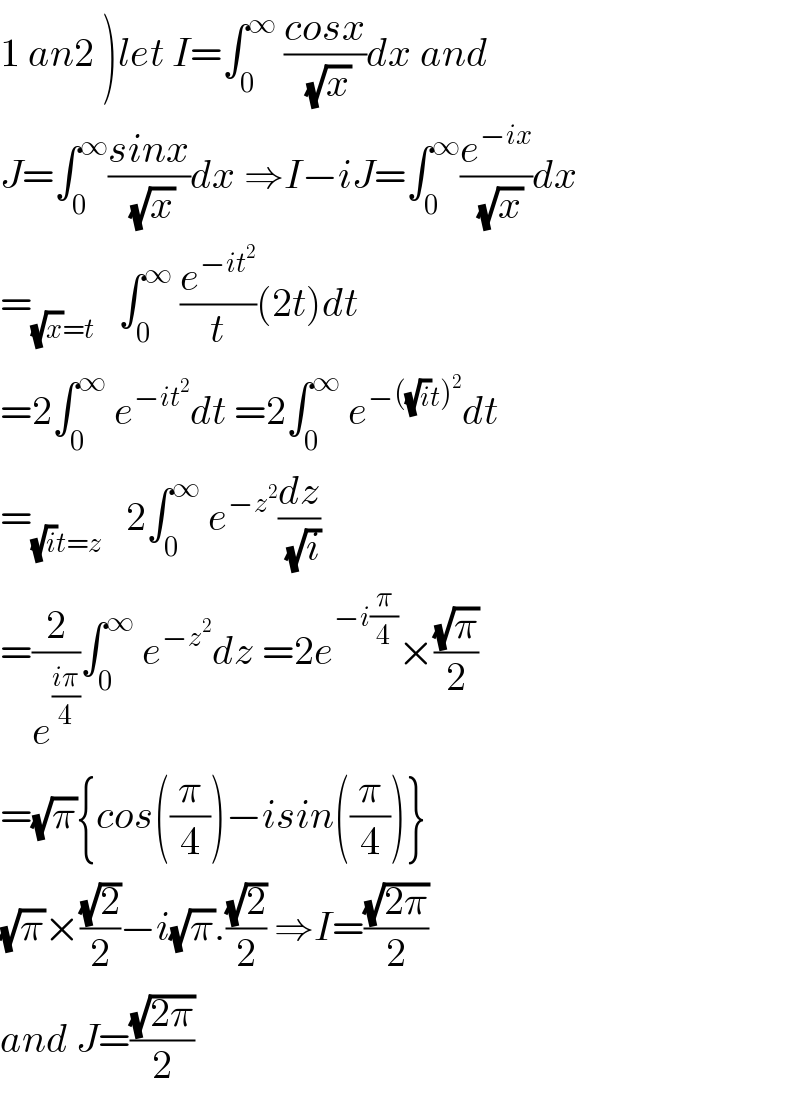
Answered by bemath last updated on 21/Jan/21

