
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 130047 by liberty last updated on 22/Jan/21
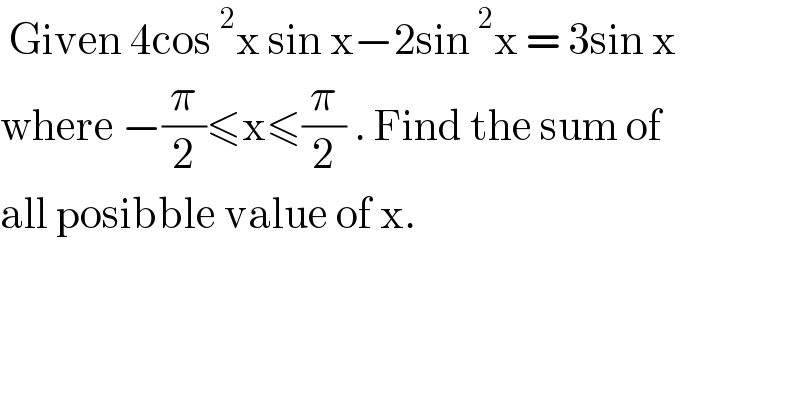
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 22/Jan/21
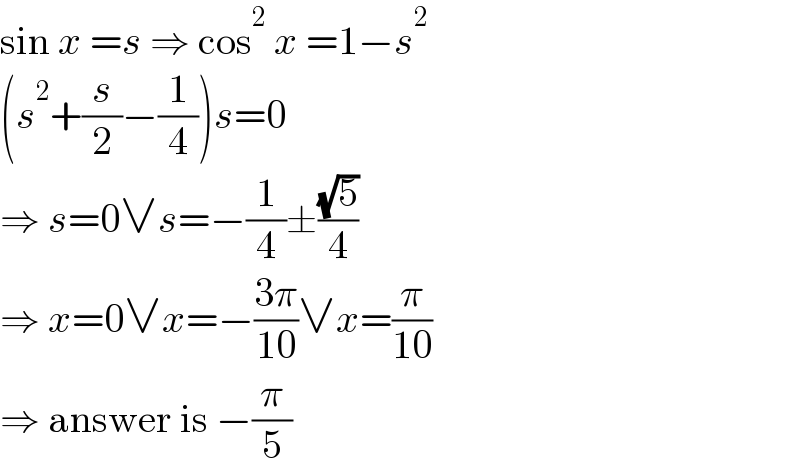
Answered by Alepro3 last updated on 22/Jan/21
![cos^2 x=1−sin^2 x ⇒ 4sin x−4sin^3 x−2sin^2 x=3sin x ⇒ sin x(4sin^2 x+2sin x−sin x)=0 ⇒ one solution is sin x=0 ⇒ x=kπ solving the 2^(nd) degree equation we have sin x_(1,2) =(−2±(√(4+16)))/8=(−1±(√5))/4 so x_(1,2) =sin^(−1) [(−1±(√5))/4]+2kπ and x_(3,4) =π−sin^(−1) [[(1−(√5))/4]+2kπ ⇒ the sum of all of this value of x is Σx=π+5kπ](Q130101.png)
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 130047 by liberty last updated on 22/Jan/21 | ||
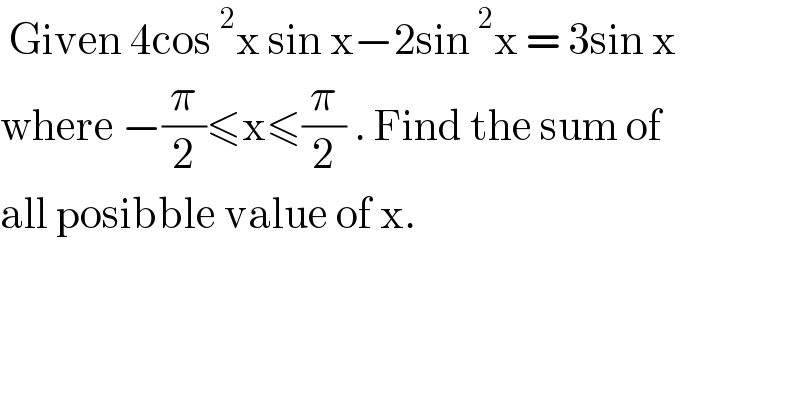 | ||
Answered by MJS_new last updated on 22/Jan/21 | ||
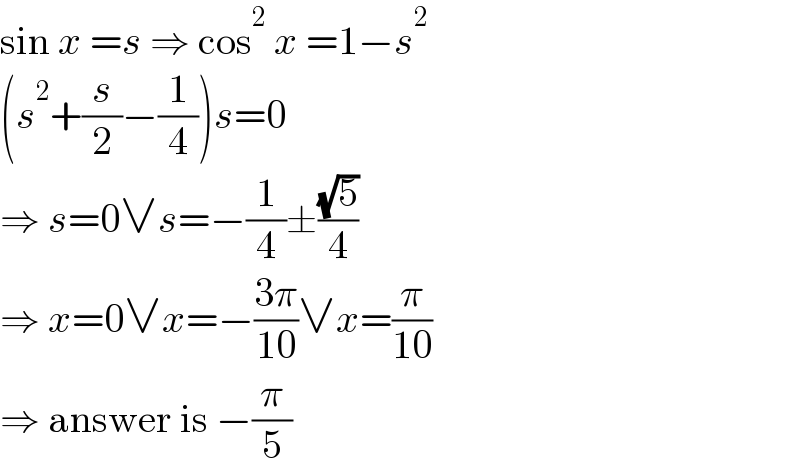 | ||
| ||
Answered by Alepro3 last updated on 22/Jan/21 | ||
![cos^2 x=1−sin^2 x ⇒ 4sin x−4sin^3 x−2sin^2 x=3sin x ⇒ sin x(4sin^2 x+2sin x−sin x)=0 ⇒ one solution is sin x=0 ⇒ x=kπ solving the 2^(nd) degree equation we have sin x_(1,2) =(−2±(√(4+16)))/8=(−1±(√5))/4 so x_(1,2) =sin^(−1) [(−1±(√5))/4]+2kπ and x_(3,4) =π−sin^(−1) [[(1−(√5))/4]+2kπ ⇒ the sum of all of this value of x is Σx=π+5kπ](Q130101.png) | ||
| ||