
Question Number 130315 by stelor last updated on 24/Jan/21

Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 24/Jan/21
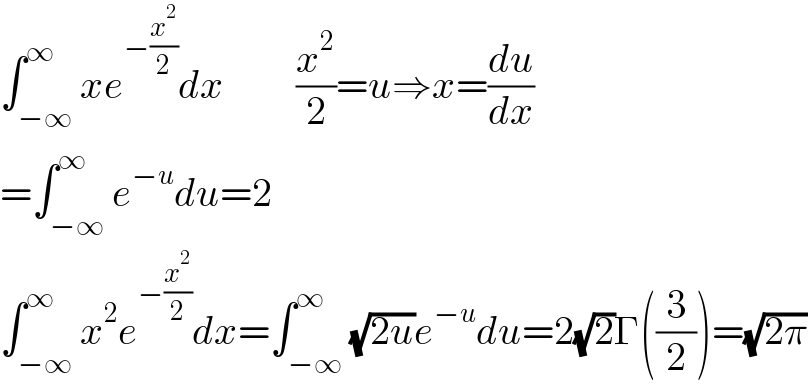
$$\int_{−\infty} ^{\infty} {xe}^{−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} {dx}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}={u}\Rightarrow{x}=\frac{{du}}{{dx}} \\ $$$$=\int_{−\infty} ^{\infty} {e}^{−{u}} {du}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\int_{−\infty} ^{\infty} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} {dx}=\int_{−\infty} ^{\infty} \sqrt{\mathrm{2}{u}}{e}^{−{u}} {du}=\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}\Gamma\left(\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)=\sqrt{\mathrm{2}\pi} \\ $$
Commented by stelor last updated on 24/Jan/21
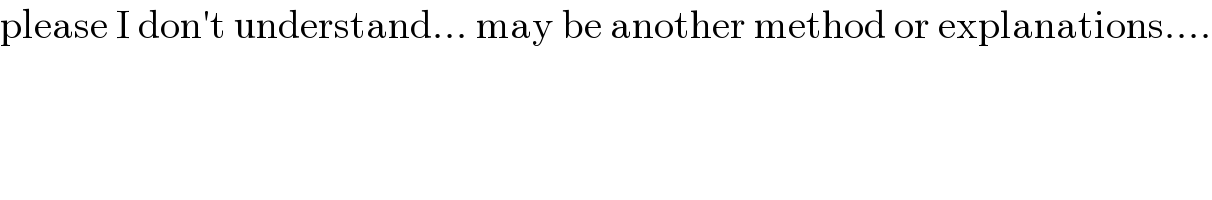
$$\mathrm{please}\:\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{don}'\mathrm{t}\:\mathrm{understand}...\:\mathrm{may}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{another}\:\mathrm{method}\:\mathrm{or}\:\mathrm{explanations}.... \\ $$
