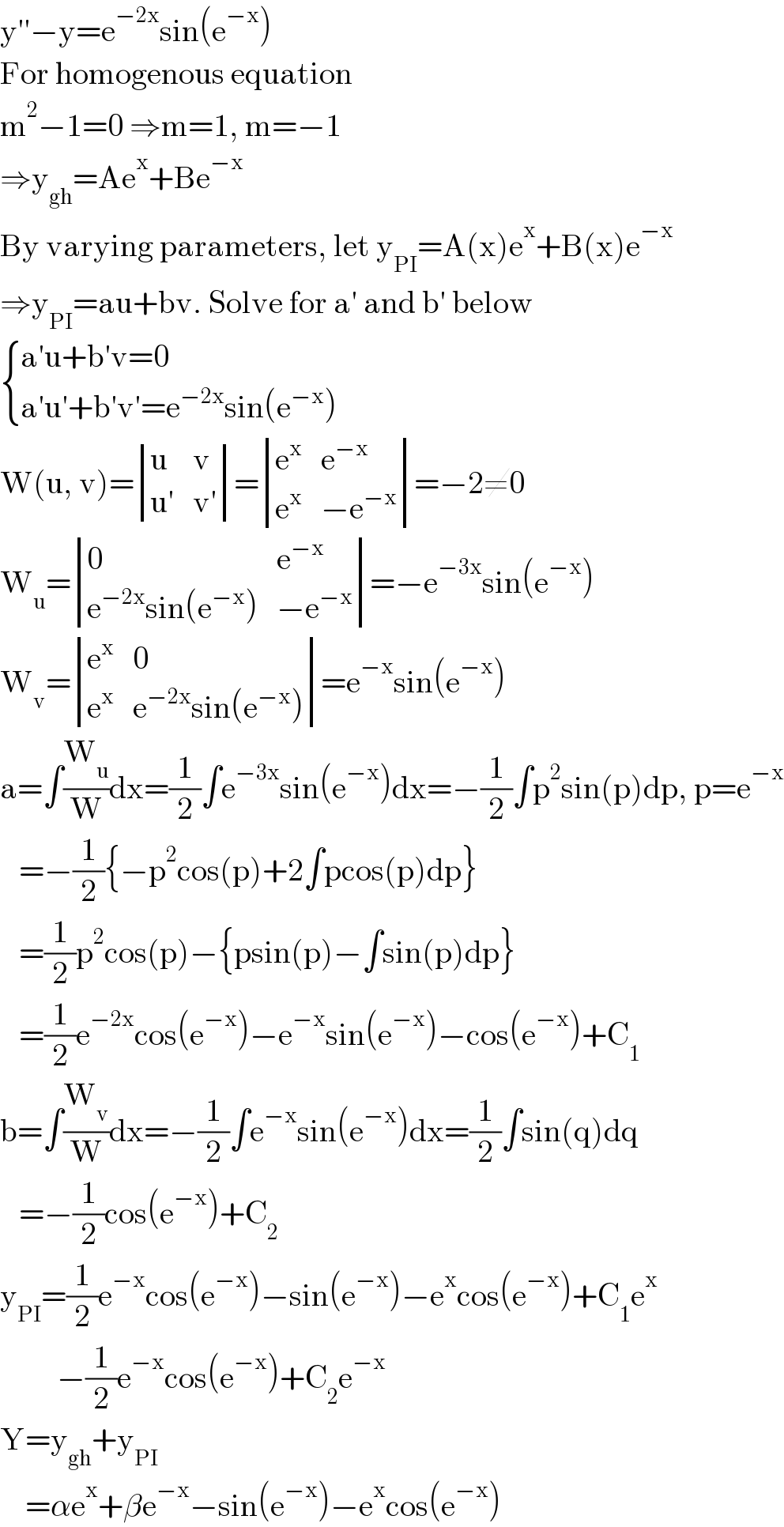Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 131086 by EDWIN88 last updated on 01/Feb/21
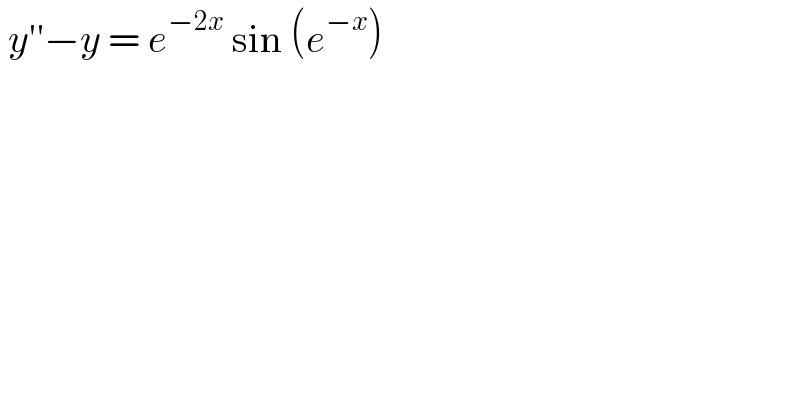
Answered by liberty last updated on 01/Feb/21
![[ D^2 −1 ]y = e^(−2x) sin (e^(−x) ) (D−1)(D+1)y=e^(−2x) sin (e^(−x) ) (D−1)[e^x (D+1)y ] = e^(−x) sin (e^(−x) ) (D−1)D(e^x y)=e^(−x) sin (e^(−x) ) (D−1)e^x y = ∫e^(−x) sin (e^(−x) )dx (D−1)e^x y = cos (e^(−x) )+C_1 (D−1)y = e^(−x) cos (e^(−x) )+C_1 e^(−x) (D−1)e^(−x) y = e^(−2x) +C_1 e^(−2x) D(e^(−x) y) = e^(−2x) +C_1 e^(−2x) e^(−x) y = ∫(e^(−2x) +C_1 e^(−2x) )dx y = e^x [ −e^(−x) sin (e^(−x) )−cos (e^(−x) )−(1/2)C_1 e^(−2x) +C_2 ]](Q131087.png)
Commented by EDWIN88 last updated on 01/Feb/21

Commented by EDWIN88 last updated on 01/Feb/21
զարմանալի
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 01/Feb/21