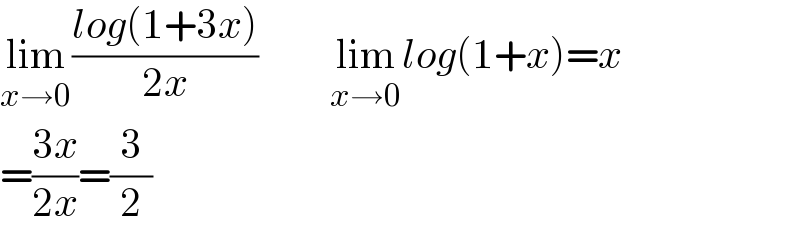Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 133738 by mathlove last updated on 23/Feb/21
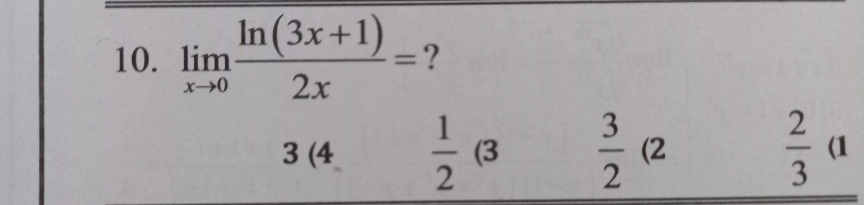
Answered by Ar Brandon last updated on 24/Feb/21
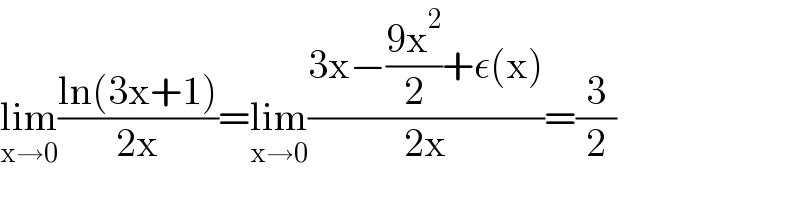
Commented by mathlove last updated on 24/Feb/21

Commented by Ar Brandon last updated on 24/Feb/21
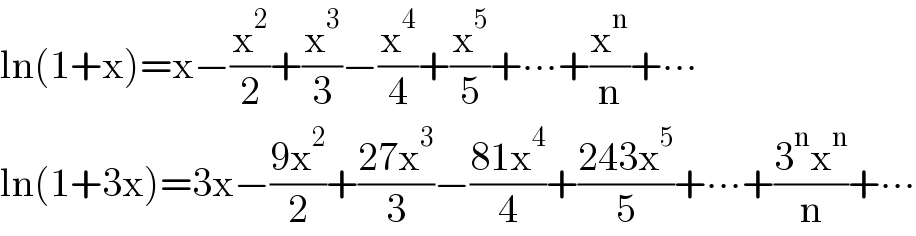
Answered by bramlexs22 last updated on 24/Feb/21
![10. lim_(x→0) ((ln (3x+1))/(2x))=lim_(x→0) (([(3/(3x+1))])/2)=(3/2)](Q133752.png)
Answered by Dwaipayan Shikari last updated on 24/Feb/21