
Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 133776 by bramlexs22 last updated on 24/Feb/21
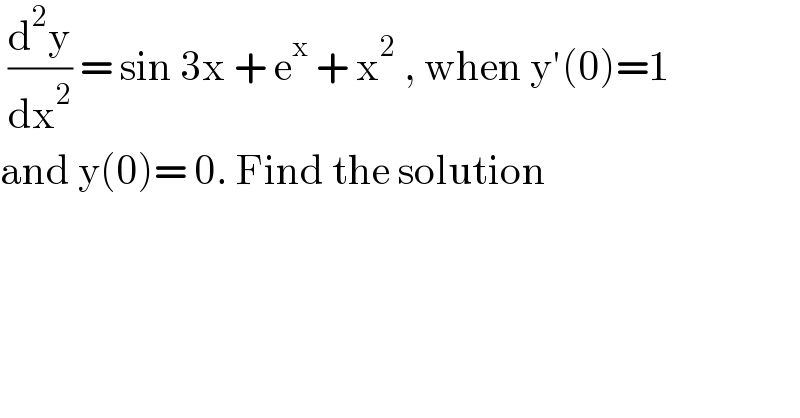
Answered by bobhans last updated on 24/Feb/21
![(d/dx) [ (dy/dx) ] = sin 3x+e^x +x^2 d[(dy/dx)] = (sin 3x+e^x +x^2 ) dx ∫ d[(dy/dx) ] = ∫ (sin 3x+e^x +x^2 )dx ⇒(dy/dx) = −(1/3)cos 3x+e^x +(1/3)x^3 +C_1 y′(0) = −(1/3)+1+C_1 =1 ; C_1 =(1/3) ∫ dy = ∫ (−(1/3)cos 3x+e^x +(1/3)x^3 +(1/3))dx y=−(1/9)sin 3x+e^x +(1/(12))x^4 +(1/3)x+C_2 y(0)=1+C_2 =0 ⇒C_2 =−1 ∴y=−((sin 3x)/9)+e^x +((x^4 +4x−12)/(12))](Q133779.png)
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation | ||
Question Number 133776 by bramlexs22 last updated on 24/Feb/21 | ||
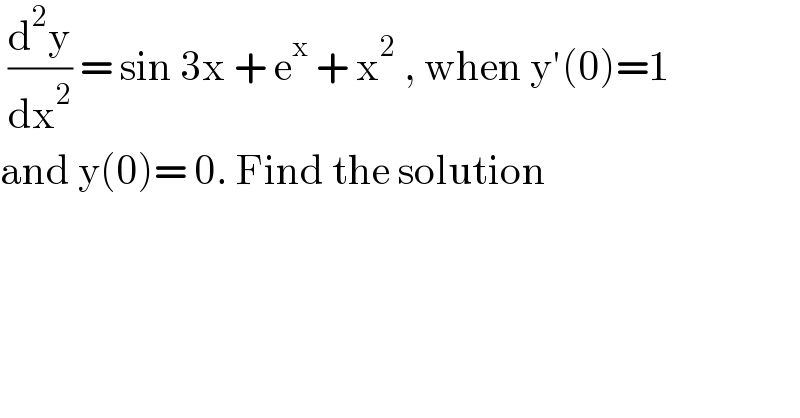 | ||
Answered by bobhans last updated on 24/Feb/21 | ||
![(d/dx) [ (dy/dx) ] = sin 3x+e^x +x^2 d[(dy/dx)] = (sin 3x+e^x +x^2 ) dx ∫ d[(dy/dx) ] = ∫ (sin 3x+e^x +x^2 )dx ⇒(dy/dx) = −(1/3)cos 3x+e^x +(1/3)x^3 +C_1 y′(0) = −(1/3)+1+C_1 =1 ; C_1 =(1/3) ∫ dy = ∫ (−(1/3)cos 3x+e^x +(1/3)x^3 +(1/3))dx y=−(1/9)sin 3x+e^x +(1/(12))x^4 +(1/3)x+C_2 y(0)=1+C_2 =0 ⇒C_2 =−1 ∴y=−((sin 3x)/9)+e^x +((x^4 +4x−12)/(12))](Q133779.png) | ||
| ||