
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 13649 by ajfour last updated on 22/May/17
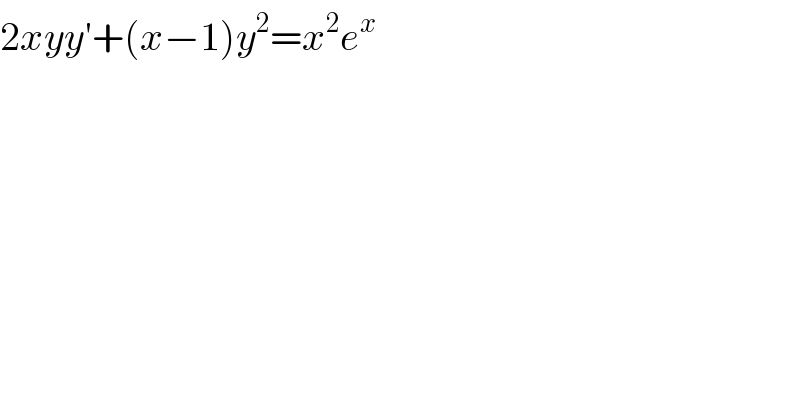
$$\mathrm{2}{xyy}'+\left({x}−\mathrm{1}\right){y}^{\mathrm{2}} ={x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{{x}} \\ $$
Answered by ajfour last updated on 22/May/17

$${let}\:{y}^{\mathrm{2}} ={tx}\:\:\:\:\:\Rightarrow\:\:\:\mathrm{2}{yy}'={t}+{x}\frac{{dt}}{{dx}} \\ $$$${substituting} \\ $$$${tx}+{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{{dt}}{{dx}}+{tx}^{\mathrm{2}} −{tx}={x}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{{x}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dt}}{{dx}}+{t}={e}^{{x}} \:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:;\:\:\:\:{or}\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0}\:\: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:\:{e}^{{x}} \frac{{dt}}{{dx}}+{te}^{{x}} ={e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} \\ $$$$\int{d}\left({te}^{{x}} \right)=\int{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} {dx} \\ $$$$\:\:\:{te}^{{x}} =\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}+{c} \\ $$$$\:\:{y}^{\mathrm{2}} =\frac{{xe}^{{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}+{cxe}^{−{x}} \\ $$$${y}=\sqrt{\frac{{xe}^{{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}+{cxe}^{−{x}} }\:. \\ $$
