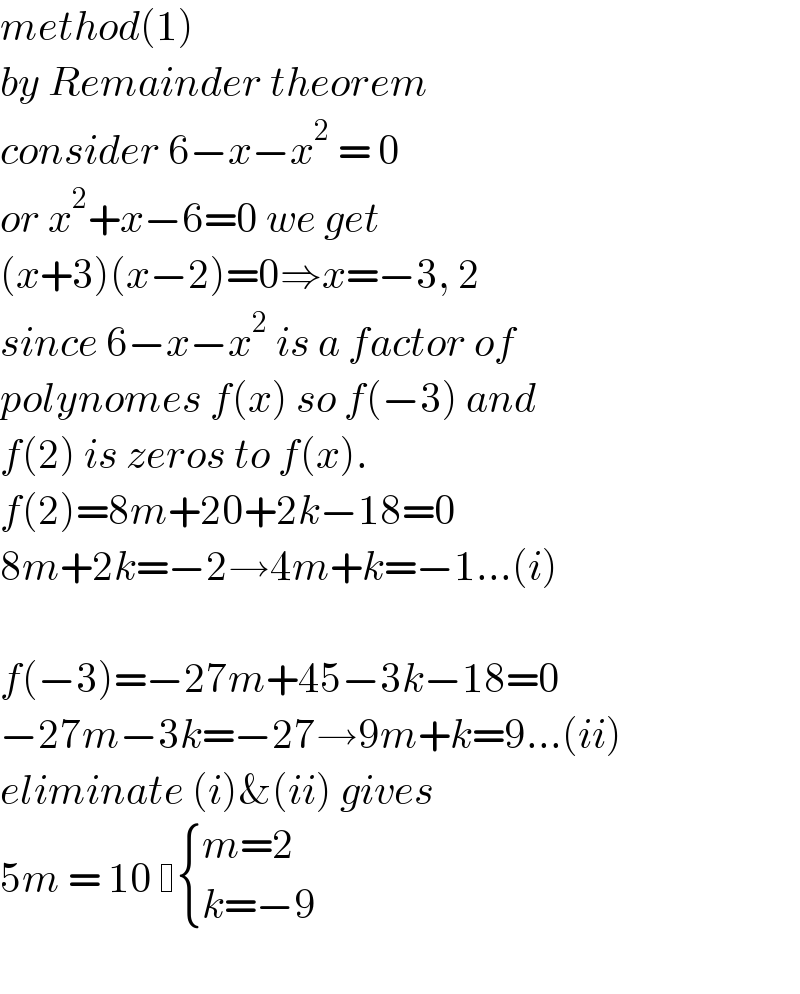Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Relation and Functions Next in Relation and Functions
Question Number 136693 by liberty last updated on 25/Mar/21

Commented by Olaf last updated on 25/Mar/21
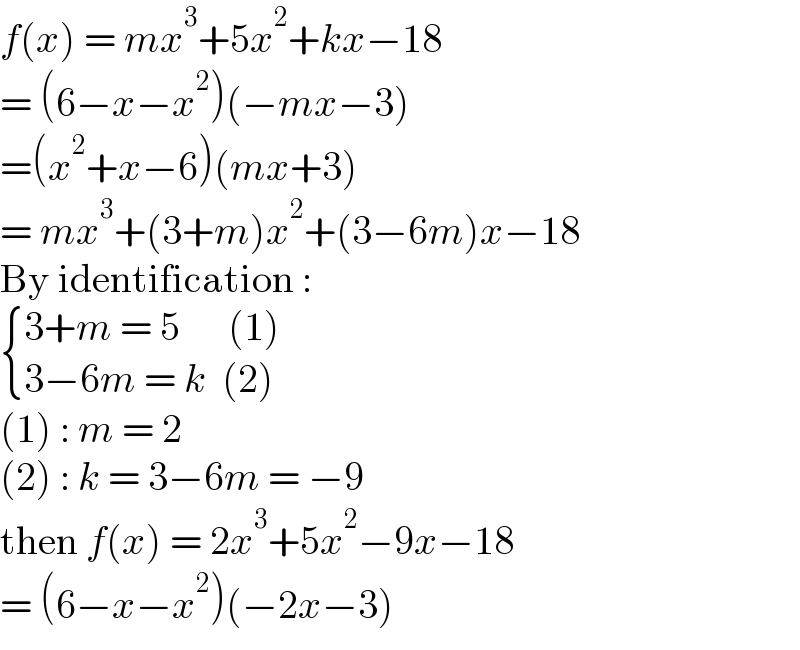
Answered by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 25/Mar/21

Answered by bramlexs22 last updated on 25/Mar/21