
Question Number 138219 by otchereabdullai@gmail.com last updated on 11/Apr/21

$$\:\mathrm{Consider}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{function}\:\mathrm{y}=\frac{\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{3x}+\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{3x}−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\:\mathrm{Determine}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{intercept}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{function} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{2}\right)\:\mathrm{Find}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{asymptotes}\:\mathrm{if}\:\mathrm{they}\:\mathrm{exist} \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{3}\right)\:\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{turning}\:\mathrm{point}\:\mathrm{and}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{determine}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{type}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{turnin}\:\mathrm{point}\:\mathrm{they} \\ $$$$\mathrm{are}. \\ $$$$\left.\mathrm{4}\right)\:\mathrm{sketch}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{graph}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{function}. \\ $$
Answered by bobhans last updated on 11/Apr/21
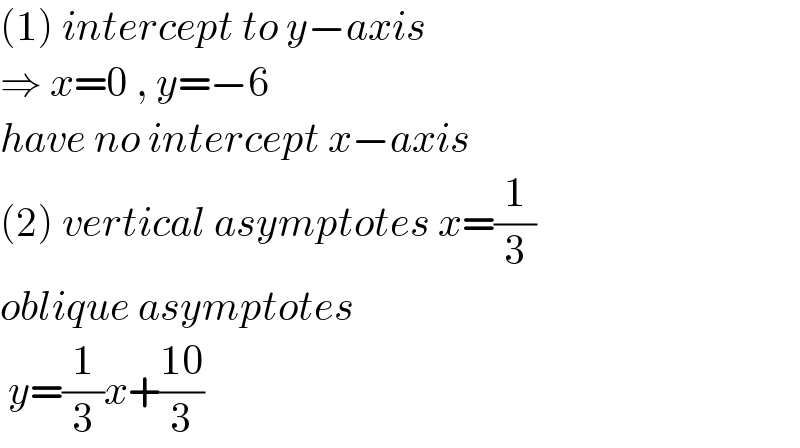
$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:{intercept}\:{to}\:{y}−{axis}\: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{x}=\mathrm{0}\:,\:{y}=−\mathrm{6} \\ $$$${have}\:{no}\:{intercept}\:{x}−{axis}\: \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:{vertical}\:{asymptotes}\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$${oblique}\:{asymptotes}\: \\ $$$$\:{y}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}{x}+\frac{\mathrm{10}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$
Commented by bobhans last updated on 11/Apr/21

Commented by otchereabdullai@gmail.com last updated on 11/Apr/21

$$\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{sir}!\:\mathrm{sir}\:\mathrm{left}\:\mathrm{option}\left(\:\mathrm{3}\right) \\ $$
Answered by EDWIN88 last updated on 11/Apr/21
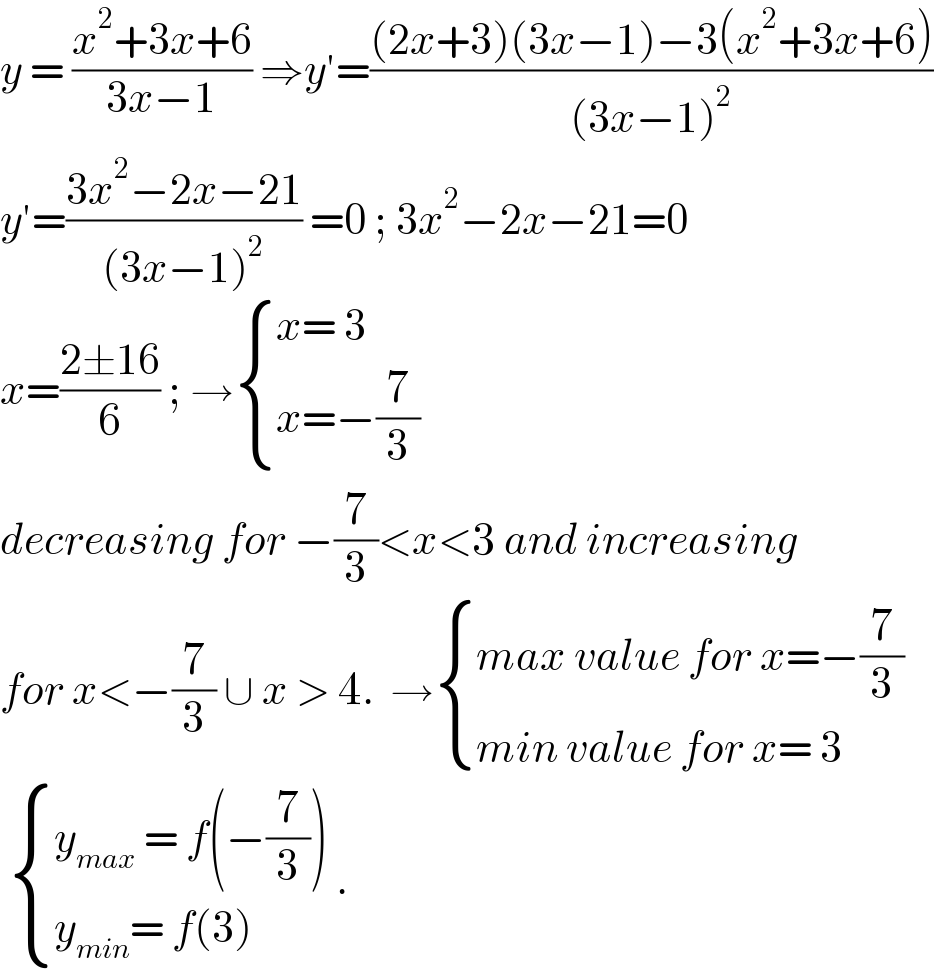
$${y}\:=\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{6}}{\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{1}}\:\Rightarrow{y}'=\frac{\left(\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{3}\right)\left(\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{3}\left({x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{6}\right)}{\left(\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${y}'=\frac{\mathrm{3}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{21}}{\left(\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{1}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\mathrm{0}\:;\:\mathrm{3}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{21}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}=\frac{\mathrm{2}\pm\mathrm{16}}{\mathrm{6}}\:;\:\rightarrow\begin{cases}{{x}=\:\mathrm{3}}\\{{x}=−\frac{\mathrm{7}}{\mathrm{3}}}\end{cases} \\ $$$${decreasing}\:{for}\:−\frac{\mathrm{7}}{\mathrm{3}}<{x}<\mathrm{3}\:{and}\:{increasing} \\ $$$${for}\:{x}<−\frac{\mathrm{7}}{\mathrm{3}}\:\cup\:{x}\:>\:\mathrm{4}.\:\:\rightarrow\begin{cases}{{max}\:{value}\:{for}\:{x}=−\frac{\mathrm{7}}{\mathrm{3}}}\\{{min}\:{value}\:{for}\:{x}=\:\mathrm{3}}\end{cases} \\ $$$$\:\begin{cases}{{y}_{{max}} \:=\:{f}\left(−\frac{\mathrm{7}}{\mathrm{3}}\right)}\\{{y}_{{min}} =\:{f}\left(\mathrm{3}\right)}\end{cases}\:. \\ $$
