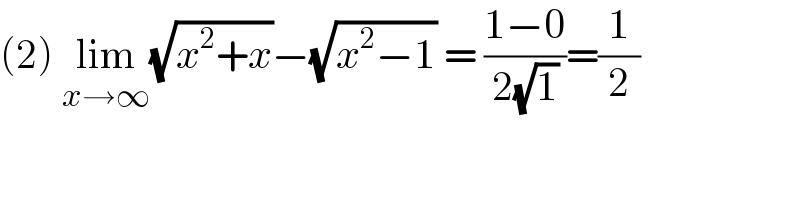Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 143561 by ZiYangLee last updated on 15/Jun/21

Answered by mr W last updated on 15/Jun/21
![a=lim_(x→∞) [(1−(1/x))^2 ]^x =lim_(x→∞) [(1−(1/x))^(−x) ]^(−2) =e^(−2) =(1/e^2 ) b=lim_(n→∞) ((√(n+1))/( (√n)+(√(n−1)))) =lim_(n→∞) ((√(1+(1/n)))/( 1+(√(1−(1/n)))))=(1/2)](Q143564.png)
Commented by ZiYangLee last updated on 15/Jun/21

Answered by Mathspace last updated on 15/Jun/21

Answered by bobhans last updated on 15/Jun/21