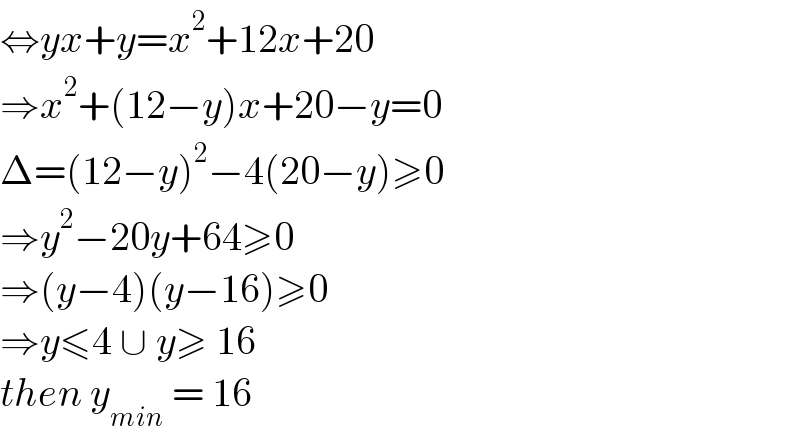Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 143781 by bemath last updated on 18/Jun/21

Answered by liberty last updated on 18/Jun/21
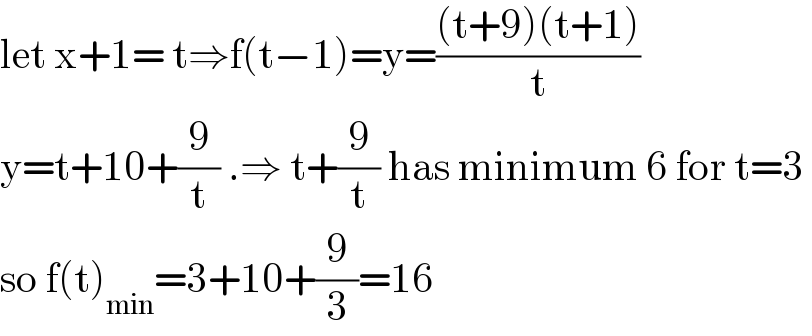
Answered by TheHoneyCat last updated on 18/Jun/21
![(df/dx)(x)=(((2x+12)(x+1)−(x^2 +12x+20))/((x+1)^2 )) =((x^2 +2x−8)/((x+1)^2 )) =(((x−2)(x+4))/((x+1)^2 )) ∀x∈R_+ ((x+4)/((x+1)^2 ))>0 therefore: x∈[0,2[ ⇒ (df/dx)(x)<0 x∈]2,+∞[ ⇒ (df/dx)(x)>0 and (df/dx)(2)=0 so f′s minimal value on R_+ is reached for x=2 Min_R_+ f=f(2)=((12×4)/2)=24_■](Q143784.png)
Commented by abdullahoudou last updated on 18/Jun/21
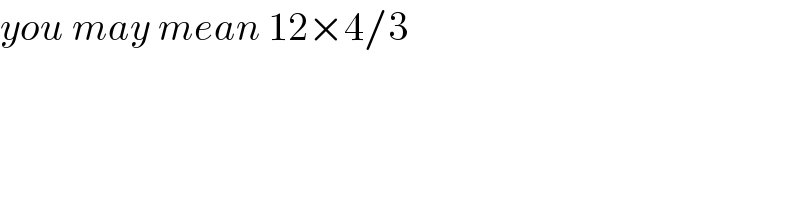
Commented by TheHoneyCat last updated on 19/Jun/21
Of course, I had to make a mistake at the very last line. �� Yes indeed, f(2)=12x4/3=16. Thanks @abdullahoudou, for paying attention to the little details. ��
Answered by john_santu last updated on 19/Jun/21